Method for reducing sodium oxide in aluminum oxide by using carbon dioxide
A technology of carbon dioxide and medium sodium oxide, which is applied in the preparation of alumina/hydroxide, purification of aluminate/alumina/aluminum hydroxide, etc., can solve problems such as deformation and cracking of alumina products, and reduce product performance changes , reduce costs, and save the cost of high-temperature roasting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
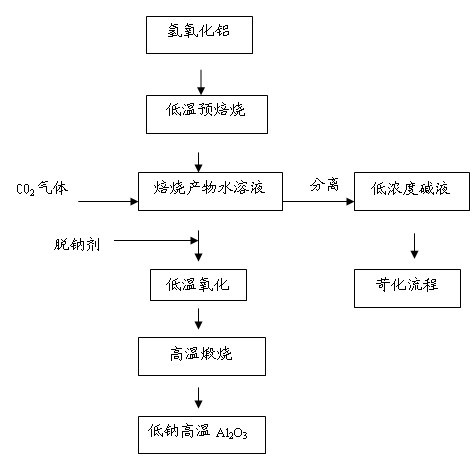
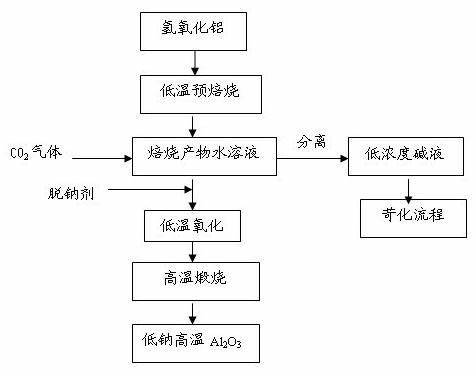
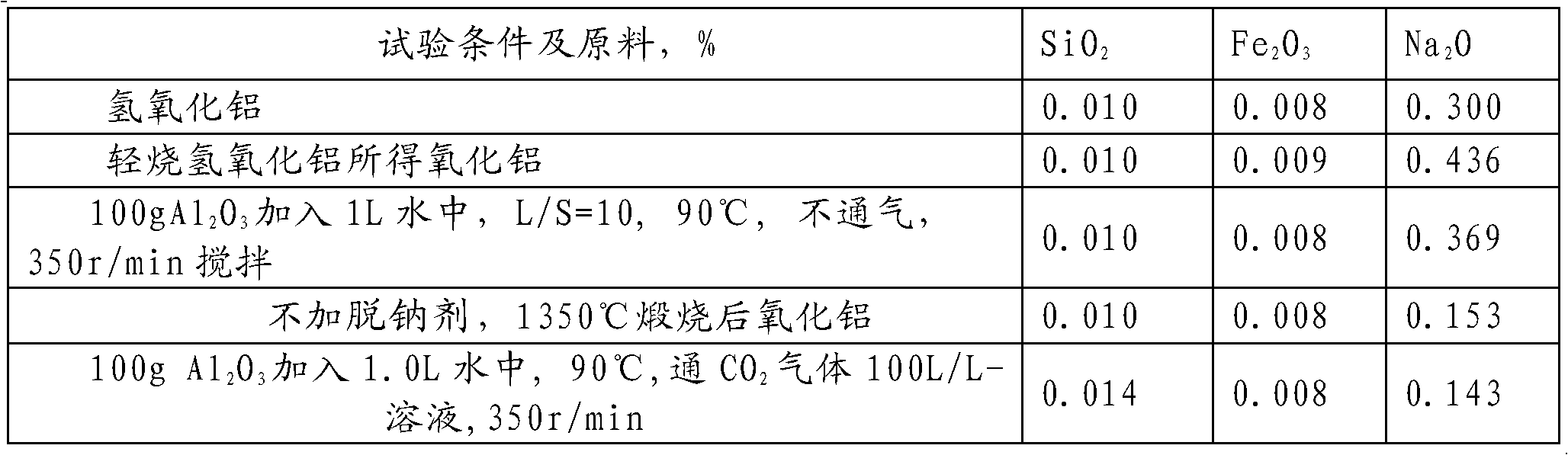
[0018] Step 1. Pre-calcin industrial aluminum hydroxide at 600°C for 1 hour, then add the calcined product to distilled water to obtain an aqueous solution of the calcined product. The liquid-solid ratio of the distilled water to the alumina in the calcined product is L / S=10, that is 100g alumina, 1.0L distilled water, set aside;
[0019] Step 2. The aqueous solution of the calcined product in Step 1 was stirred at a speed of 350 r / min for 1 hour under a constant temperature water bath at 90°C.
[0020] Step 3. Connect the above to CO 2 The aqueous solution of gas is separated into solid and liquid, and boric acid is added to the obtained solid as a sodium removal agent. The added amount is 0.15% of the solid amount. The dry air is first dried at 115°C, and then at 1350°C, pressure greater than 100Pa, dry air atmosphere , The heating rate is less than 1℃ / min, and the alumina is calcined at a high temperature under the condition of natural cooling, and the sodium oxide in the alumin...
Embodiment 2
[0022] Step 1. Pre-calcin industrial aluminum hydroxide at 500°C for 1 hour, and then add the calcined product to distilled water. The liquid-to-solid ratio of distilled water to alumina in the calcined product is L / S=10, that is, 150g alumina. 1.5L distilled water, set aside;
[0023] Step 2. The aqueous solution of the roasted product in step 1 is heated to 0.15m under the condition of a constant temperature water bath at 90°C 3 / (L·hour) flow into CO 2 Gas while stirring at 350r / min for 1 hour.
[0024] Step 3. Connect the above to CO 2 The aqueous solution of gas is separated into solid and liquid, and aluminum fluoride is added to the obtained solid as a sodium removal agent. The addition amount is 0.05% of the solid amount. First, it is dried at 115°C, and then it is dried at 1350°C and a pressure greater than 100Pa. It is calcined at high temperature under the condition of air atmosphere and the heating rate is less than 1°C / min. After natural cooling, alumina with sodium ox...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Step 1. Pre-calcin industrial aluminum hydroxide at 600°C for 1 hour, then add the calcined product to distilled water. The liquid-to-solid ratio of distilled water to alumina in the calcined product is L / S=10, that is, 130g alumina. 1.3L distilled water, set aside;
[0027] Step 2. The aqueous solution of the roasted product in step 1 is heated to 0.2m in a constant temperature water bath at 90°C 3 / (L·hour) flow into CO 2 Gas while stirring at 350r / min for 1 hour.
[0028] Step 3. Connect the above to CO 2 The solid-liquid separation of the gas aqueous solution, the addition of boric acid as a sodium removal agent to the obtained solid, the addition amount is 0.20% of the solid content, first dry at 115 ℃, and then at 1350 ℃, pressure greater than 100 Pa, dry air atmosphere Calcination at high temperature under the condition of heating rate less than 1°C / min, and natural cooling to obtain alumina with sodium oxide<0.10% (see Table 1).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com