Rapid staining method for biopolymers
A technology of biopolymers and dyeing methods, applied in the direction of measuring devices, instruments, material analysis by electromagnetic means, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0094] Example 1 Separation of proteins by electrophoresis and then staining.
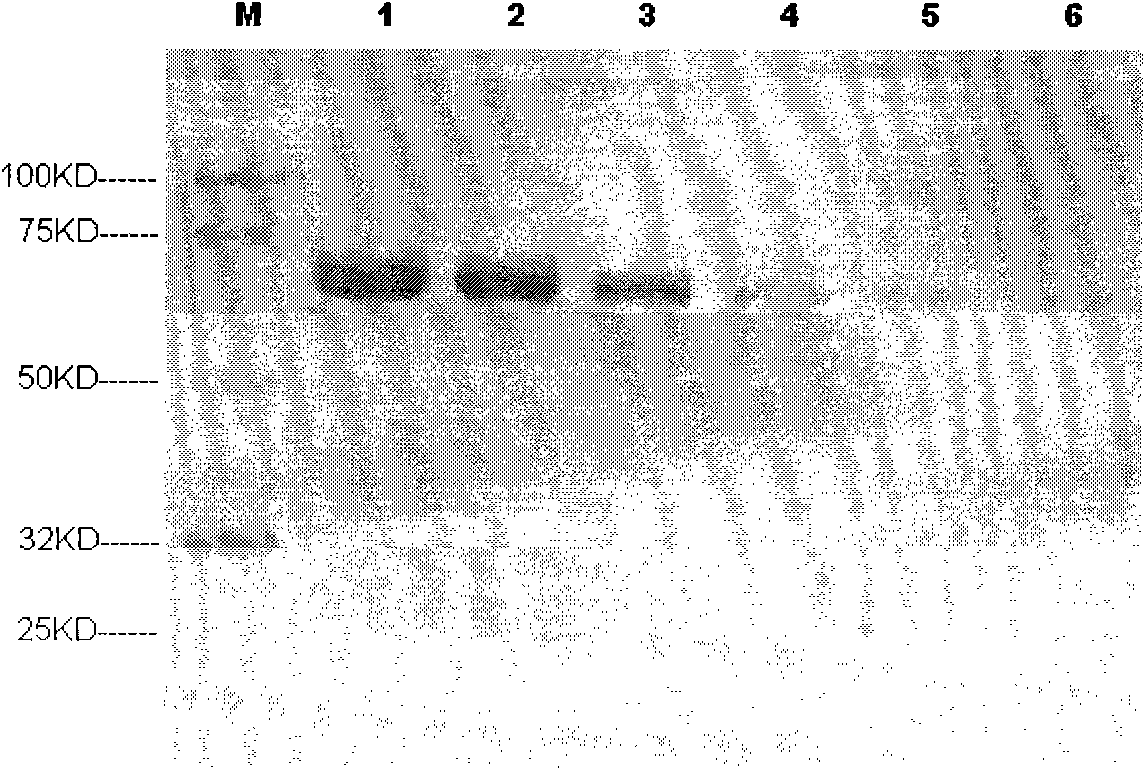
[0095] Bovine serum albumin staining. 1500ng, 750ng, 300ng, 150ng, 75ng, and 30ng of bovine serum albumin were loaded on lanes 1 to 6 of two PAGE gels (Genscript, MG008W10) respectively. After electrophoresis, one gel was used for rapid staining, specifically , after electrophoresis, take out the gel, put the gel in such as Figure 4 In the sandwich structure shown. Solution A is an aqueous solution containing 10-50% (v / v) isopropanol, 5-35% (v / v) ethanol, and 1-30mmol / L ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, and solution B is an aqueous solution containing 0.05-0.5% ( Mass volume ratio) Coomassie brilliant blue, 20-60% (v / v) ethanol, 1-30mmol / L ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 2-30% (v / v) acetic acid aqueous solution, C is pH 4.0~ 10% phosphoric acid or similar buffer solution (preferably: A is an aqueous solution containing 25% isopropanol, 10% ethanol, 5mmol / L ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, B is ...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Take DNA Marker (Genscript, 100bp ladder) respectively, and load the sample on the agarose gel with a concentration of 2%, 500ng / lane, and the nucleic acid is respectively loaded on the 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, In lanes 6 and 7, in TBE (aqueous solution containing 445 mmol / L Tris base, 445 mmol / L borate, and 10 mmol / L EDTA) buffer, constant current flow was 300 mA for 20 minutes. After electrophoresis, filter paper soaked with positively charged dye (diluted by ethidium bromide 10,000 times) was tiled on the positive plate, the agarose gel after electrophoresis was located on it, and two layers of soaked gel were tiled on top of the agarose. Wet the filter paper of TBE, add the negative electrode above to form a sandwich structure, and apply a voltage of 50V to the two electrodes for 3 minutes. After binding to DNA driven by an electric field, it is imaged under UV light. The dyeing time is 3 minutes, see the results Figure 5 .
Embodiment 3
[0100] Example 3: Combination of electrophoretic separation and staining of various biopolymers.
[0101] Take 500 μg of protein (bovine serum albumin) with a molecular weight of 67KD and 500 μg of a polypeptide with a molecular weight of 6KD, respectively, and add them to 1ml of water to prepare a mixed aqueous solution of various biopolymers. Add 1ml of solution B (containing 0.3% Coomassie brilliant blue, 46 % ethanol, 5mmol / L ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, 8% aqueous solution of acetic acid), keep the dye in contact with the biopolymer for 1 minute, dye the biopolymer, and then take the solution and load it on one end of the cellulose acetate membrane medium (Length 10cm, immersed in pH 8.6 concentration of 0.07mol / L barbiturate buffer), medium applied voltage 200v, separation time 20 minutes, you can see that the peptide and protein can be separated and clearly colored, the result See Figure 8 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com