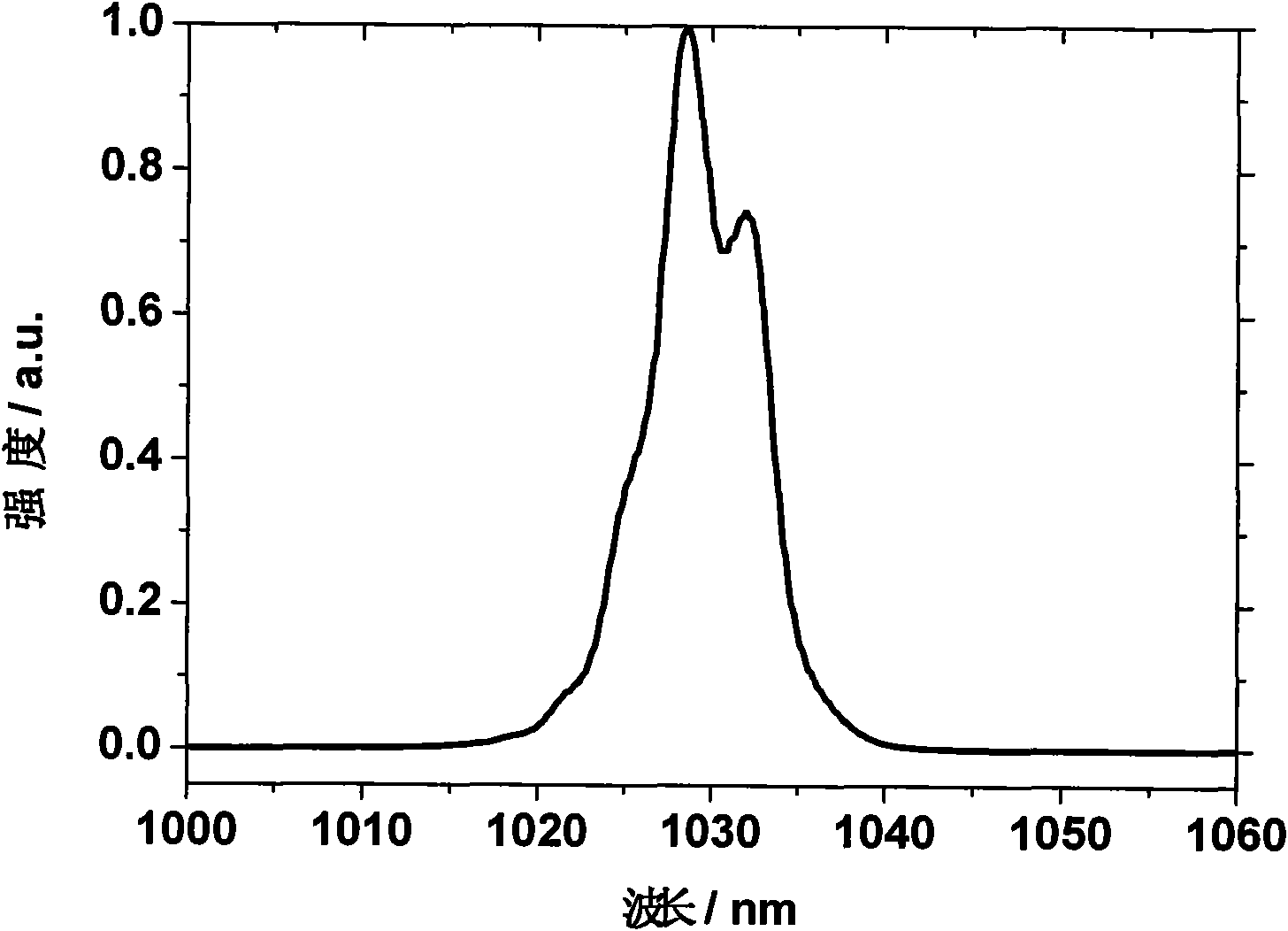
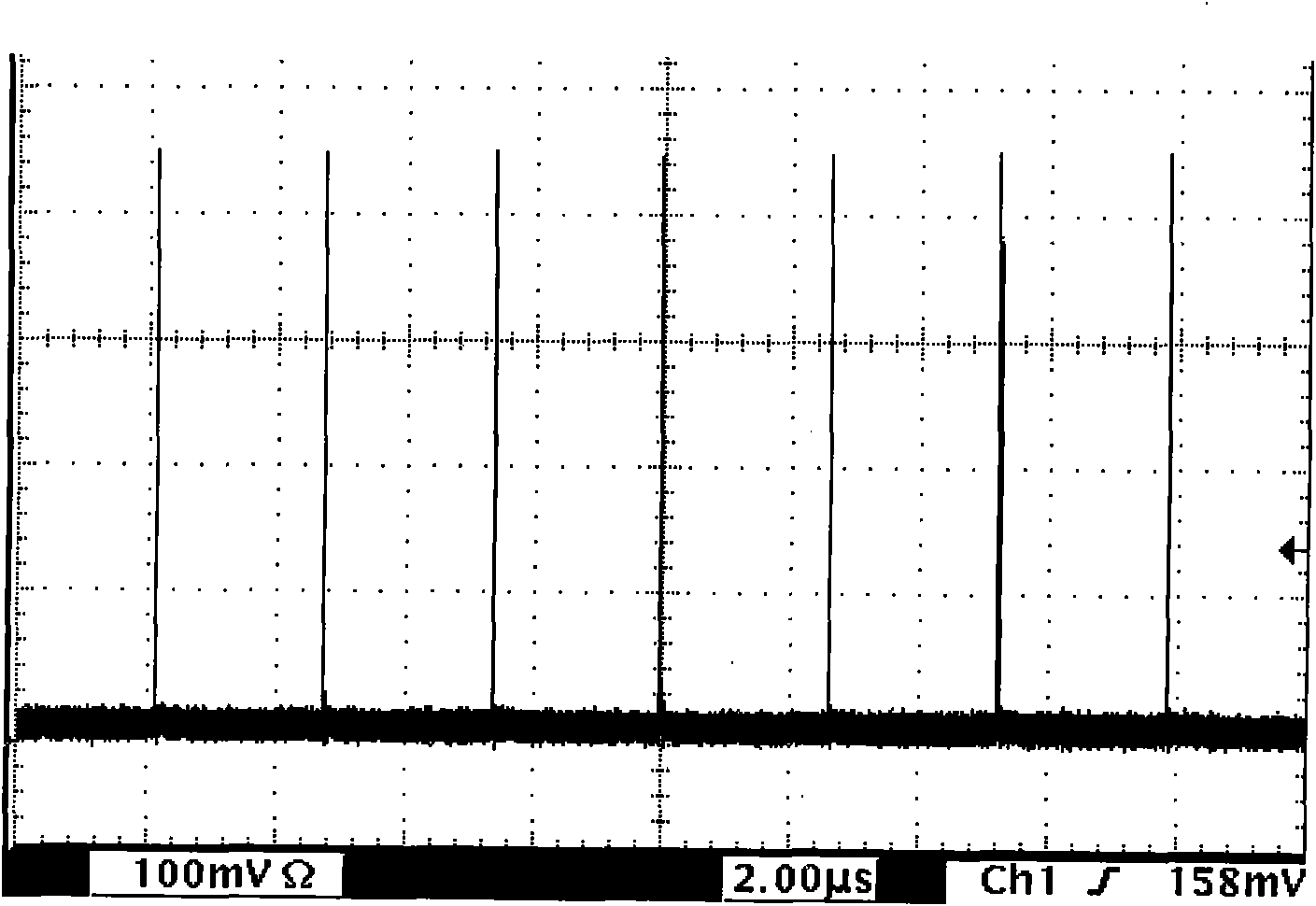
High-energy low-repetition-frequency fiber laser
A technology of fiber laser and repetition rate, which is applied in cladding optical fiber, optical waveguide and light guide, instrument, etc., can solve the problems of lengthening laser, good mode-locking effect, and high price, so as to improve single pulse energy, facilitate broadening, and simplify structure effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
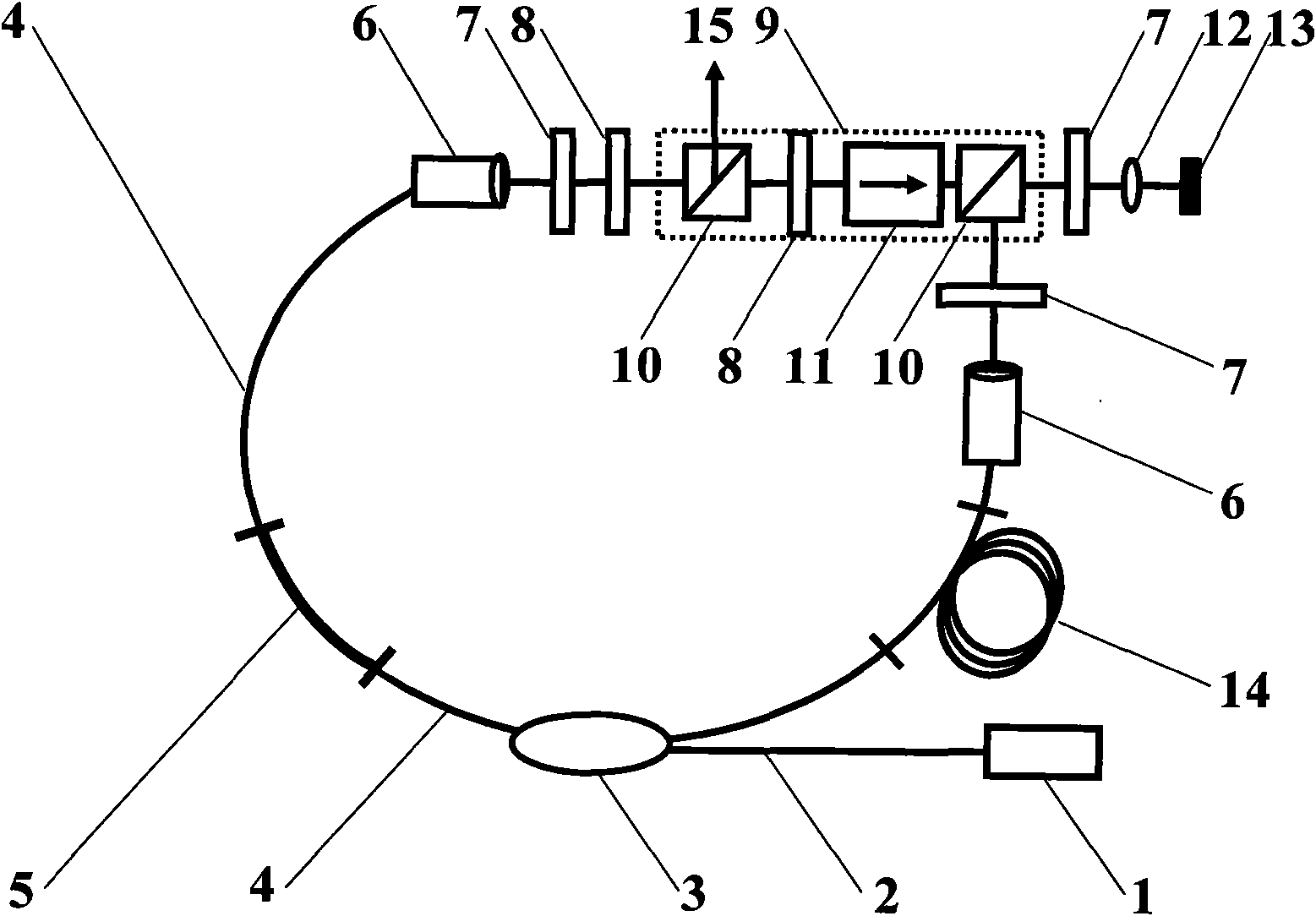
[0067] For ring cavity fiber lasers, such as figure 1Shown is a preferred embodiment of the fiber laser with high energy and low repetition rate of the present invention, in the fiber laser: the pump light source 1 used to provide the energy required to generate laser light is connected to the wavelength division multiplexer through the pump light transmission fiber 2 The wavelength division multiplexer 3 is used as a pump coupler to connect the pump light source 1 to the resonant cavity of the fiber laser to provide an energy inlet. A ring-shaped resonant cavity is formed by connecting the single-mode transmission fiber 4, the gain fiber 5 and the mode-locking device. In this embodiment, the mode locking device adopts a saturable absorber 13 , and a focusing lens 12 is connected before the saturable absorber 13 for focusing the generated laser light on the saturable absorber 13 . Since the difference between the present invention and the prior art is that the length of the s...
Embodiment 2
[0070] For ring cavity fiber lasers, such as Figure 4 Shown is another preferred embodiment of the fiber laser with high energy and low repetition rate of the present invention. Most of the devices and their connections in this embodiment are the same as those in Embodiment 1, except that this embodiment uses fiber-optic unidirectional isolation The split-type one-way space isolator 9 is replaced by a device 16, and the one-way isolator 16 is also used to make the generated laser unidirectionally transmit in the resonator to form an oscillation, and can be placed in Figure 4 The position shown can also be placed arbitrarily at the other end of the wavelength division multiplexer 3, such as Figure 4 shown by the dotted line. Two polarizing beamsplitters 10 are still connected in the resonant cavity, one of which is used as a laser output port 15 to output ultrashort pulse laser; 13. Form a T-shaped structure.
Embodiment 3
[0072] For ring cavity fiber lasers, such as Figure 5 Shown is another preferred embodiment of the fiber laser with high energy and low repetition rate of the present invention. In the fiber laser: the pump light source 1 used to provide the energy required to generate laser light is connected to the wavelength division through the pump light transmission fiber 2 The multiplexer 3, the wavelength division multiplexer 3 is used as a pump coupler to connect the pump light source 1 to the resonant cavity of the fiber laser to provide an energy inlet. A ring-shaped resonant cavity is formed by connecting the single-mode transmission fiber 4, the gain fiber 5 and the mode-locking device. In this embodiment, the mode-locking device adopts a saturable absorber 13. In this embodiment, an optical circulator 17 is used to replace the polarization splitter prism 10 in Embodiment 2. The optical circulator 17 is connected to the two ends of the single-mode transmission fiber 4 and the sat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com