VCO tuning curve compensation method and module thereof
A tuning curve, circuit module technology, applied in electrical components, power oscillators, multi-terminal-to-network, etc., can solve the problems of poor VCO phase noise performance, poor phase noise performance, high power consumption, etc., to simplify the implementation process, The effect of large tuning range and improved stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment
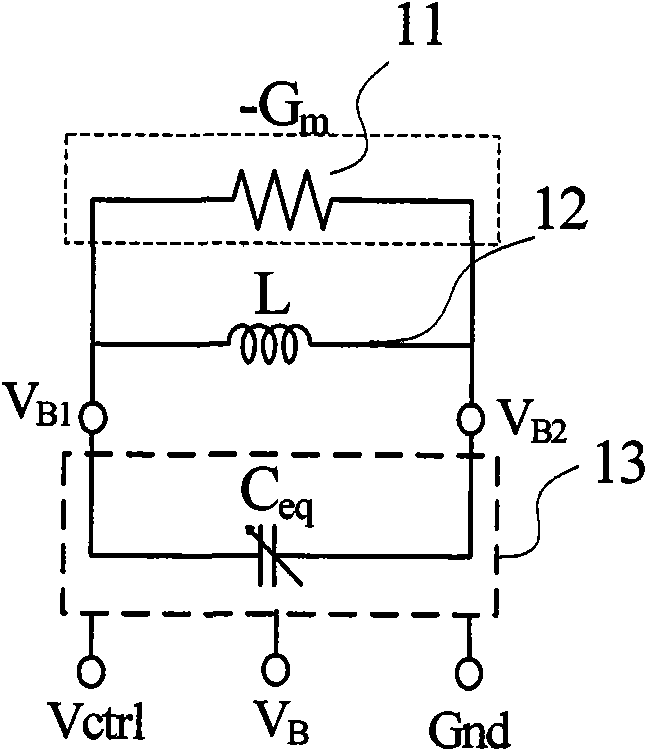
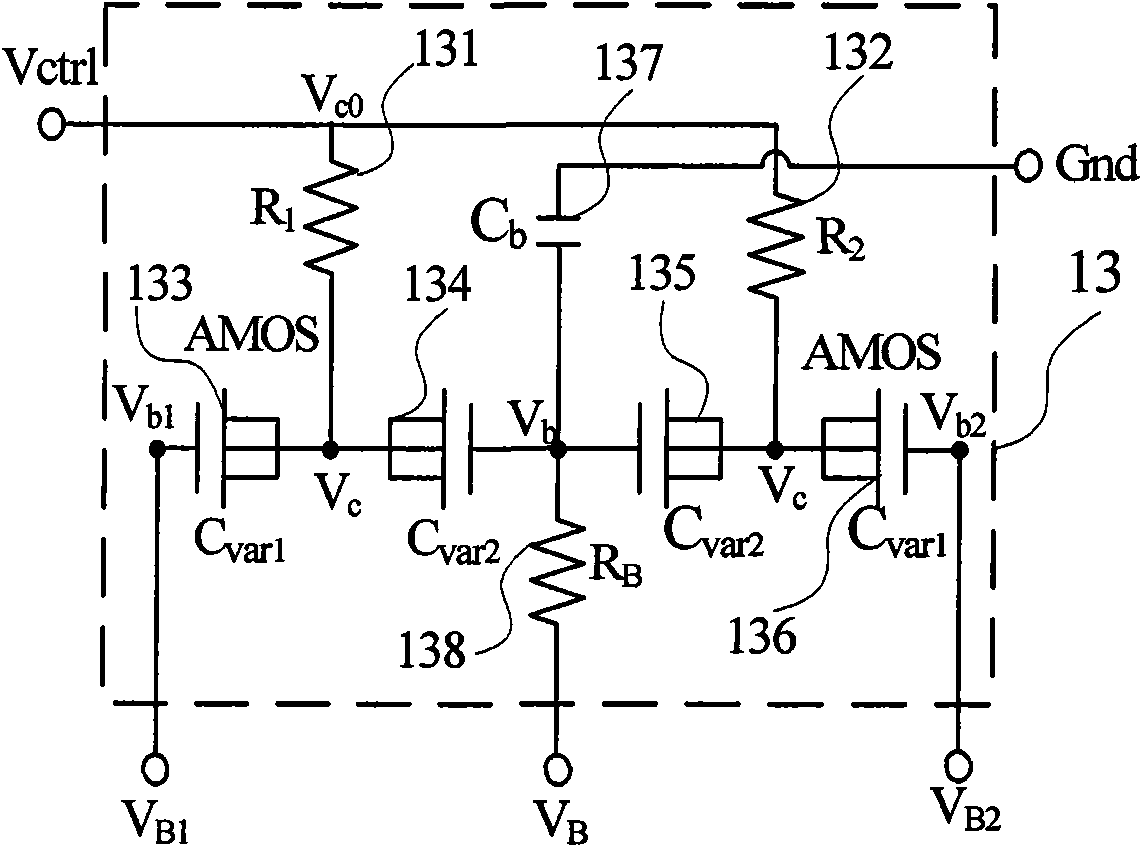
[0054] Figure 3a It is a functional block diagram of the tuning curve compensation VCO in the first embodiment. The VCO structure is an NMOS and PMOS complementary VCO with a tail current source, and a bias voltage V is added to the gate of the tail current source 37. B . The PMOS transistors 35 and 36 form a cross-coupled negative resistance amplifier, while the NMOS transistors 33 and 34 are cross-coupled to form another negative resistance amplifier. The two form a complementary NMOS and PMOS negative resistance amplifier with a tail current source. The variable capacitor 32 is electrically connected in parallel with the on-chip inductance 31 and the NMOS and PMOS complementary negative resistance amplifiers with a tail current source, Figure 3b for Figure 3a The tuning curve compensation VCO block diagram of the first embodiment is an electrical schematic diagram of the AMOS capacitor network for tuning curve compensation of the variable capacitor 32 . The equivalen...
no. 2 Embodiment
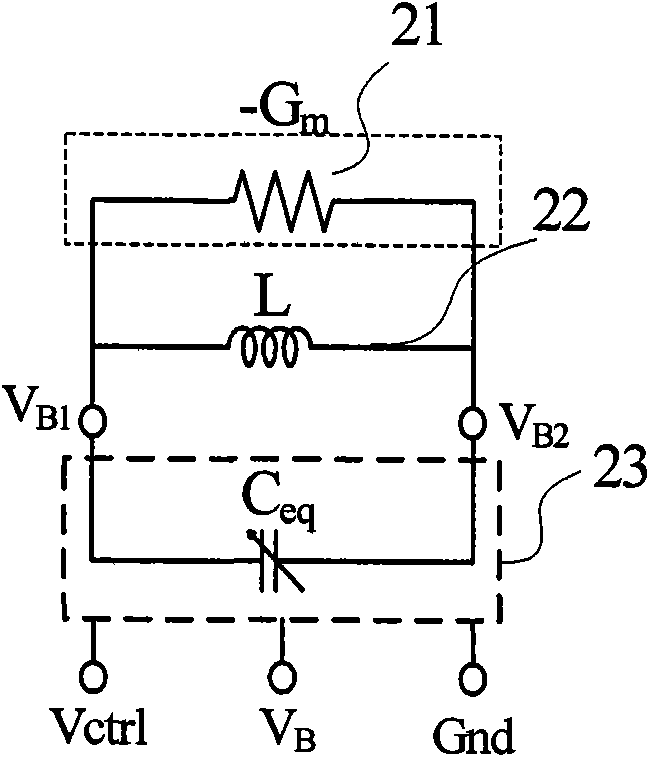
[0056] Figure 4a It is a schematic block diagram of the tuning curve compensation VCO in the second embodiment, and the PMOS transistor 43 is applied with a bias voltage V on the gate. B tail current source. PMOS transistors 44 and 45 constitute a cross-coupled negative resistance amplifier. The VCO structure is a PMOS negative resistance amplifier type VCO with tail current, an on-chip symmetrical inductor 41 with a center tap and a PMOS negative resistance amplifier with a tail current source, and the variable capacitor 42 is electrically connected in parallel. The variable capacitor 42 is composed of a capacitance network that adopts tuning curve compensation, and its specific schematic diagram is as follows Figure 4b As shown in the dashed box, the tuning curve compensation method adopted by the equivalent capacitance is the positive frequency characteristic compensation method shown in Figure 1, Figure 4b 431-438 are the same as 131-138 in Fig. 1 respectively. Simi...
no. 3 Embodiment
[0058] Figure 5a It is a functional block diagram of the tuning curve compensation VCO in the third embodiment. The VCO structure is an NMOS negative resistance amplifier type VCO with tail current. NMOS transistor 55 applies a bias voltage V to the grid B The drain of the tail current source is connected to the center tap of the on-chip symmetrical inductor 51 . NMOS transistors 53 and 54 constitute a cross-coupled negative resistance amplifier. An on-chip symmetrical inductor 51 with a center tap and an NMOS cross-coupled negative resistance amplifier are electrically connected in parallel with the variable capacitor 52, and the parallel connection port is V B1 and V B2 . The variable capacitor 52 is composed of a capacitor network that uses tuning curve compensation. The specific schematic diagram of the equivalent capacitor 52 is shown in the dotted line box, and the tuning curve compensation method adopted by the equivalent capacitor is the positive frequency chara...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com