Exchange modification method for reducing content of sodium oxide in beta-type molecular sieve
A molecular sieve, sodium oxide technology, applied in the direction of crystalline aluminosilicate zeolite, etc., can solve the problems of difficult implementation, ammonia nitrogen pollution, difficulty and so on
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
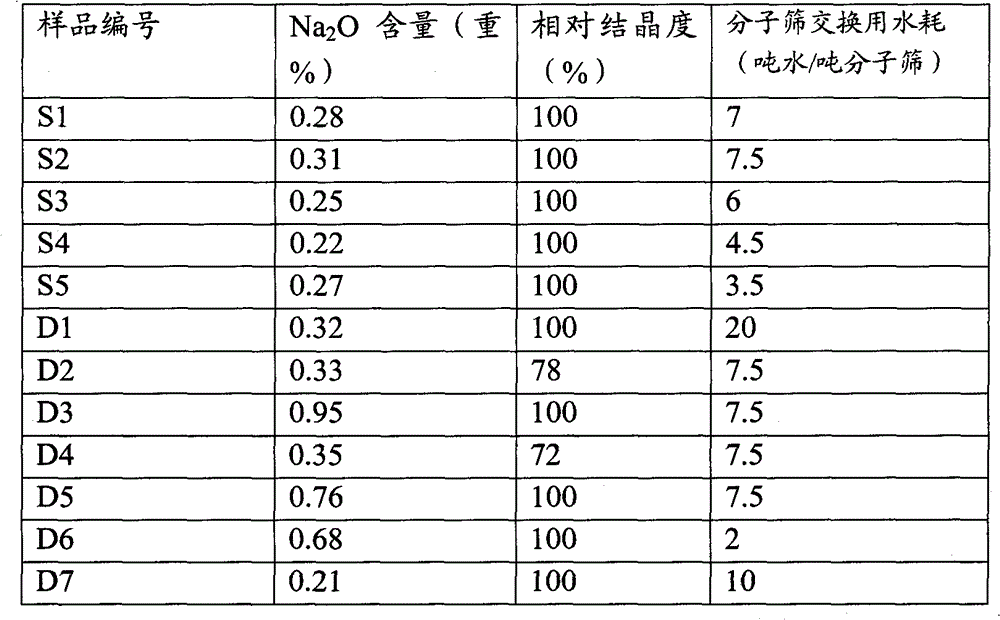
[0019] Weigh 12.8 grams of citric acid, add an appropriate amount of cold water and stir to dissolve it, then add 5.07 grams of 36% by weight hydrochloric acid, then continue to add cold water to dilute the solution to 1000ml to form a low-concentration mixed acid, control the solution temperature: 2 ± 0.5 ° C, at During stirring, add 143 grams of Naβ molecular sieve former powder dry basis (in the molecular sieve exchange liquid, H 2 O: the weight ratio of molecular sieve raw powder dry basis=7:1), then stirred and reacted at 2±0.5°C for 1.5 hours, then filtered the slurry, and the filter cake was drenched with deionized water 5 times the dry basis weight of Naβ molecular sieve raw powder Wash and dry to obtain a β-molecular sieve sample exchanged once with a low-temperature acidic solution, which is denoted as S1. Its properties and exchange water consumption are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0021] Weigh 10.1 grams of oxalic acid, add an appropriate amount of cold water and stir to dissolve it, then add 15.75 grams of nitric acid with a concentration of 20% by weight, then continue to add cold water to dilute the solution to 1000 ml to form a low-concentration mixed acid, control the solution temperature: 1 ± 0.5 ° C, Add 133 grams of Naβ molecular sieve former powder dry base (in the molecular sieve exchange liquid, H 2O: the weight ratio of molecular sieve raw powder dry basis=7.5:1), then stirred and reacted at 1±0.5°C for 2 hours, then filtered the slurry, and the filter cake was drenched with deionized water 5 times the dry basis weight of Naβ molecular sieve raw powder Wash and dry to obtain a β-molecular sieve sample exchanged once with a low-temperature acidic solution, which is denoted as S2. Its properties and exchange water consumption are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 3
[0023] Weigh 6.9 grams of acetic acid, add an appropriate amount of cold water and stir to dissolve it, then add 3.92 grams of phosphoric acid with a concentration of 50% by weight, then continue to add cold water to dilute the solution to 1000 ml to form a low-concentration mixed acid, control the solution temperature: 3 ± 0.5 ° C, Add Naβ molecular sieve former powder dry base 167 grams (in the molecular sieve exchange liquid, H 2 O: the weight ratio of molecular sieve raw powder dry basis=6:1), then stirred and reacted at 3±0.5°C for 2 hours, then filtered the slurry, and the filter cake was drenched with deionized water 5 times the dry basis weight of Naβ molecular sieve raw powder Wash and dry to obtain a β molecular sieve sample exchanged once with a low-temperature acidic solution, which is denoted as S3. Its properties and exchange water consumption are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com