Antibiotic resistance maker-free bacillus subtilis constructing method and method for screening bacillus subtilis with inactivated target gene
A Bacillus subtilis, resistance marker technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial determination/inspection, DNA preparation, etc. The effect of high efficiency, simple construction of integrated mutation vector, and simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1B
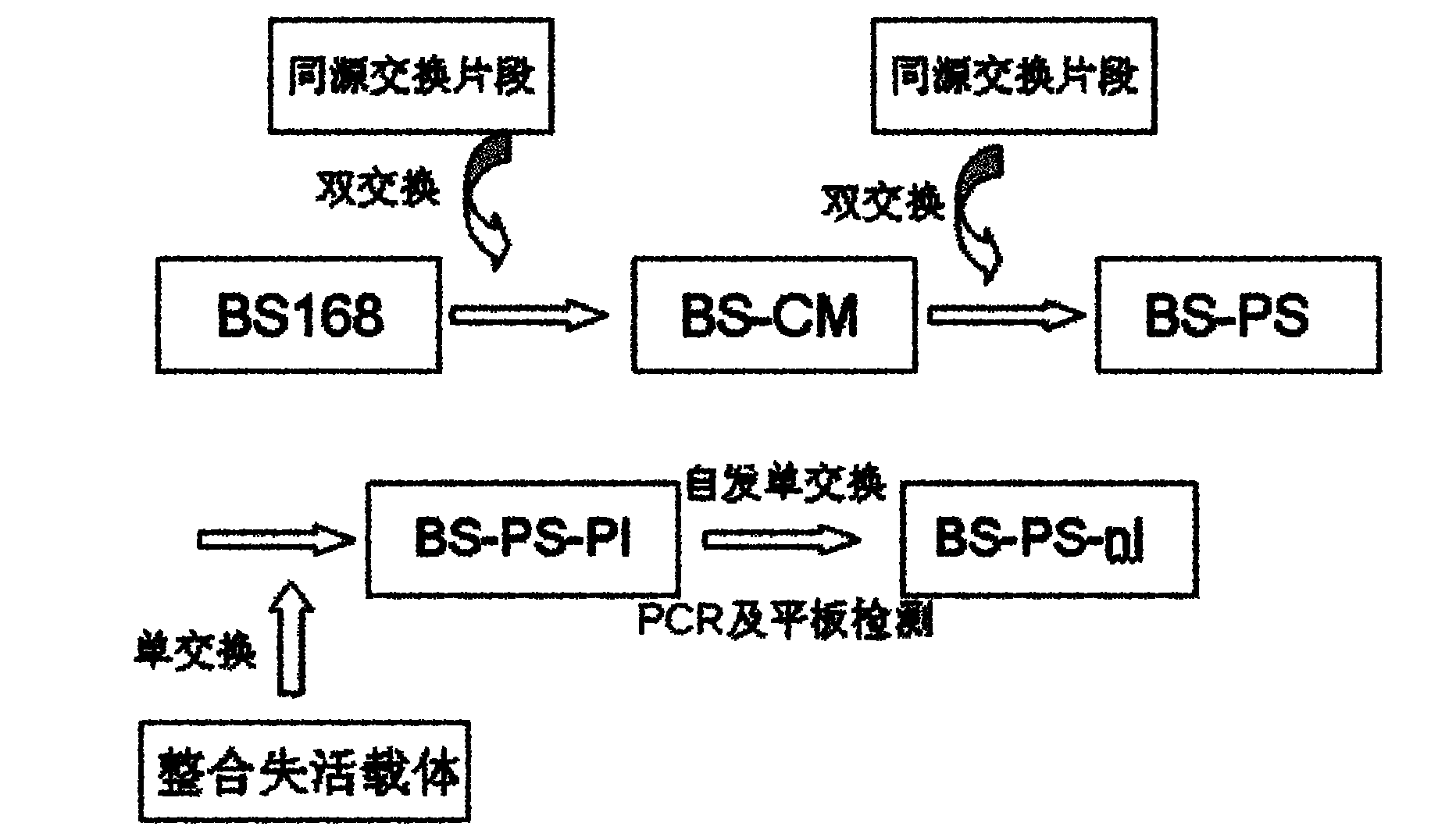
[0048] Construction of embodiment 1BS-PS mutant strain
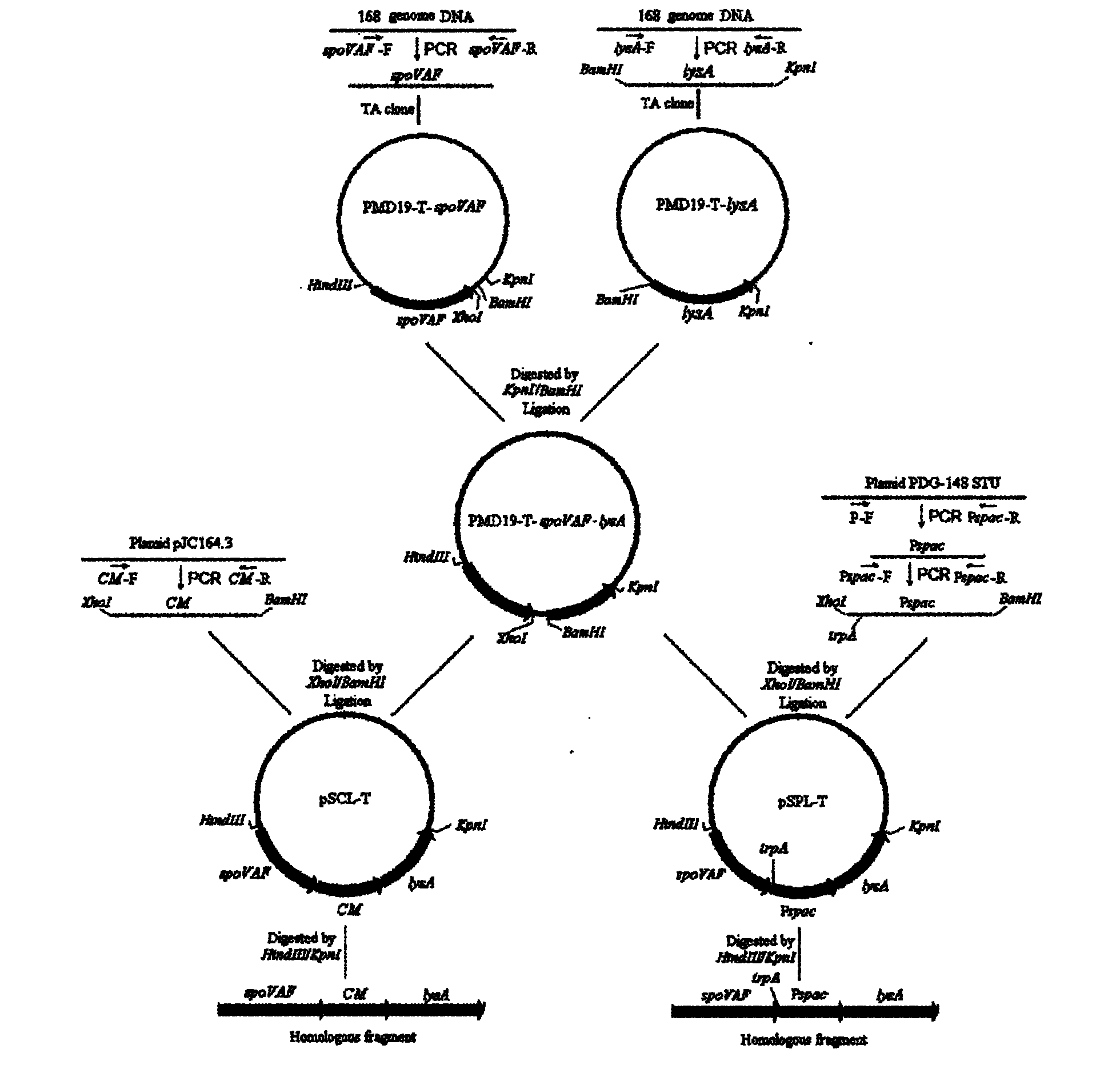
[0049] (1) Construction of SpovAF-CM-LysA homologous exchange fragment
[0050] build route see figure 2 . With spoVAF-F (SEQ ID NO.1) and spoVAF-R (SEQ ID NO.2) as primers, with Bacillus subtilis 168 (BS168) genomic DNA as template PCR amplification spoVAF gene; with LysA-F (SEQ ID NO. NO.3) and LysA-R (SEQ ID NO.4) were primers, and the Lys gene was amplified by PCR using BS168 genomic DNA as a template; CM-F (SEQ ID NO.5) and CM-R (SEQ ID NO. 6) was used as a primer, and the CM (chloramphenicol resistance gene) including the promoter and the terminator was amplified by PCR using the pJC164.3 plasmid (BGSC, containing the CM gene) as the template. The three amplified genes were respectively cloned into the pMD19-T (purchased from Takara Company) vector, and after verification and correct sequencing, they were named pMD19-T-spoVAF, pMD19-T-LysA, and pMD19-T-CM respectively. Store at -20°C for later use.
[0051] T...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Example 2 Utilize the non-antibiotic resistance marker gene screening technology to screen the Bacillus subtilis with target gene inactivation
[0065] (1) Construction of BS-PS strain protease nprE and aprE inactivation integration vector
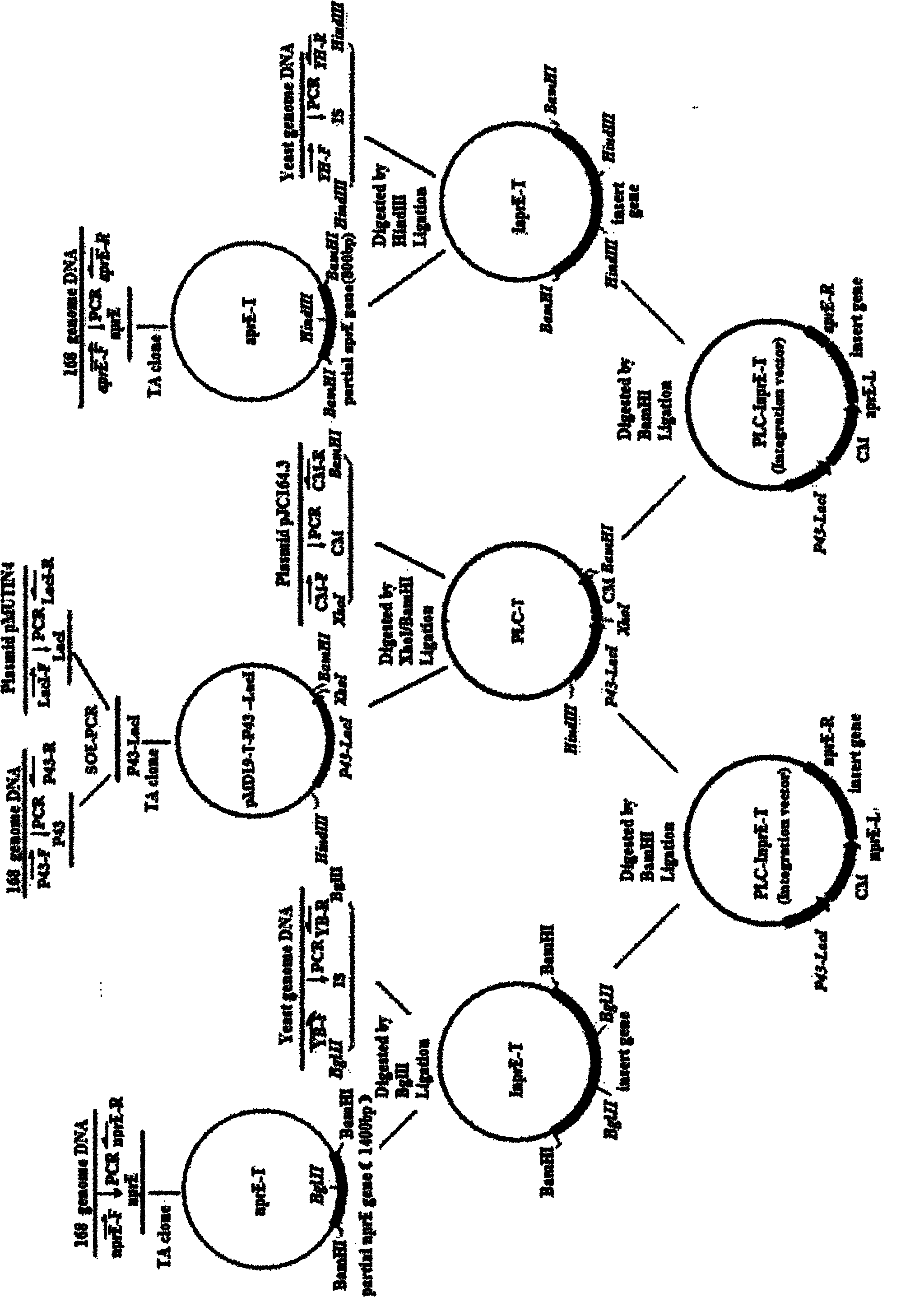
[0066] In the present invention, two protease genes aprE and nprE secreted by Bacillus subtilis are selected, and an insertion inactivation strategy is adopted to conduct mutation inactivation research. Using E. coli pMD19-T as the backbone, a general integration vector PLC-T was constructed. The PLC-IaprE-T integration vector for insertion inactivation of aprE gene and the PLC-InprE-T integration vector for insertion inactivation of nprE gene were constructed on the basis of general vectors. Build routes like Figure 5 shown.
[0067] The specific construction process of the PLC-T integration vector is as follows:
[0068]Using P43-F (SEQ ID NO.9) / P43-R (SEQ ID NO.10) as primers, using BS168 genomic DNA as a template for PCR am...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com