Method for promoting microbes to synthesize docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) by exogenous additive factor
A technology for docosahexaenoic acid and microbial synthesis, applied in the biological field, can solve the problem of not improving the potential of microbial synthesis of DHA from the source, and achieve the effects of improving the level of biosynthesis, increasing the percentage content, and improving the metabolic process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Before fermentation, a certain amount of acetic acid was added to the fermentation medium of Schizochytrium and Thraustochytrium respectively. Utilize the biosensor to measure the glucose concentration in the culture medium, stop fermentation when the residual glucose concentration in the culture medium is 0g / L.
[0033] The experimental results are shown in Tables 1 and 2:
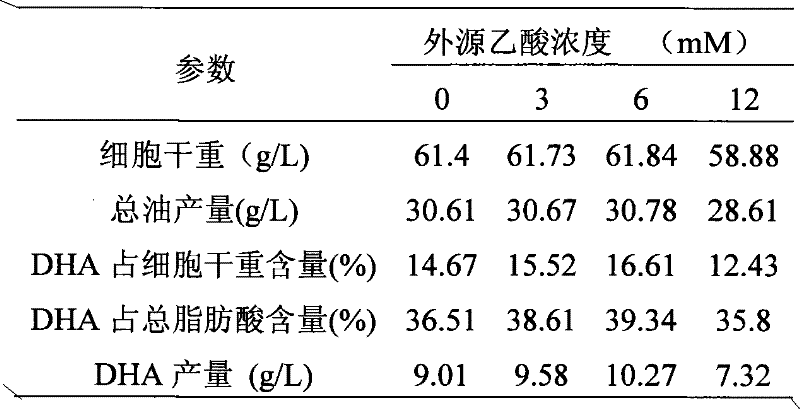
[0034] Table 1 Effect of exogenous acetic acid on the fermentation of Schizochytrium
[0035]
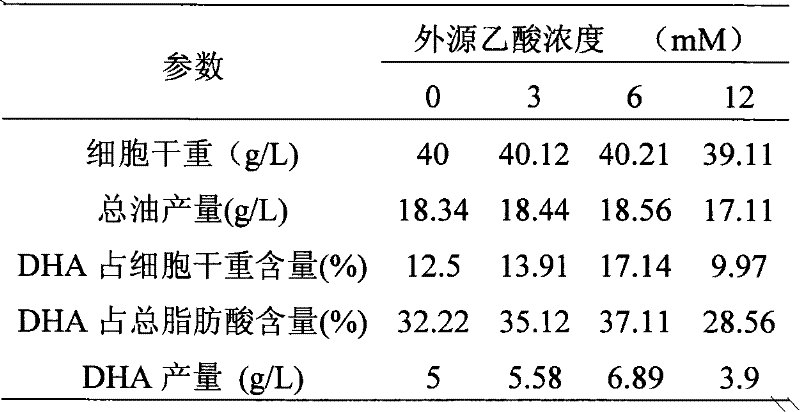
[0036] Table 2 Effect of exogenous acetic acid on the fermentation of Thraustochytrium
[0037]
[0038]Acetic acid is the direct source of acetyl-CoA, and the amount of acetyl-CoA is directly related to the ability of fatty acid synthesis. It can be seen from Tables 1 and 2 that with the increase of acetic acid concentration, each parameter showed a trend of first increasing and then decreasing. When the concentration of acetic acid is 3mM~6mM, it is beneficial to the biosynthesis of DHA. Espe...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Considering that with the consumption of glucose, the precursors of fatty acid synthesis are also reduced. In order to further increase the production of DHA, when no acetic acid is added at the beginning of the fermentation or the acetic acid is added at the optimal concentration, in the later stage of fermentation, mainly Refers to adding acetic acid to the fermentation broth when the glucose concentration is 20-25g / L, using a biosensor to measure the glucose concentration in the culture medium, and stopping the fermentation when the residual glucose concentration in the culture medium is 0g / L. The results are shown in Tables 3 and 4 below:
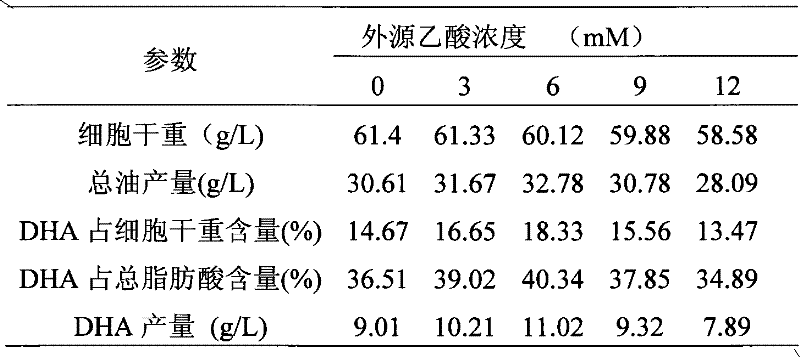
[0041] Table 3 Effect of precursor acetic acid on the fermentation of Schizochytrium at the later stage of fermentation
[0042]
[0043] Table 4 The effect of precursor material acetic acid on the fermentation of Schizochytrium
[0044]
[0045] Note: a means adding before fermentation; b means adding in late fermentation...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Before fermentation, a certain amount of simvastatin was added to the fermentation medium of Schizochytrium and Cryptodinoflagellate respectively. Utilize the biosensor to measure the glucose concentration in the culture medium, stop fermentation when the residual glucose concentration in the culture medium is 0g / L. The results are shown in Tables 5 and 6.
[0049] Table 5 Effect of exogenous simvastatin on the fermentation of Schizochytrium
[0050]
[0051] Table 6 The effect of exogenous simvastatin on the fermentation of Cryptidinosa
[0052]
[0053] Acetyl-CoA is a common precursor of mevalonate pathway and fatty acid synthesis pathway, and simvastatin is an inhibitor of the key enzyme HMG-COA reductase in the mevalonate pathway. When an appropriate amount of simvastatin, mevalonate The pathway is inhibited so that more acetyl-CoA flows to the synthesis of fatty acids, which is more conducive to the synthesis of DHA. As shown in Tables 5 and 6, 0.5-4 μM o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com