Method for manufacturing viscose through ultrasonic polymerization reduction of plant fibers
A plant fiber and viscose fiber technology, which is applied in the field of viscose fiber manufacturing, can solve the problems of large reactor area, unstable product quality, and uneven reduction of polymerization, so as to eliminate uneven reaction and reduce process control points , to avoid the effect of poly dead angle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
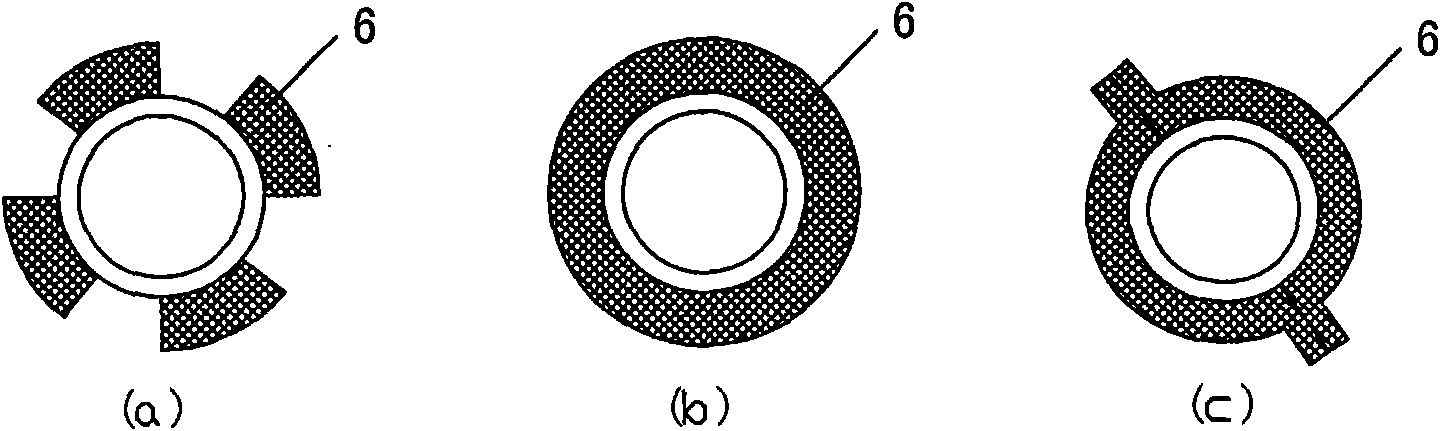
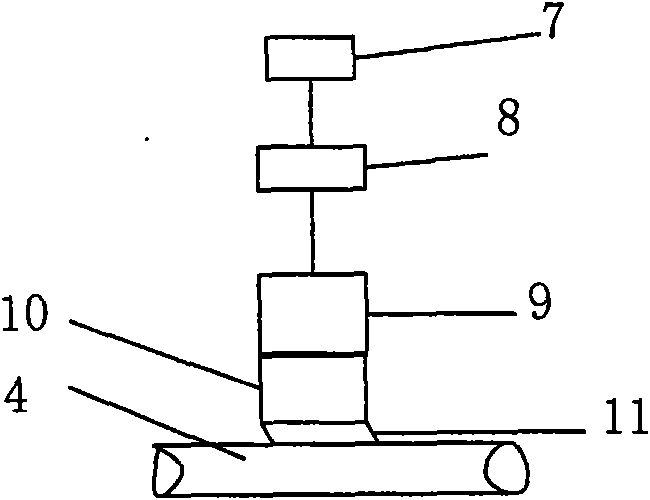
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1 (bamboo fiber one)
[0047] The specific process steps are as follows:
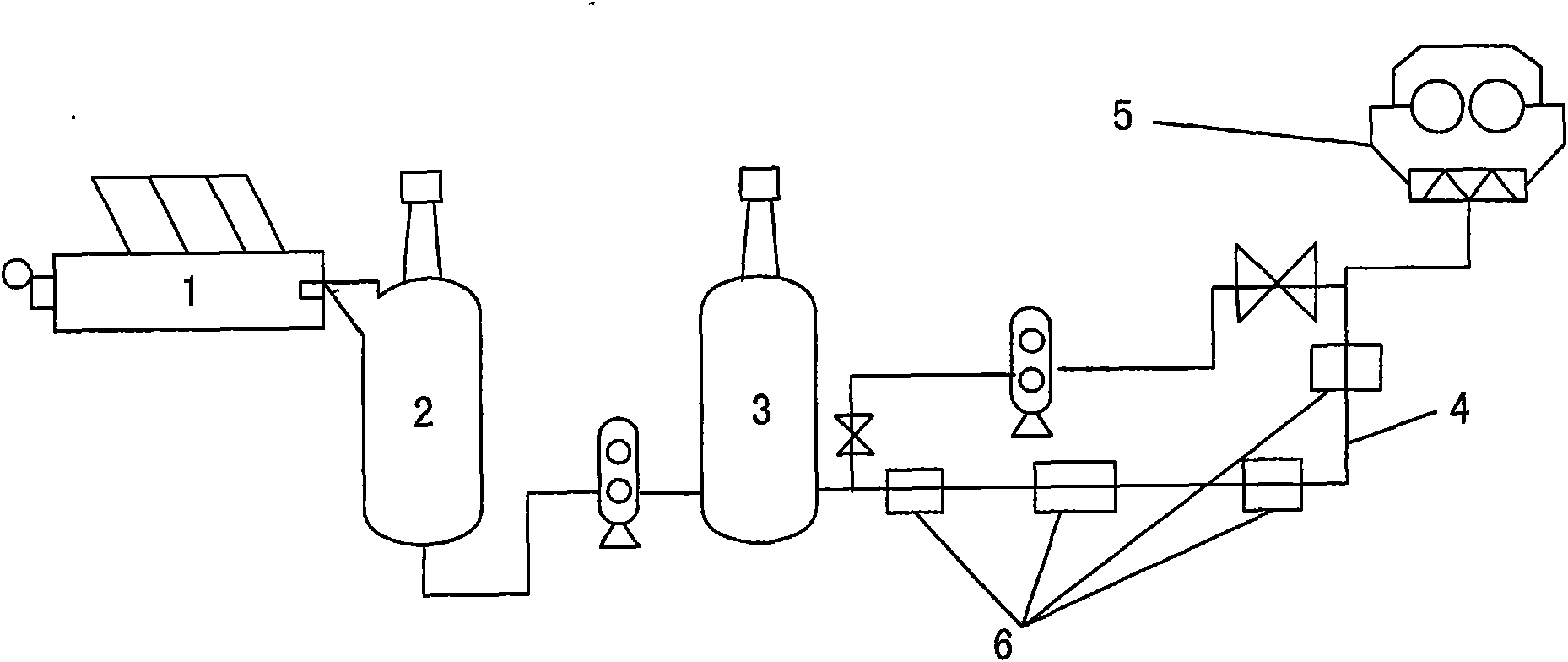
[0048] 1. Put bamboo fiber with an average degree of polymerization of about 1000 on the meal feeding machine, set a certain feeding speed (25kg / min), and then add lye with a concentration of 85g / l and a temperature of 60°C to 90°C. The flow rate is 10m 3 / h~20m 3, and then through stirring, the pulp is broken and mixed with lye fully to prepare a mixture of solid and liquid, which is called pulp porridge, and this process is called impregnation in technology.
[0049] Function: Make the bamboo fiber raw material into a solid and liquid mixture, dissolve β-cellulose at the same time, increase the content of α-fiber, and produce alkali cellulose.
[0050] Control parameters: lye temperature: 75±15°C lye concentration: 85g / l
[0051] Porridge concentration: 3.5±2% (mass percentage) Dipping time: 30±20min
[0052] 2. Pump the porridge in the auxiliary dipping barrel to the ...
Embodiment 2
[0062] Embodiment 2 (bamboo fiber two)
[0063] The specific process steps are as follows:
[0064] 1. Put bamboo fiber with an average degree of polymerization of about 800 on the meal feeding machine, set a certain feeding speed (25kg / min), and then add lye with a concentration of 80g / l and a temperature of 60°C to 90°C. The flow rate is 10m 3 / h~20m 3 , when adding lye, add auxiliary agent: methyl isopropyl ketone (MIBK)-alcohol mixed solvent, wherein MIBK: ethanol=50: 50 (volume ratio, the same below), its purpose is to accelerate lignin and impurity in bamboo fiber dissolution. Then, through stirring, the pulp is crushed and fully mixed with lye to prepare a mixture of solid and liquid, which is called pulp porridge, and this process is called impregnation in technology.
[0065] Function: Make the bamboo fiber raw material into a solid and liquid mixture, dissolve β-cellulose at the same time, increase the content of α-fiber, and produce alkali cellulose.
[0066] C...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Embodiment 3 (bamboo fiber three)
[0079] The specific process steps are as follows:
[0080] 1. Put bamboo fiber with an average degree of polymerization of about 1200 on the meal feeder, set a certain feeding speed (25kg / min), and then add lye with a concentration of 100g / l and a temperature of 60°C to 90°C. The flow rate is 10m 3 / h~20m 3 , when adding lye, add auxiliary agent: methyl isopropyl ketone (MIBK)-alcohol mixed solvent, wherein MIBK: ethanol=80: 50, its purpose is to accelerate the stripping of lignin and impurity in the bamboo fiber. Then, through stirring, the pulp is crushed and fully mixed with lye to prepare a mixture of solid and liquid, which is called pulp porridge, and this process is called impregnation in technology.
[0081] Function: Make the bamboo fiber raw material into a solid and liquid mixture, dissolve β-cellulose at the same time, increase the content of α-fiber, and produce alkali cellulose.
[0082] Control parameters: lye tempe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com