CVD diamond thick-film ophthalmology scalpel manufacturing device and manufacturing method
A diamond thick film and manufacturing device technology, applied in the field of tools, can solve the problems of inapplicability to precision and ultra-precision machining, deep surface damage layer, slow polishing speed, etc., to overcome processing difficulties, high diamond surface quality, and low grinding pressure Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
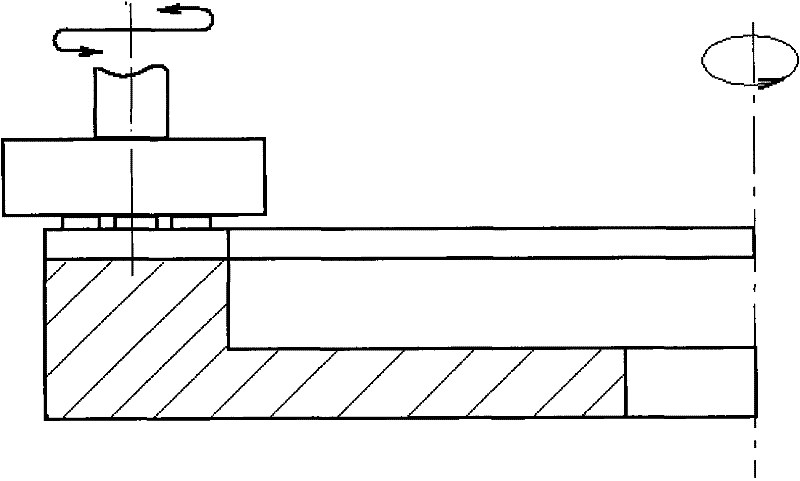
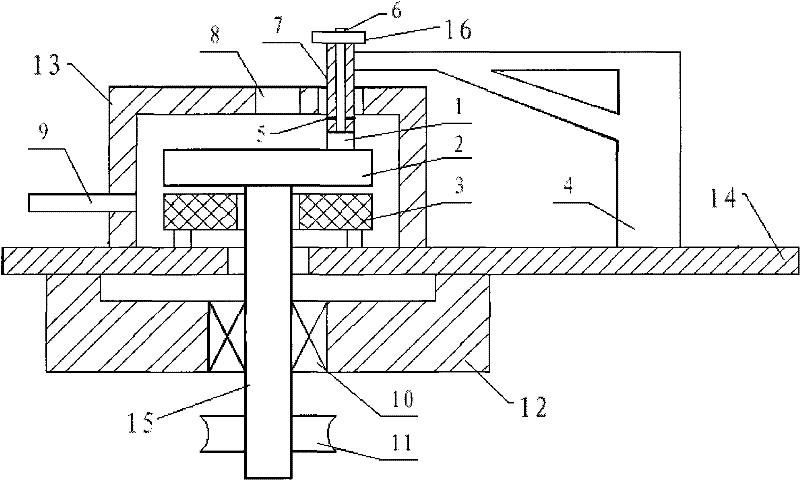
[0031] Embodiment 1: as Figure 1-3 Shown, a kind of manufacture method of CVD diamond thick film ophthalmic scalpel comprises the following steps:
[0032] Step 1: Cut the CVD diamond thick film material by laser method, and cut it into the required size;
[0033] Step 2: Shape grinding and polishing; using planetary grinding and polishing, the speed is 60 rpm, and the pressure is 1Kpa;
[0034] Step 3: Thickness grinding and polishing; grinding into thin slices, speed 3000 rpm, pressure 200Kpa; natural diamond is a typical brittle material, CVD diamond thick film is relatively more brittle, and because of its polycrystalline structure, the grinding hardness is The average hardness of diamond does not have the softest direction like natural diamond (the difference in grinding hardness between the soft and hard directions on the diamond grain is more than 100 times), so grinding is more difficult. In the process of grinding it into a thin sheet of 0.2X1X6mm, the diamond is e...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Embodiment 2: structure as embodiment 1,
[0051] The invention uses the original planetary grinding and polishing method, thermochemical grinding method and ultra-high-precision air bearing as the main shaft of the grinding and polishing machine. The diamond thick film material is brittle, the hardness is average, there is no softest direction, and the technical difficulty of being easy to damage realizes the high-precision requirements of the ophthalmic scalpel. After the completion of the project, it will open a new era of domestic diamond scalpels, fully meet the processing accuracy and sharpness requirements of imported diamond scalpels, replace traditional metal blades, and greatly reduce the damage to the eyes caused by ophthalmic surgery.
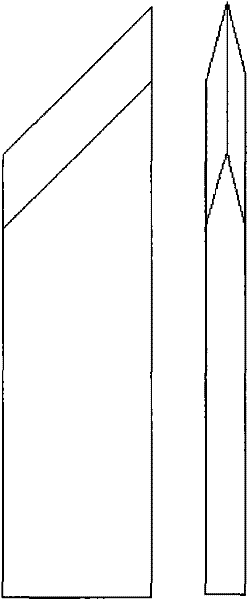
[0052] The typical shape of diamond tip part of diamond ophthalmic scalpel is as follows figure 1 Shown: Its external dimensions are 0.2X1X6mm, the tip angle is 45°, and the blade wedge angle is 38°. The straightness of the...
Embodiment 3
[0068] A CVD diamond thick-film ophthalmic scalpel with an external dimension of 0.2X1X6mm; a blade tip angle of 45° and a blade wedge angle of 38°; the blade’s straightness reaches 0.1 μm, which is perfect under a 500-5000 times microscope; The radius of the blade arc is 0.05μm; the surface roughness of the tool is less than Ra0.005μm.
[0069] Or a CVD diamond thick film ophthalmic scalpel with a tip angle of 35° and a blade wedge angle of 30°; the straightness of the blade reaches 0.1 μm; the radius of the arc of the blade is 0.05 μm; the surface roughness of the blade is less than Ra0.005 μm.
[0070] Or a CVD diamond thick film ophthalmic scalpel with a tip angle of 50° and a blade wedge angle of 40°; the straightness of the blade reaches 0.1 μm; the radius of the blade arc is 0.05 μm; the surface roughness of the blade is less than Ra0.005 μm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com