Chemically mechanical polishing solution
A chemical machinery, polishing liquid technology, applied in polishing compositions, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve problems such as environmental pollution, affecting polishing rate, etc., and achieve high practical value.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
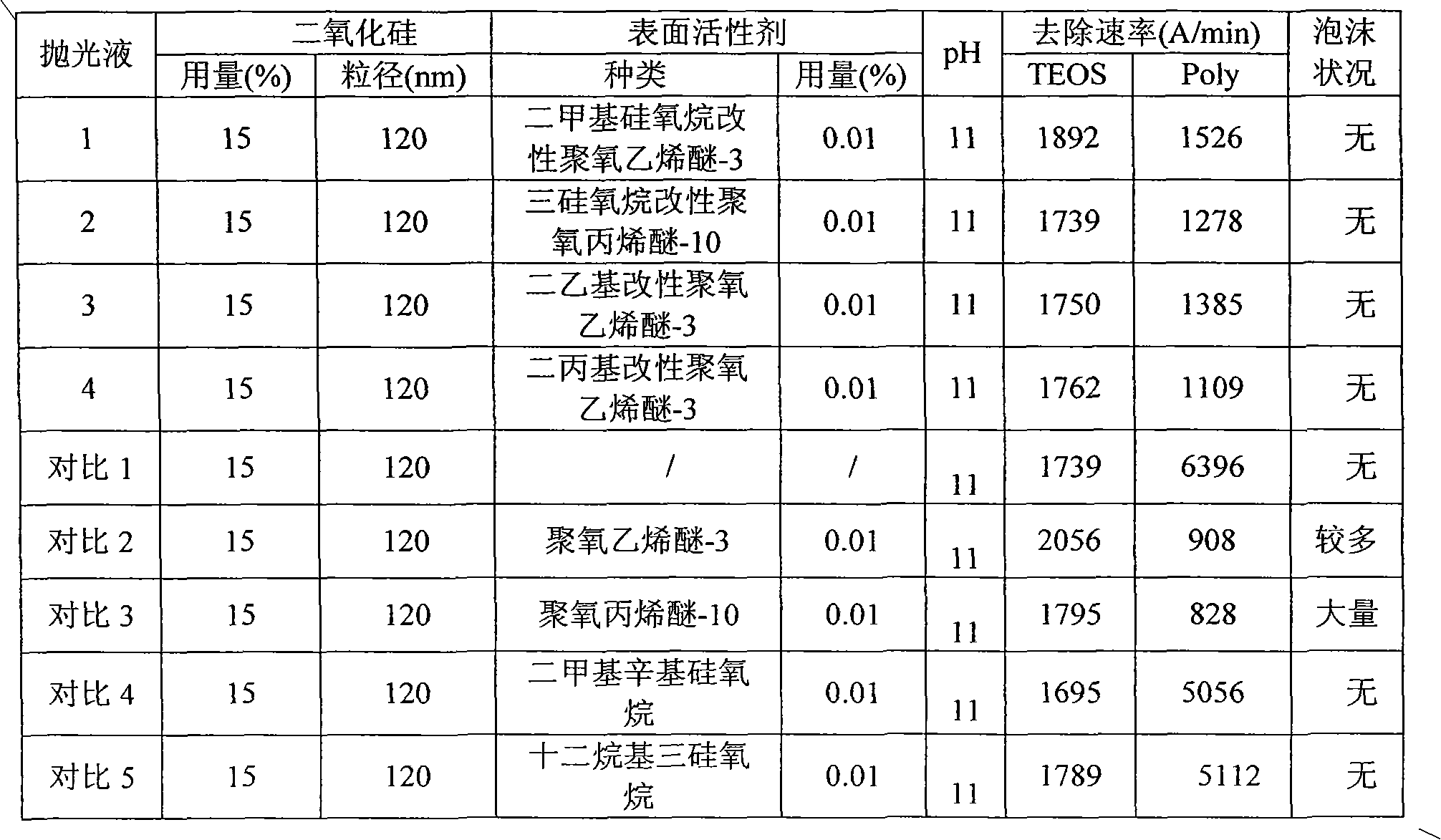
[0023] Example 1 Effect of the polishing solution of polyalkylene oxide modified with siloxane and unmodified polyalkylene oxide on the removal rate of TEOS and Poly
[0024] Silicon dioxide (TEOS) and polysilicon (Poly) were polished with polishing liquids 1-9 and comparative polishing liquids 1-5, and the removal rates of silicon dioxide and polysilicon were measured, as shown in Tables 1 and 2. It can be seen from Table 1 that compared with the polishing fluid containing ordinary polyether, the polyether modified with siloxane obviously does not produce bubbles. Compared with comparisons 4 and 5, although comparisons 4 and 5 do not generate foam, their removal rates for polysilicon are quite high, which will severely scratch the polished surface. It can be seen from Table 2 that as the content of the modified polyalkylene oxide increases, the effect on foam suppression is better. The amount of polyalkylene oxide terminated by siloxane is preferably 0.0025-0.1% by mass, mor...
Embodiment 2
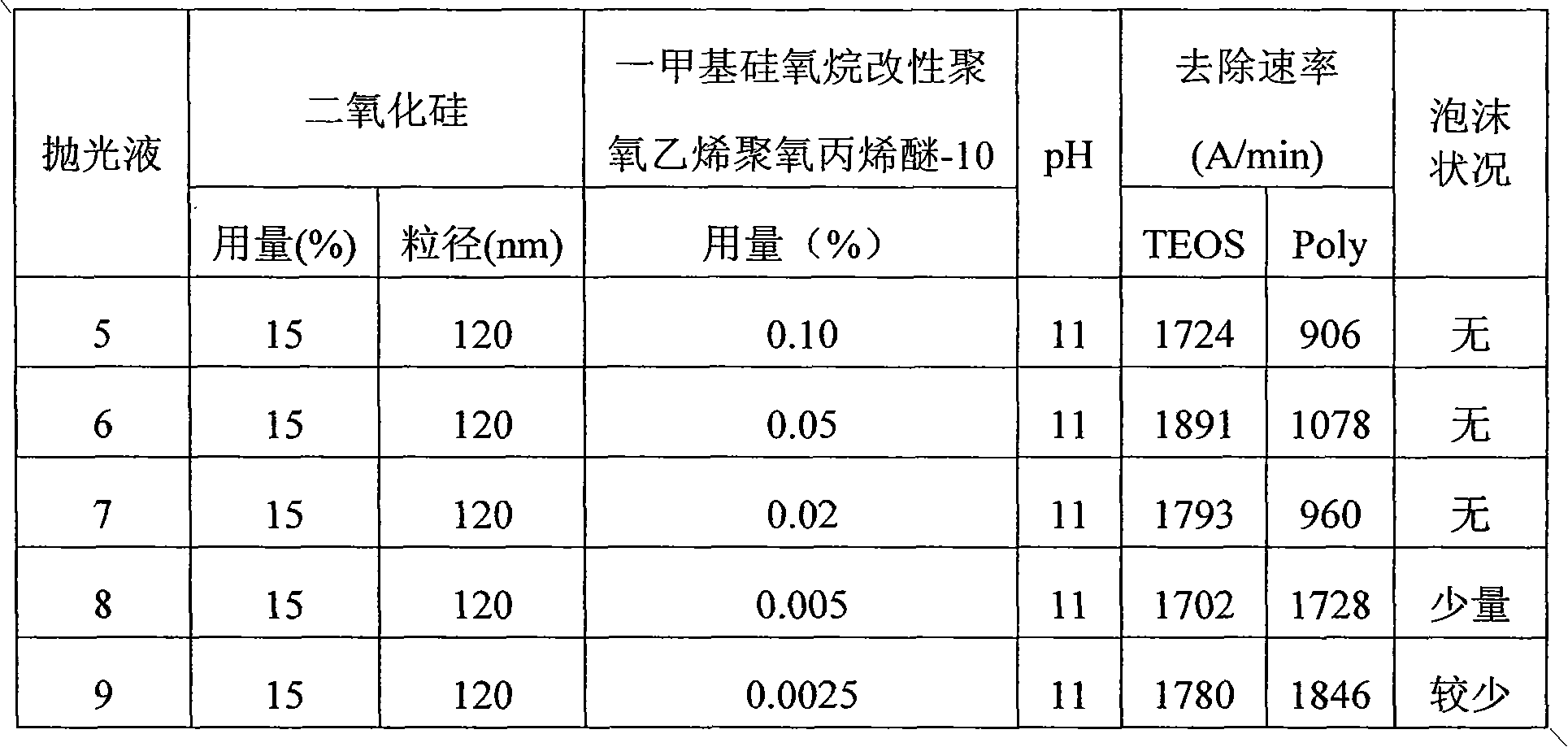
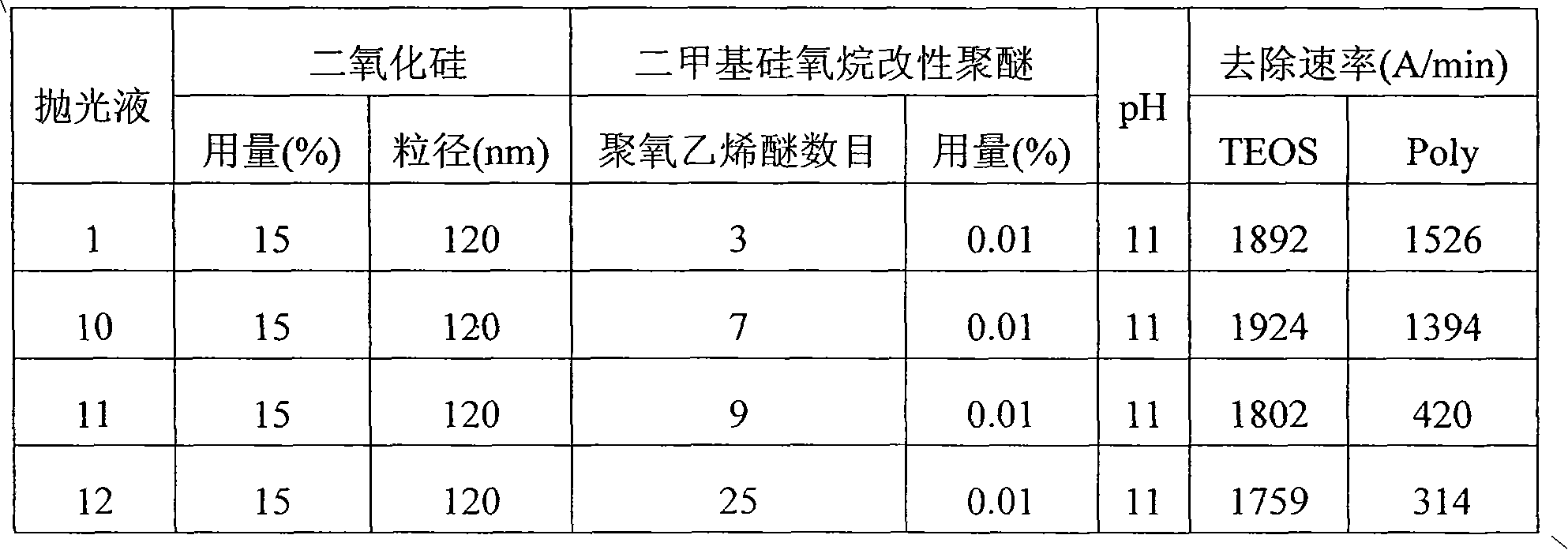
[0030] Example 2 The effect of the number of repeating units in polyalkylene oxide on the removal rate of TEOS and Poly
[0031] Polish TEOS and Poly with polishing liquid 1, 10-12, and measure the removal rate of TEOS and Poly, as shown in Table 3. It can be seen from Table 3 that the number of repeating units in the polysiloxane group has no significant effect on the removal rate of TEOS, but the more the number of repeating units, the greater the inhibition on the removal rate of Poly. In order to achieve a higher polysilicon removal rate, the number of repeating units greater than 9 must be selected.
[0032] The polishing liquid formula is shown in Table 3. Use KOH to adjust the pH, and deionized water to make up the balance. The polishing conditions are: downforce 5.0psi, polishing pad IC 1000, polishing disc rotation speed 70rpm, polishing liquid flow rate 100ml / min, polishing machine Logitec PM5.
[0033] table 3
[0034]
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 The effect of different siloxane group-terminated polyalkylene oxides on the removal rate of TEOS and Poly
[0036] TEOS and Poly were polished with polishing solutions 1, 13-14 and comparison 6, and the removal rates of TEOS and Poly were measured, as shown in Table 4. It can be seen from Table 4 that the inhibitory effect on the removal rate of Poly with substituents on siloxane is obviously better than that without substituents. To achieve a higher polysilicon rate, dimethylsiloxane and trimethylsiloxane are better. If a higher polysilicon removal rate is required, trimethylsiloxane should be selected.
[0037] The polishing liquid formula is shown in Table 4, the pH is adjusted with KOH, and the balance is made up with deionized water. The polishing conditions are: downforce 5.0psi, polishing pad IC1000, polishing disc rotation speed 70rpm, polishing liquid flow rate 100ml / min, polishing machine Logitec PM5.
[0038] Table 4
[0039]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com