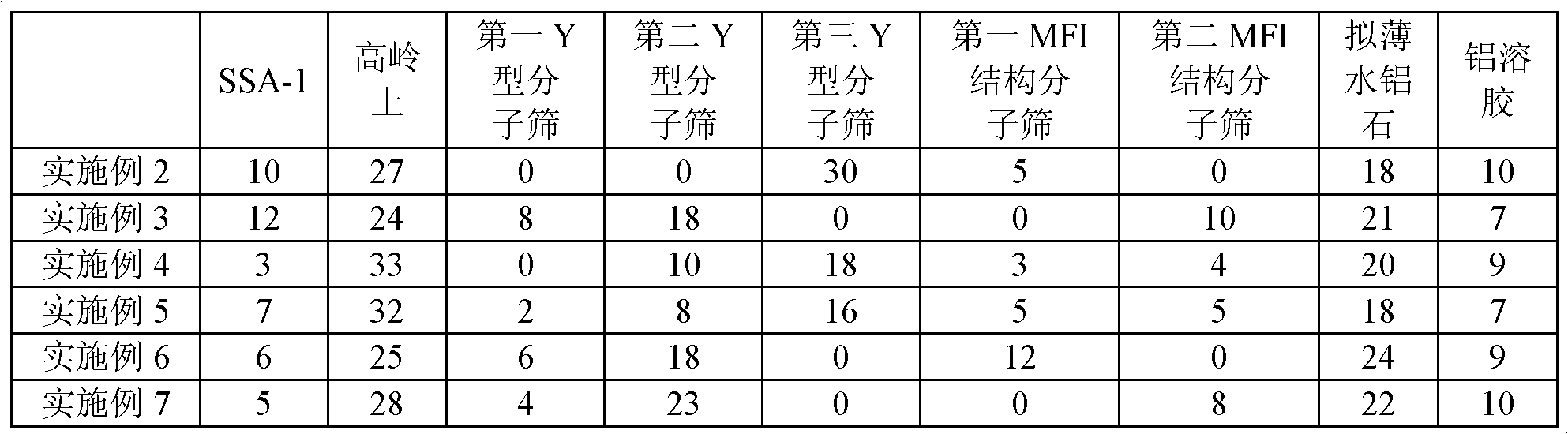
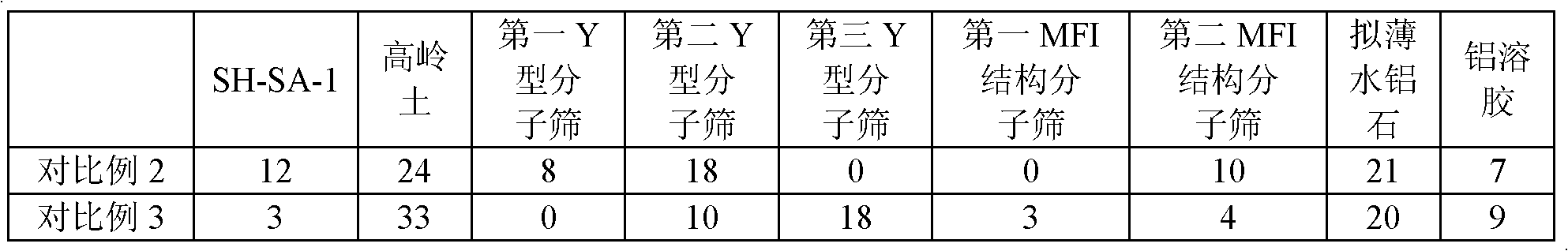
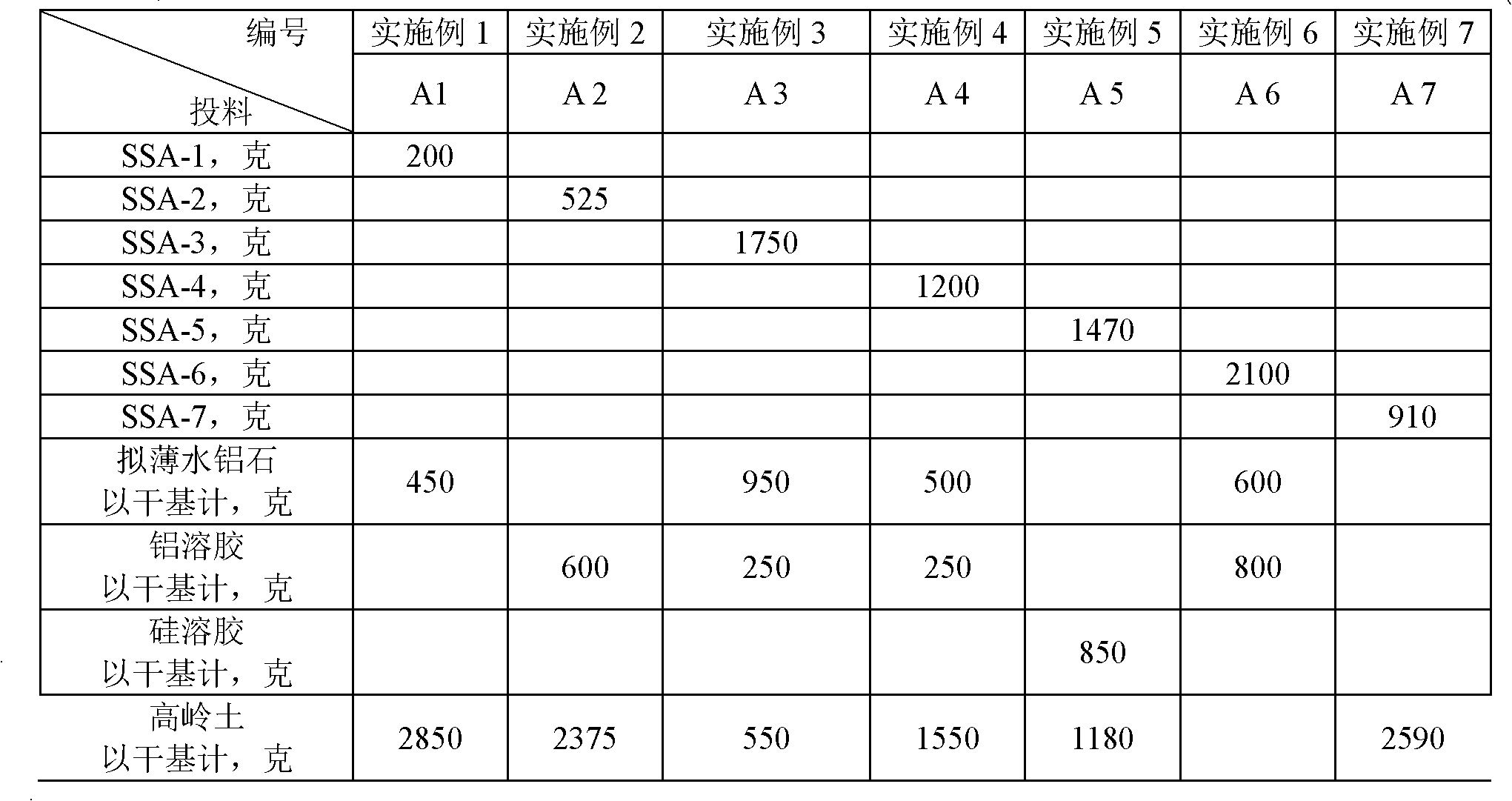
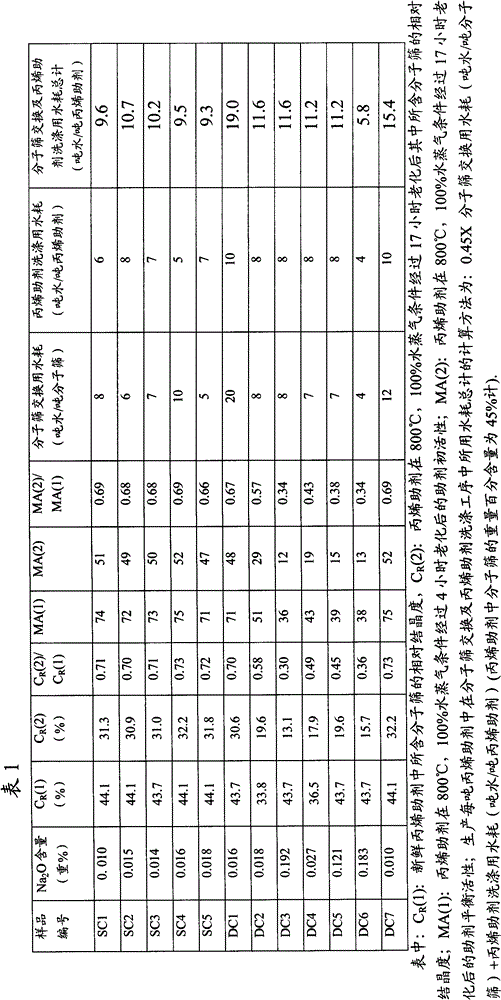
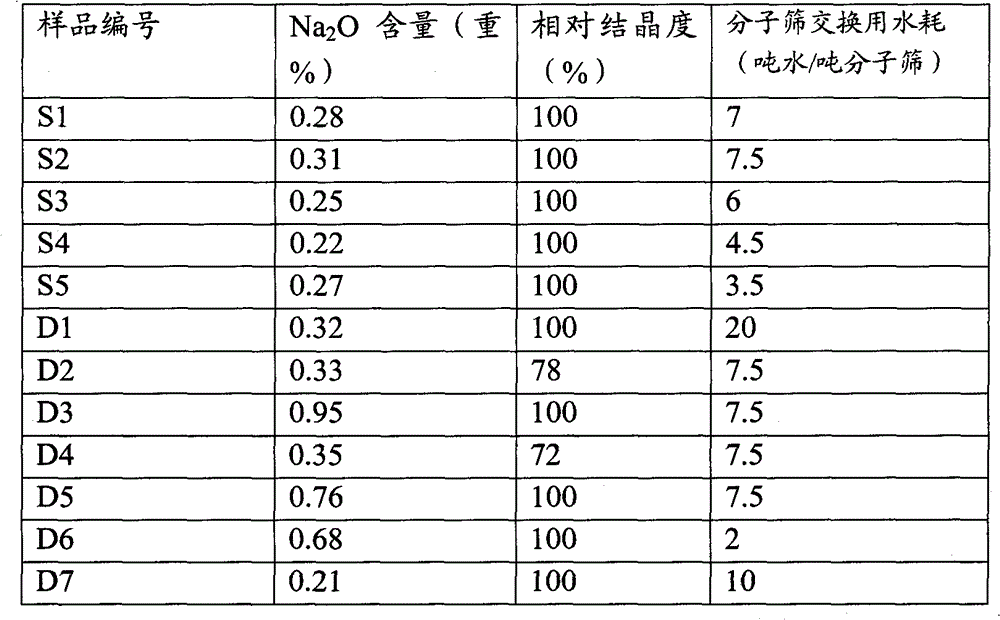
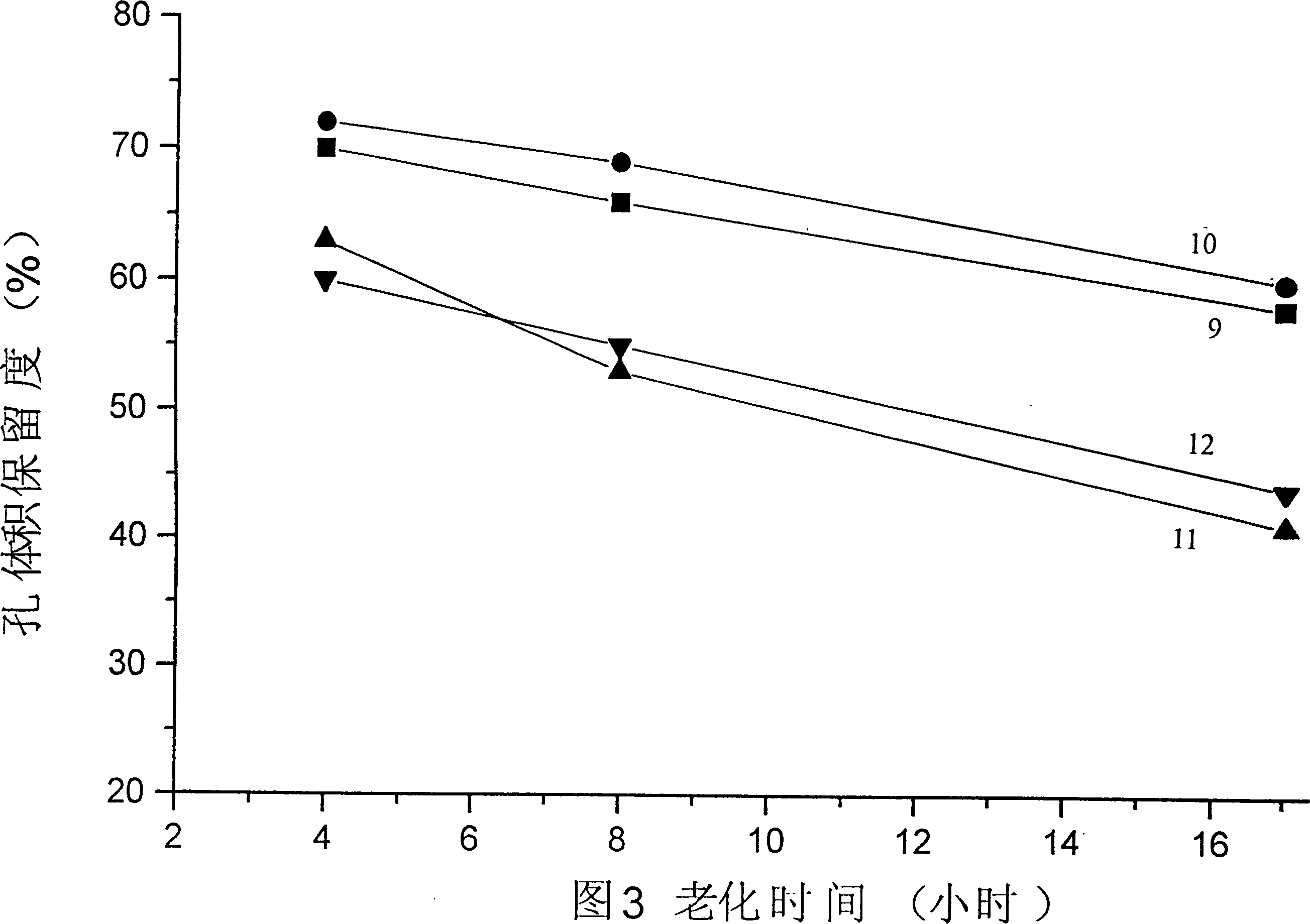Patents
Literature
67results about How to "Reduce sodium oxide content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
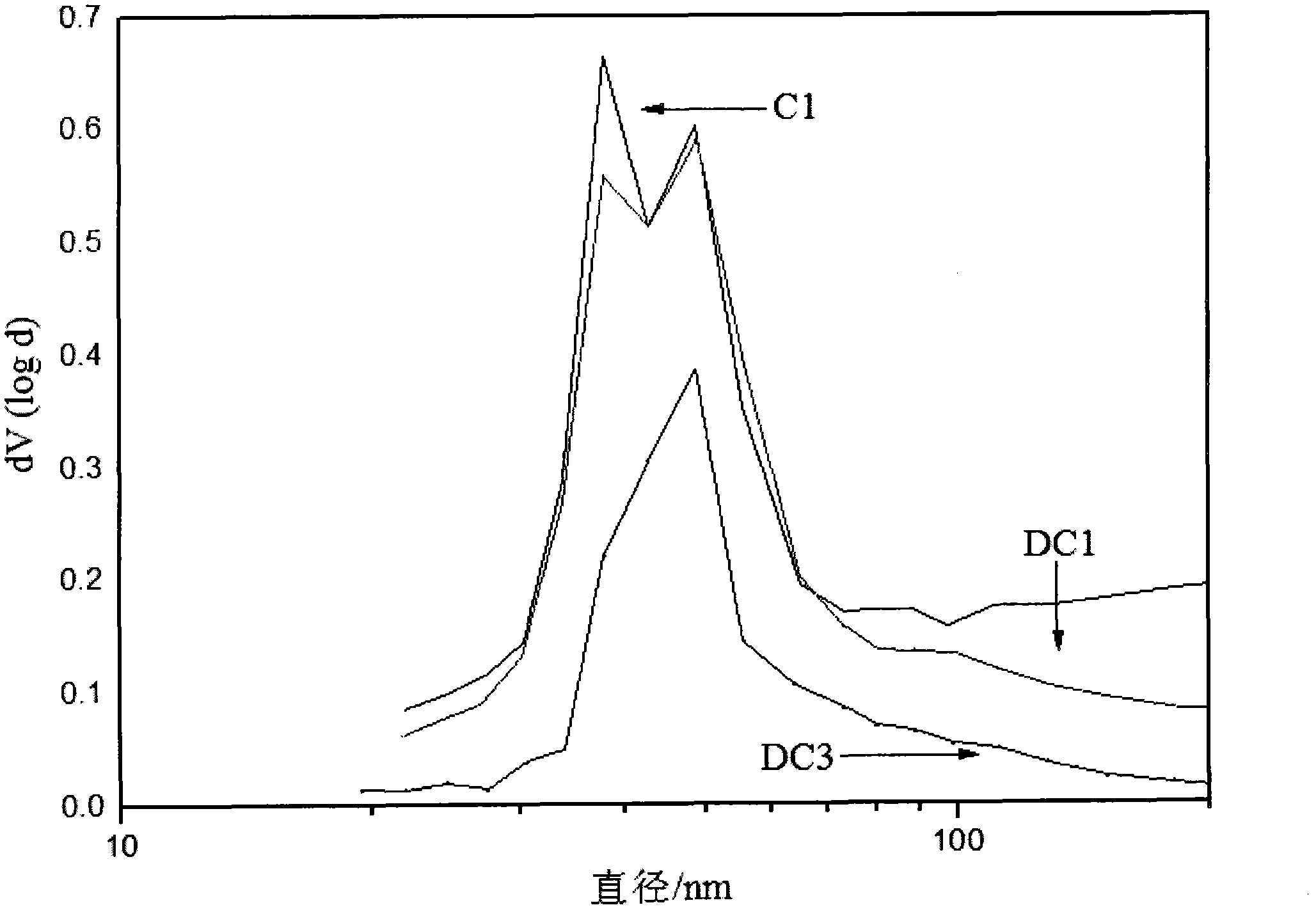
Process for preparing super-stable Y zeolite containing rare-earth elements
InactiveCN1159101CAchieve the purpose of exchangeLower activation energyCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsHigh resistanceRare-earth element
A rare-earth contained super-stable Y zeolite is prepared from the super-stable Y zeolite containing sodium oxide (3-5 wt.%), rare-earth compound and water in wt ratio of 1:(0.001-0.5):(1-10) through preparing solution of rare-earth compound, mixing and the said Y zeolite, and grinding with shearing stress of at least 10 kg / cm2 for at least 1 min. Its advantages are higher hydrothermal stability, high stability of activity, and high resistance to sodium and heavy metal pollutions.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for recycling alumina and sodium oxide from bayer process red mud
ActiveCN103030160AHigh dissolution rateEfficient cycleAlkali metal oxidesAluminium oxides/hydroxidesBrickRed mud
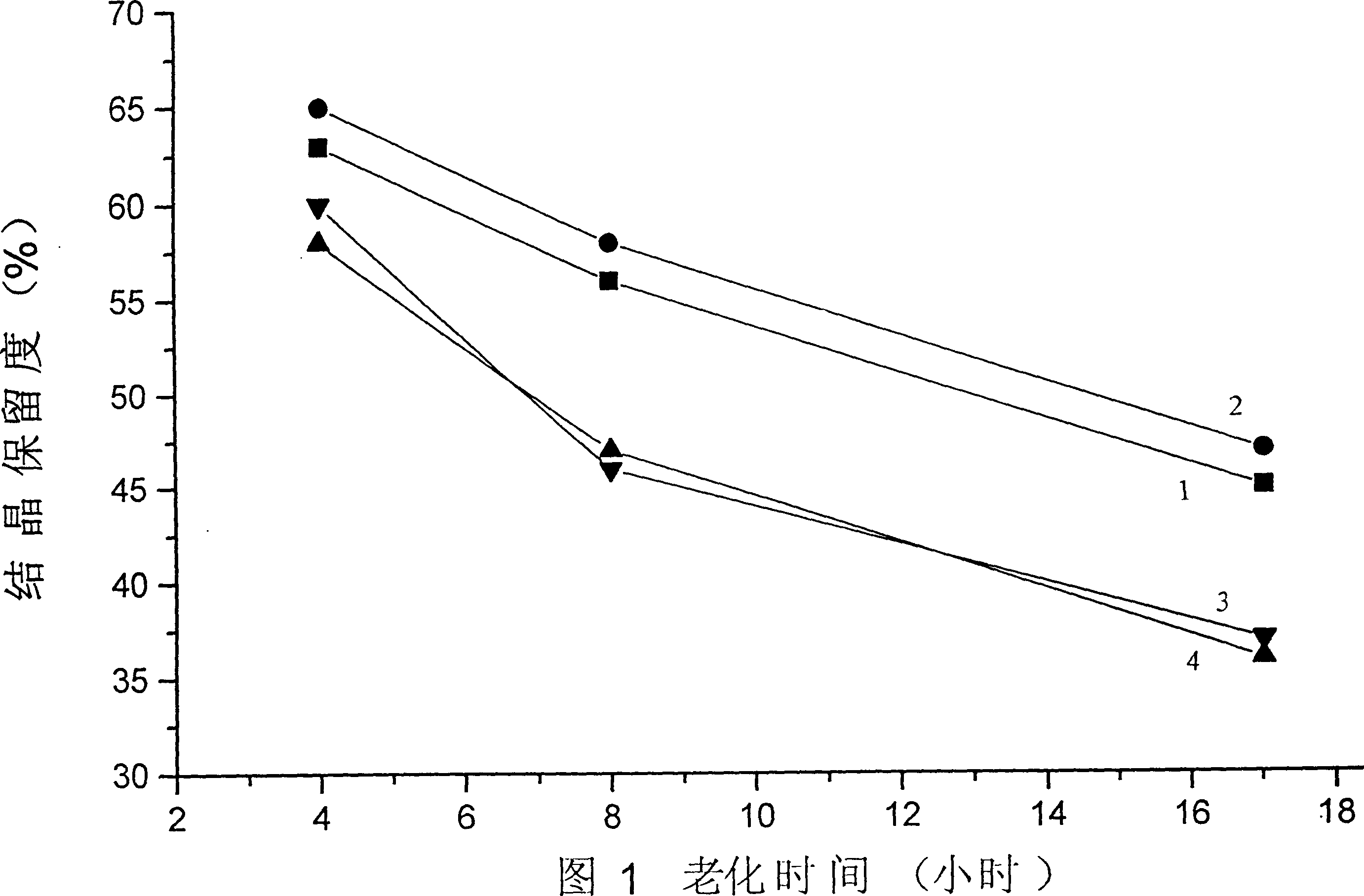
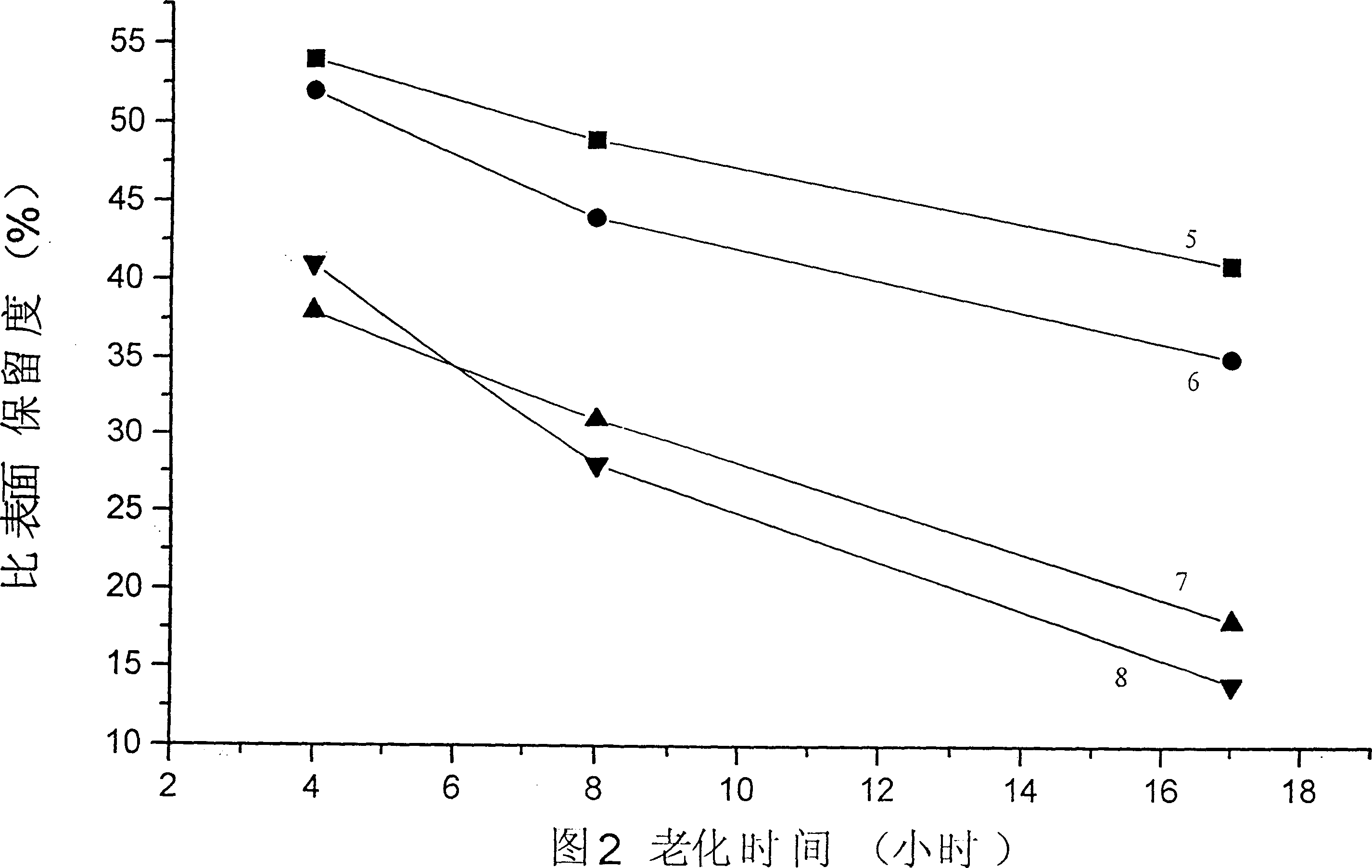
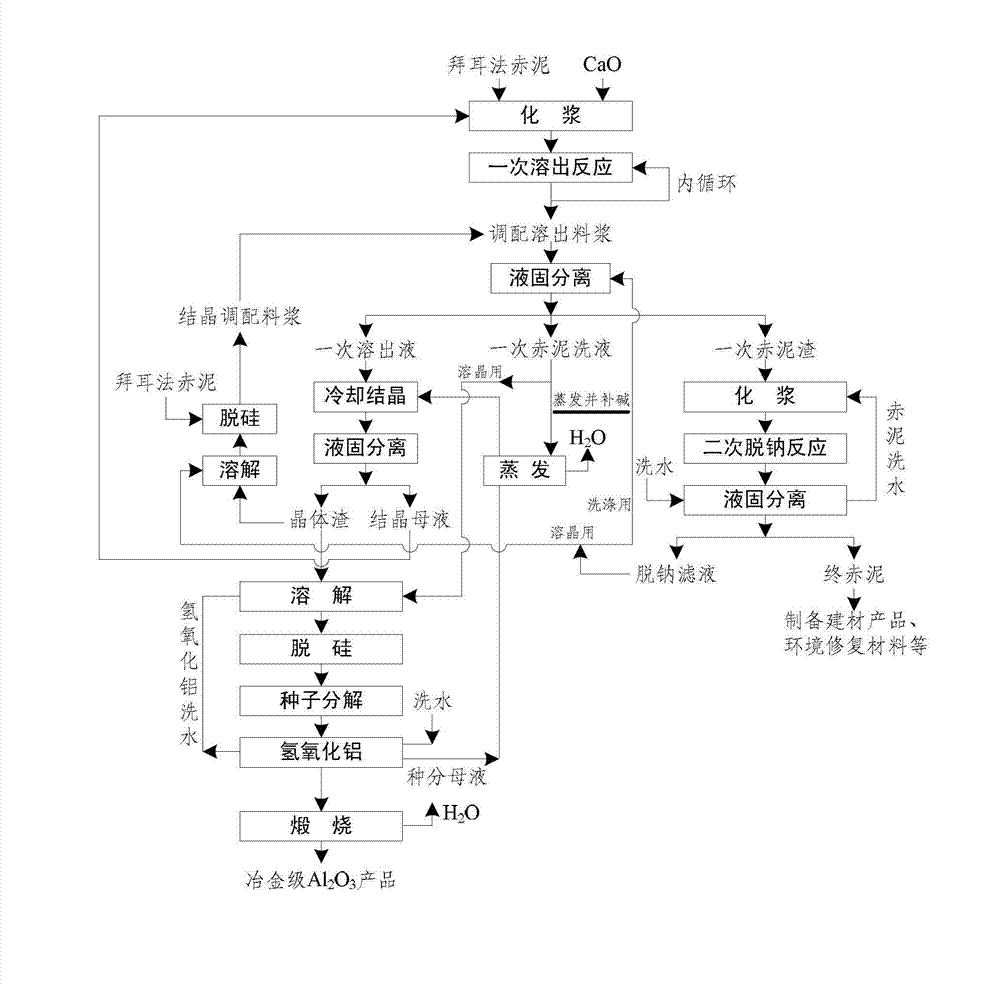
The invention relates to a method for recycling alumina and sodium oxide from bayer process red mud. In the method, by adopting a high molecular ratio and high alkali concentration sodium aluminate solution, aluminum extracting reaction can be rapidly carried out under mild operating conditions, so that the recovery rate of alumina in the red mud reaches more than 85%, and the defects, such as equipment scabbing and the like can be effectively prevented and even eliminated; by implementing an efficient crystallization process of an intermediate product of hydrated sodium aluminate, the cycle efficiency of a dissolution medium is greatly improved; due to complete transformation of a phase in the aluminum extracting reaction, a reaction process of recycling sodium oxide can be performed at low temperature and normal pressure; and after secondary sodium removal reaction, the sodium oxide content in final red mud is not more than 1% and is far less than 6-8% of the bayer process red mud. Therefore, the red mud can be doped in large proportion for preparing cement, brick and roadbed materials, concrete additives, environmental remediation materials and other fillers, and the problems such as resource utilization of the red mud, potential environment hazard and the like are hopefully solved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
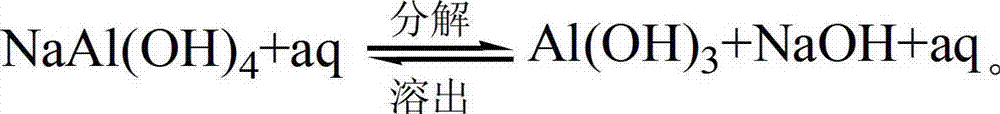
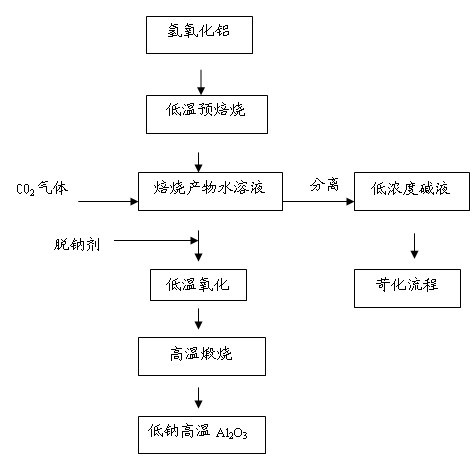
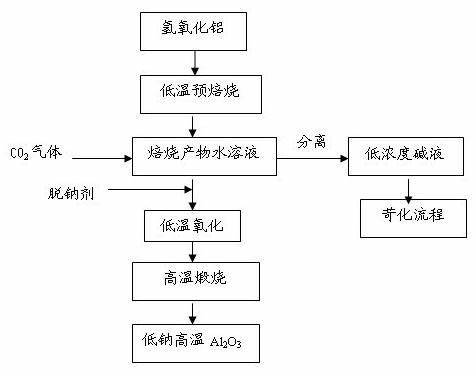
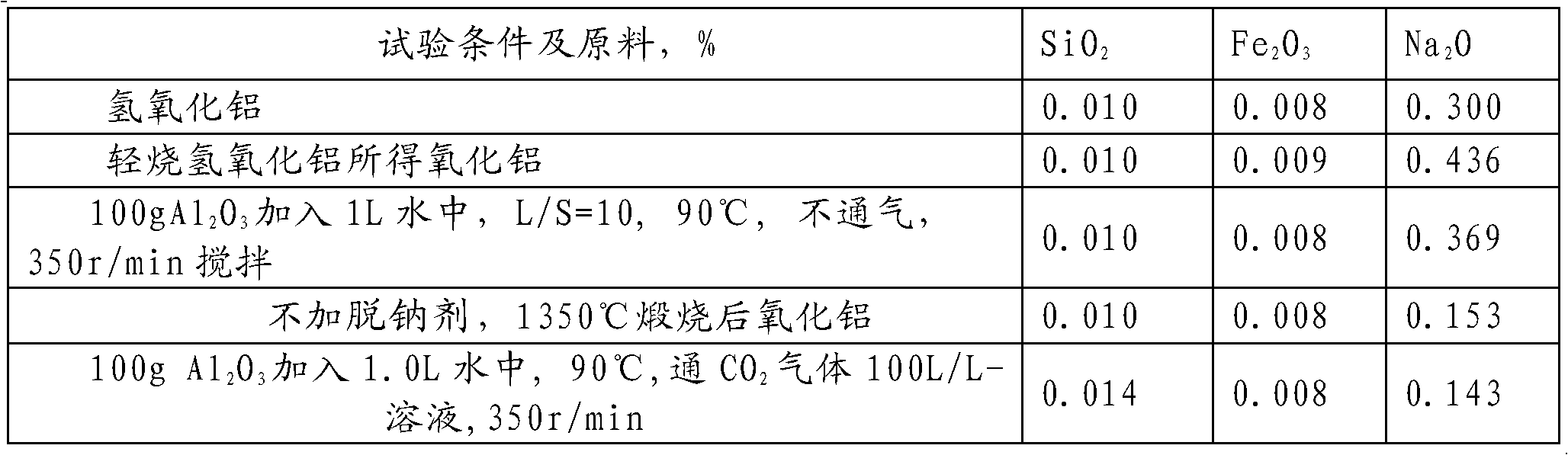
Method for reducing sodium oxide in aluminum oxide by using carbon dioxide
ActiveCN102070168AReduce sodium oxide contentLow costAluminates/aluminium-oxide/aluminium-hydroxide purificationAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationCooking & bakingFree cooling
The invention discloses a method for reducing sodium oxide in aluminum oxide by using carbon dioxide. The method comprises the following steps of: pre-baking aluminum hydroxide and adding a baked product into water to prepare baked product aqueous solution for later use; introducing CO2 gas into the baked product aqueous solution and fully stirring; adding a small number of sodium removing agents into the baked product aqueous solution into which the CO2 gas is introduced; performing liquid-solid separation; drying to obtain a solid; calcining the solid at a high temperature; and naturally cooling to obtain low-sodium aluminum oxide. By the method, the cost for manufacturing the high-temperature low-sodium aluminum oxide can be reduced, the variation in product performance caused by the sodium removing agent can be reduced, and a new approach is discovered for utilization of the carbon dioxide.
Owner:中铝山东有限公司
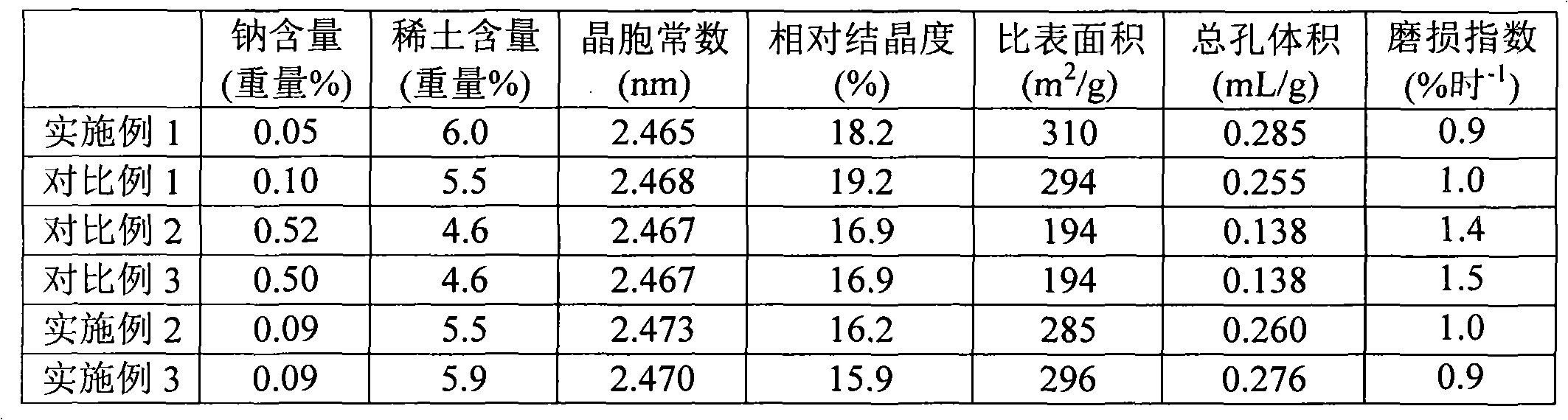
Rare earth-containing Y-type molecular sieve cracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102806096AImprove wear resistanceIncrease in sizeCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveRare earth ions
The invention relates to a preparation method of a rare earth-containing Y-type molecular sieve cracking catalyst. The preparation method comprises the steps: (1), mixing NaY molecular sieve without ion exchange and a matrix, pulping, spray-drying and molding to obtain a catalyst precursor; (2), firstly calcining the catalyst precursor at 20-400 DEG C; performing ammonium ion exchange on the calcined product; (3), performing second calcining and at least one rare-earth ion exchange on the product after ammonium ion exchange, wherein the rare-earth ion exchange is performed after the second calcining; the temperature of the ammonium ion exchange is more than that of the rare-earth ion exchange; and the second calcining temperature is more than that of the first calcining temperature. The invention also relates to a Y-type molecular sieve cracking catalyst obtained by the method. The rare earth-containing Y-type molecular sieve cracking catalyst obtained by the method provided by the invention has big total hole volume and specific surface area and has good wearing resistance.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
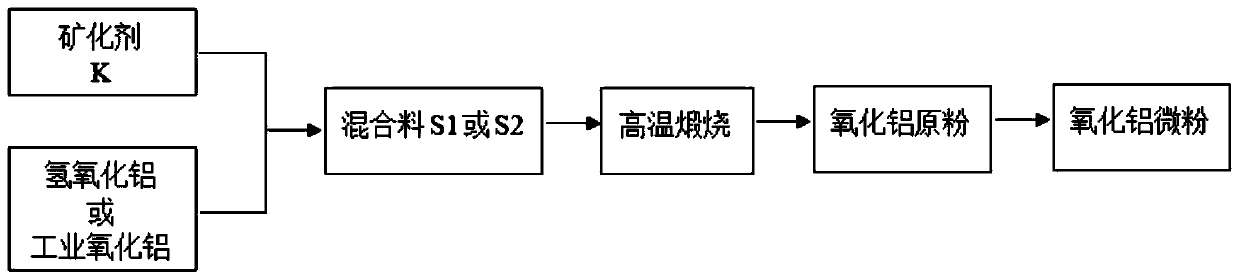
Preparation method of low-sodium and high-activity special alpha-Al2O3 micro powder
InactiveCN110342556AWide variety of sourcesHigh chemical purityAluminium compoundsAluminium hydroxideHigh activity
The invention discloses a preparation method of low-sodium and high-activity special alpha-Al2O3 micro powder. The preparation method comprises the steps that aluminum hydroxide or industrial aluminaserves as main raw materials, and ammonium chloride and aluminum fluoride serve as a mineralizer; the aluminum hydroxide or the industrial alumina and the mineralizer are mixed, a mixture is subjectedto high-temperature calcination to prepare low-sodium and high-specific-surface-area alpha-Al2O3 raw powder, the alpha-Al2O3 raw powder is placed into a ball mill for grinding, and the alpha-Al2O3 micro powder is prepared. According to the preparation method, the raw materials are wide in source, sodium removal is conducted through the ammonium chloride and aluminum fluoride composite mineralizer, the whole technology is completed through one step, neither a drying technology after acid pickling and nor silicon sand screening with silicon sodium removal is not needed, the overall cost is low,boric oxide and silicon dioxide do not remain in a final product, the alpha-Al2O3 micro powder is high in chemical purity, low in sodium oxide content, high in specific surface area and high in activity, the alpha-aluminum oxide conversion rate is greater than or equal to 96.0%, and grain size distribution is reasonable.
Owner:苏州盛曼特新材料有限公司
Sodium hydroxide recovery method of red mud
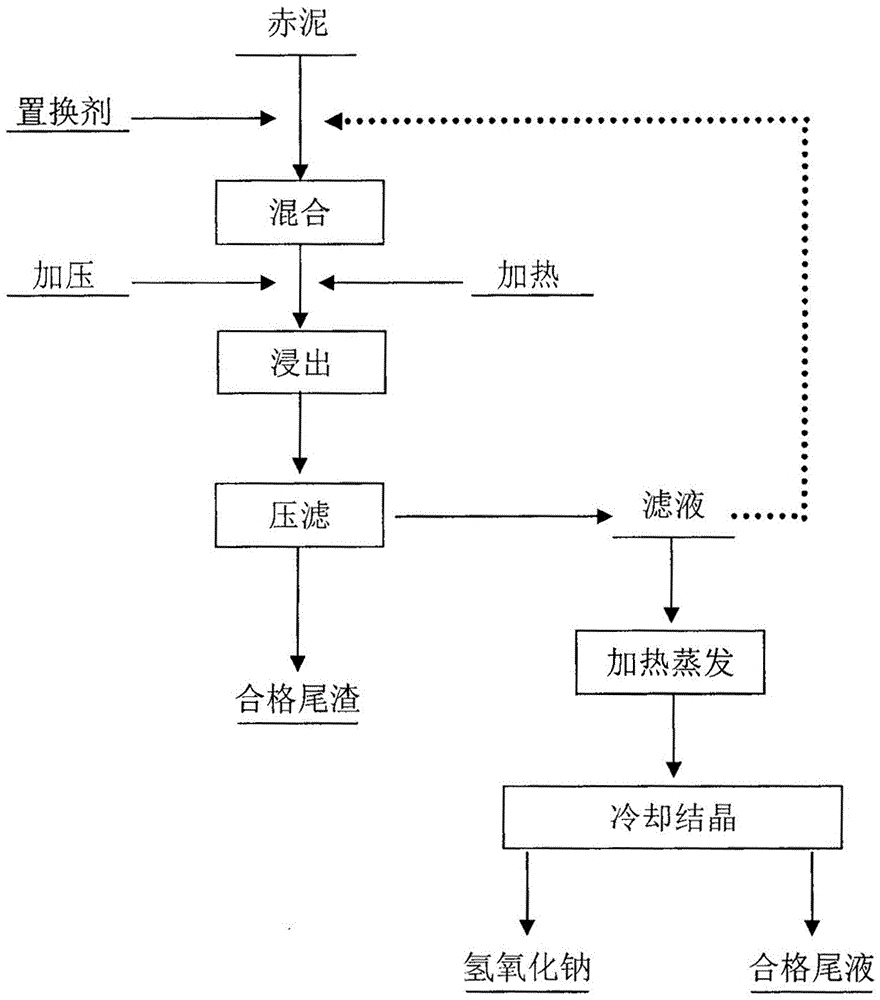
ActiveCN106809863AShort operating timeHigh sodium removal rateSolid waste disposalTransportation and packagingSolventRecovery method
The invention relates to a sodium hydroxide recovery method of red mud. The method comprises the steps of mixing the red mud and a displacement agent at a mass percentage of 5-20%, stirring in a pressing and heating stirring device for leaching for 15-45min at leaching temperature of 120-240 DEG C and leaching pressure of 0.5-2Mpa, performing pressure filtration after stirring and leaching to obtain qualified tailings and filtrate, returning the filtrate as a leaching solvent for recycling to leach the new red mud for 10-12 times, heating the recycled filtrate at 100-150 DEG C for evaporation for 60-120min, and rapidly cooling for crystallization of sodium hydroxide, wherein a leaching liquid-solid mass ratio is (2-5):1; a recovery rate of sodium hydroxide is equal to or greater than 97%; the purity of sodium hydroxide is equal to or greater than 99%; tail liquid after the crystallization is qualified. The method is short in operation time, high in sodium removal rate, low in leaching level and high in sodium hydroxide recovery rate, and the tailings are high in activity.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Method for preparing stable silica sol
InactiveCN1644498AReduce sodium oxide contentRaise the zeta potentialSilicaColloidal particleIon-exchange resin
Production of stable silica sol is carried out by taking basic sodium silica sol as material, removing sodium ion and adding ammonia or ammonia water to 8.5-9.5 to obtain stable silica sol. The content of silica is 10-35%, the content of sodium oxide is 0.3-0.5%, pH value is 8.5-10.5 particle size of colloidal particle is 8-20 nanometer. The hydrogen-state ion exchange resin or super-filter membrane technology is carried out by removing most Na+ in basic silica sol, decreasing sodium oxide content in silica sol, and adding ammonia. It achieves higher potential and stability.
Owner:章浩龙
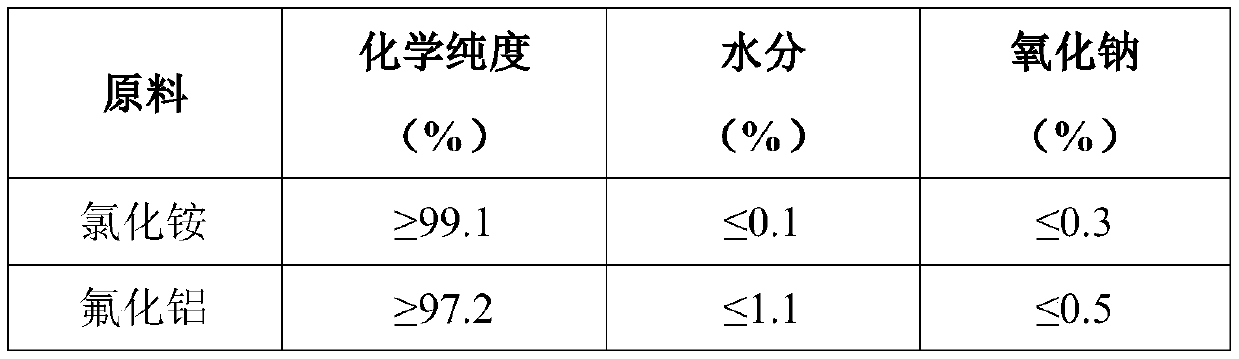
Preparation method of low-sodium orthohexagonal flaky alpha-alumina micropowder
The invention discloses a preparation method of a low-sodium orthohexagonal flaky alpha-alumina micropowder. The method which takes cheap industrial aluminum hydroxide as a raw material comprises thefollowing steps: mixing the industrial aluminum hydroxide, a dispersant and deionized water to prepare a slurry; carrying out grinding, sodium removal, solid-liquid separation, primary water washing,solid-liquid separation, drying, presintering and secondary water washing to obtain a low-sodium alumina precursor; and then adding a morphology inducer, and performing stirring, mixing and calciningto obtain the low-sodium orthohexagonal flaky alpha-alumina micropowder. The low-sodium regular orthohexagonal flaky alpha-alumina micropowder prepared by the method has a sodium oxide content of below 0.05%, an alpha-Al2O3 content of above 98%, has an orthohexagonal particle morphology, has a side length of below 1.5 [mu]m and a thickness of below 0.5 [mu]m, and can be applied to the fields of semiconductor materials, monocrystalline sapphire, reinforcing agents, protective layers and the like. The preparation method has the characteristics of wide sources of raw materials, simple device andproduction process, low production cost, realization of industrial production, environmental friendliness and the like.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
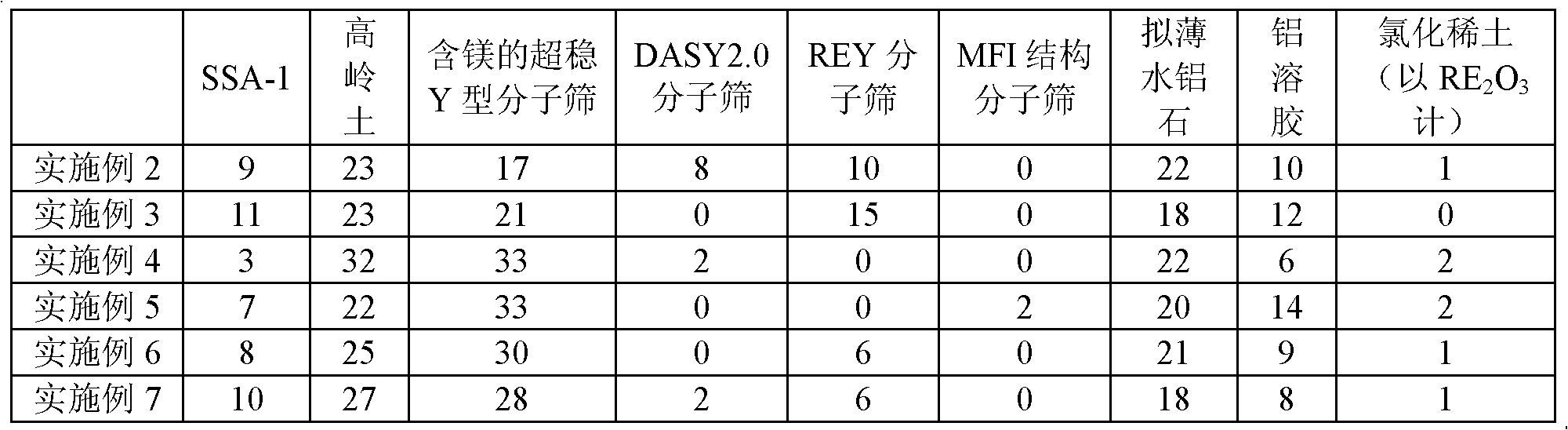
Catalytic cracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102974388AThe preparation process is environmentally friendlyLow costCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsRare earthIon exchange
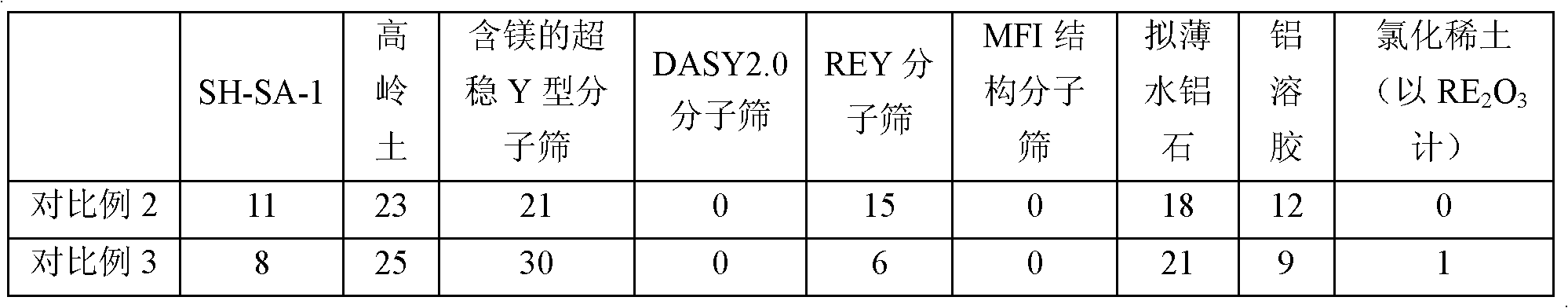
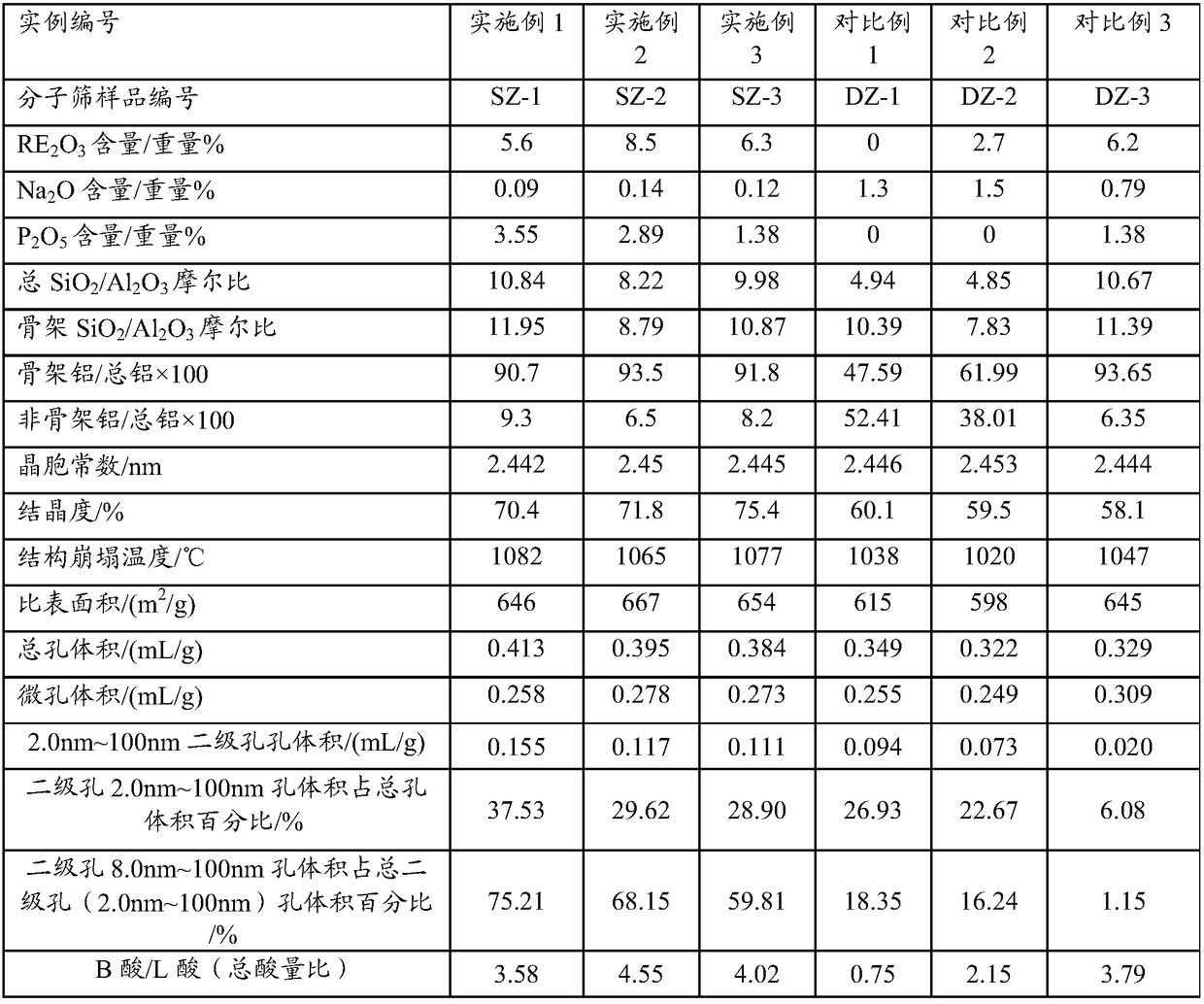
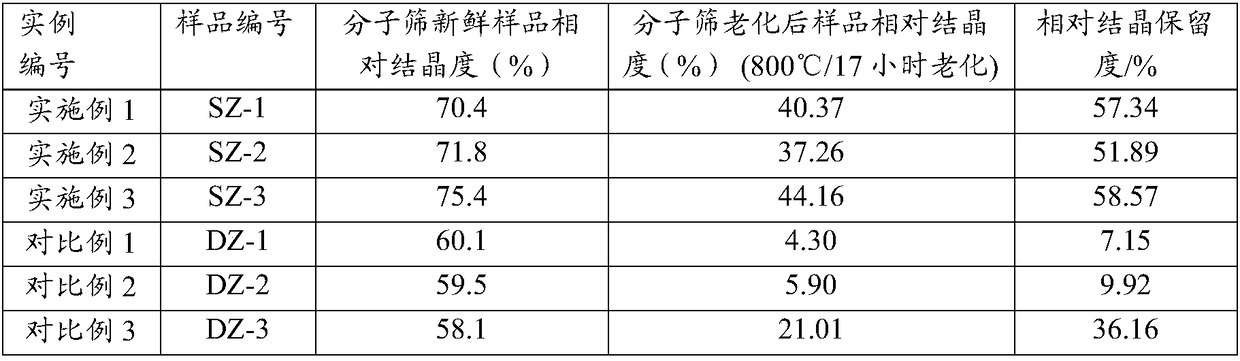
The invention relates to a catalytic cracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking catalyst comprises a cracking-active component, a mesoporous silica-alumina material, clay, and a binder. The preparation method of the mesoporous silica-alumina material comprises the steps that: a mesoporous silica-alumina material without ion exchange is mixed with water, and the mixture is beaten into slurry; and the obtained slurry contacts an inorganic acid under room temperature to 100 DEG C for at least 0.2h, such that the sodium oxide content in the mesoporous silica-alumina material is no higher than 0.2wt%, wherein a weight ratio of the mesoporous silica-alumina material without ion exchange to water to inorganic acid is 1:5-30:0.03-0.3. The cracking-active component comprises 30-99wt% of magnesium-containing ultra-stable Y-type molecular sieve and 1-70wt% of at least one type of molecular sieve selected from rare-earth-containing DASY molecular sieve, REY molecular sieve, and MFI-structured molecular sieve. During a catalytic cracking treatment process upon raw oil with relatively high basic nitrogen content, the catalytic cracking catalyst shows relatively high catalytic cracking activity, and assists in achieving relatively high conversion rate and especially relatively high diesel oil yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking catalyst
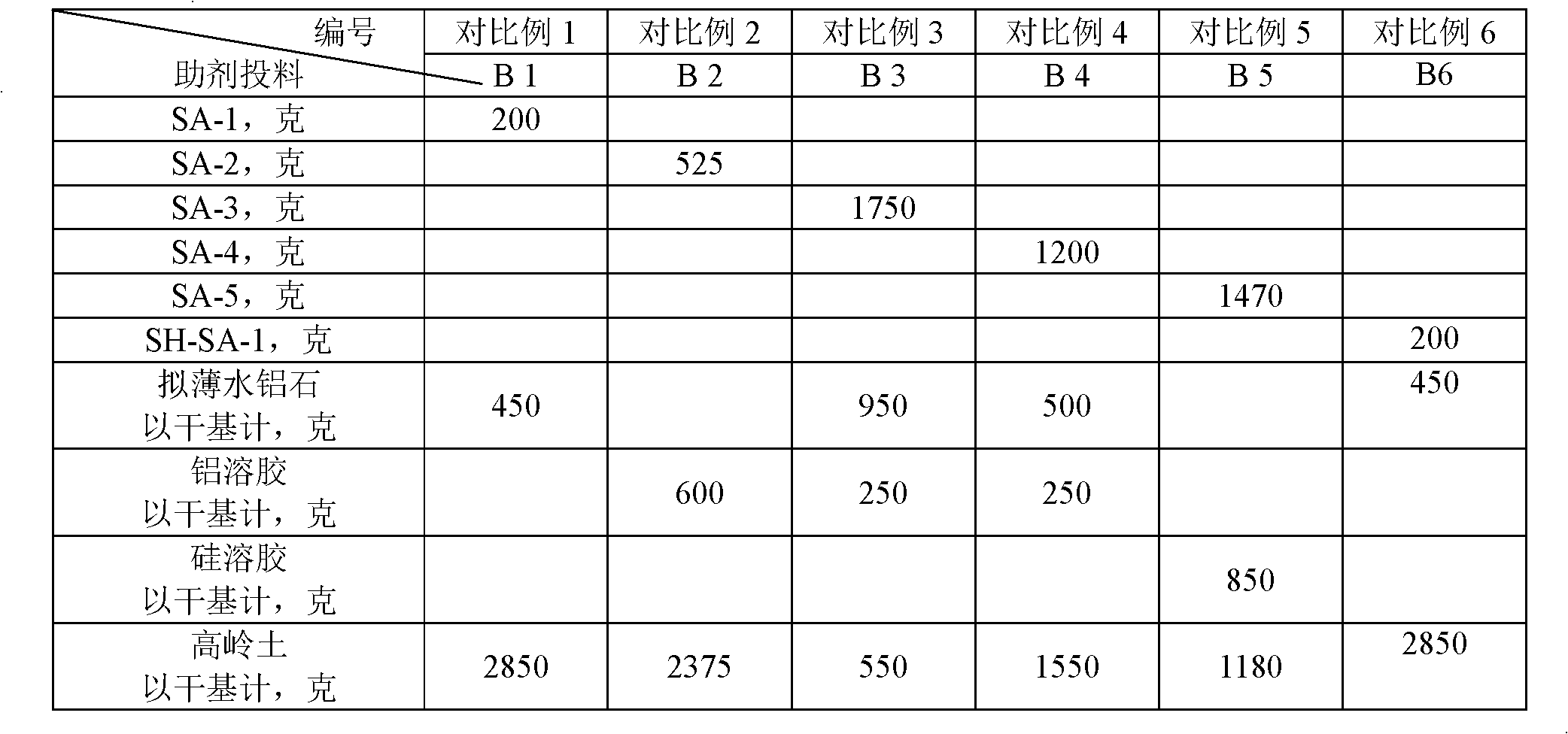
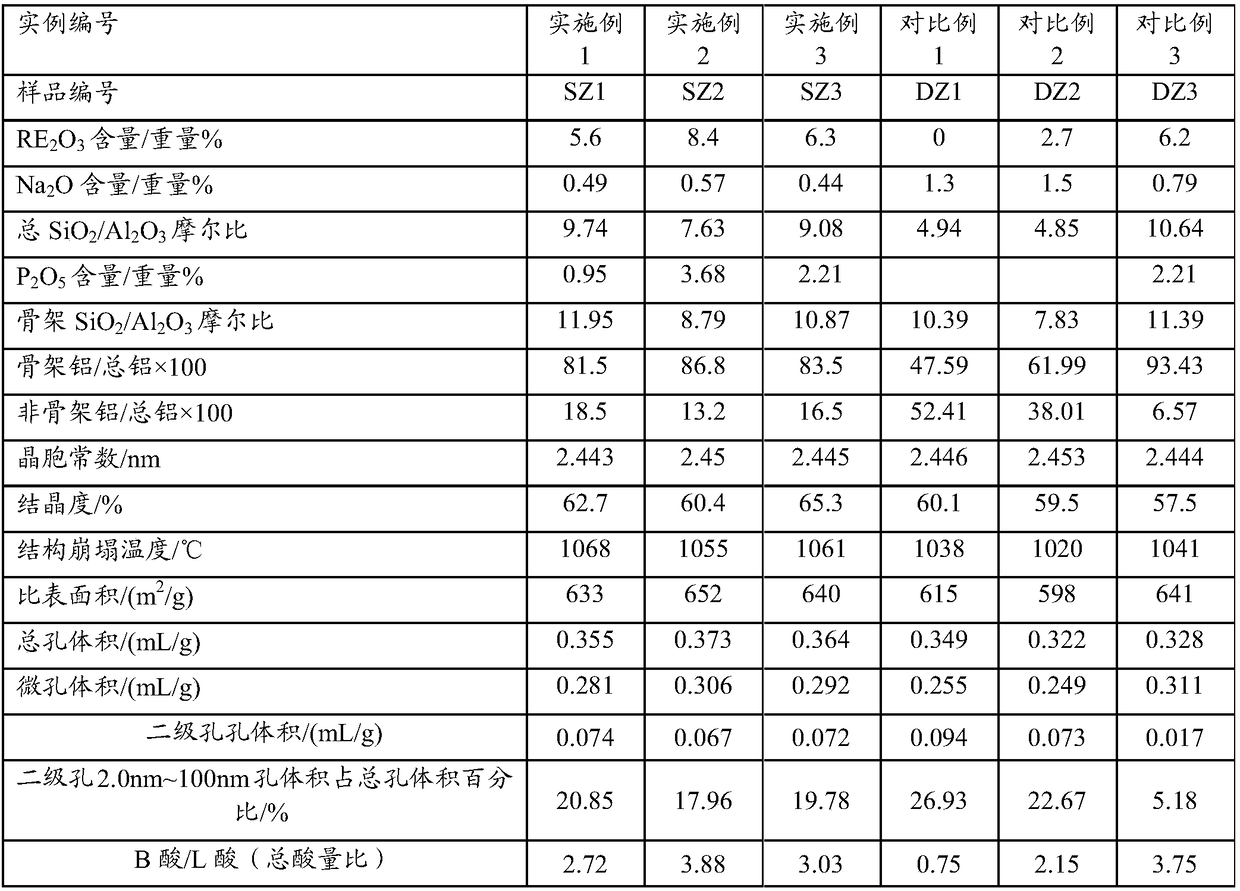
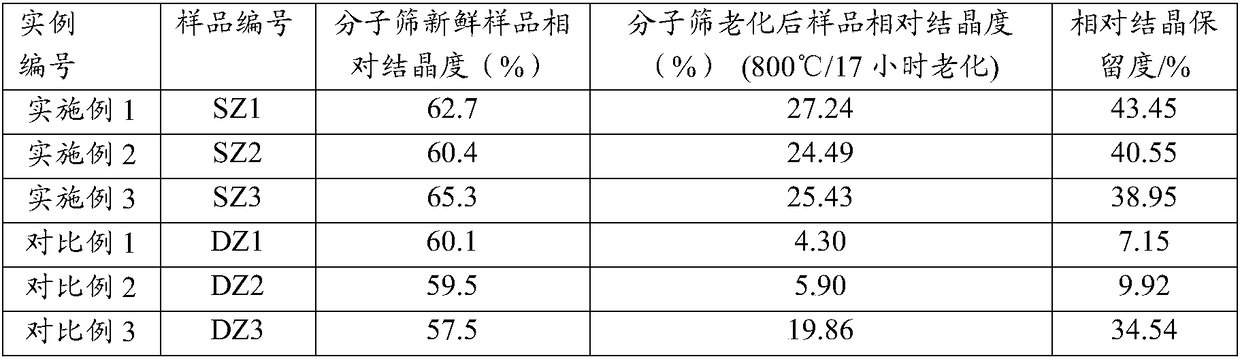
ActiveCN108452833AReduce sodium oxide contentLow non-framework aluminum contentCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveRare earth
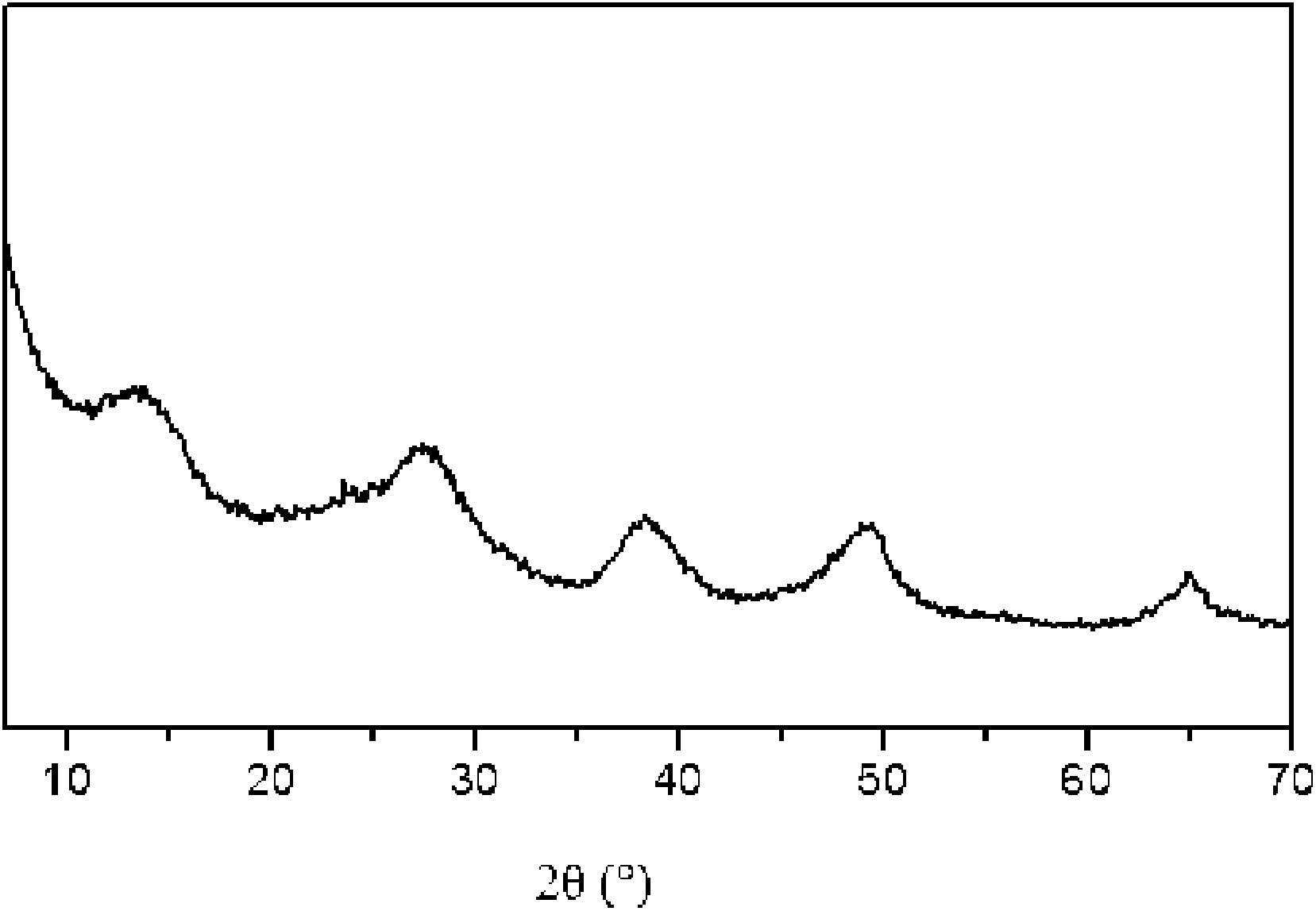
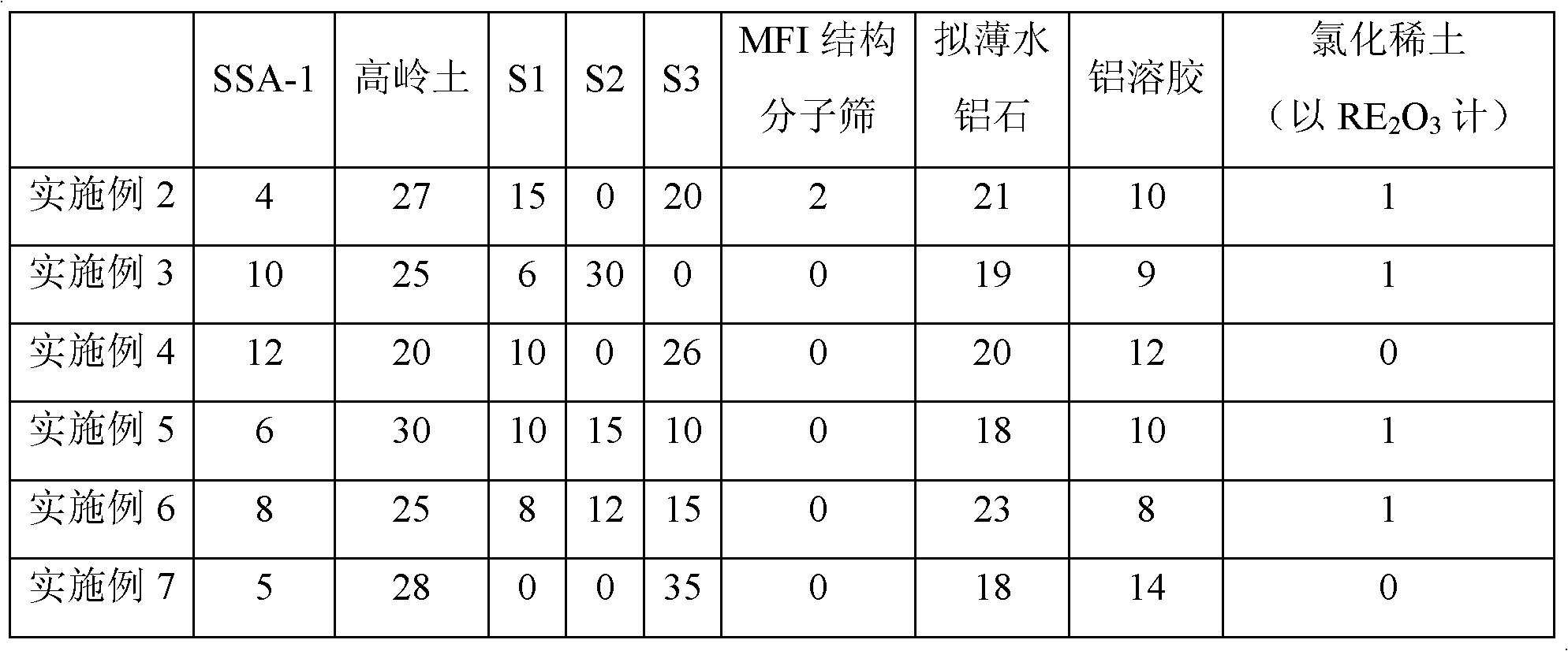
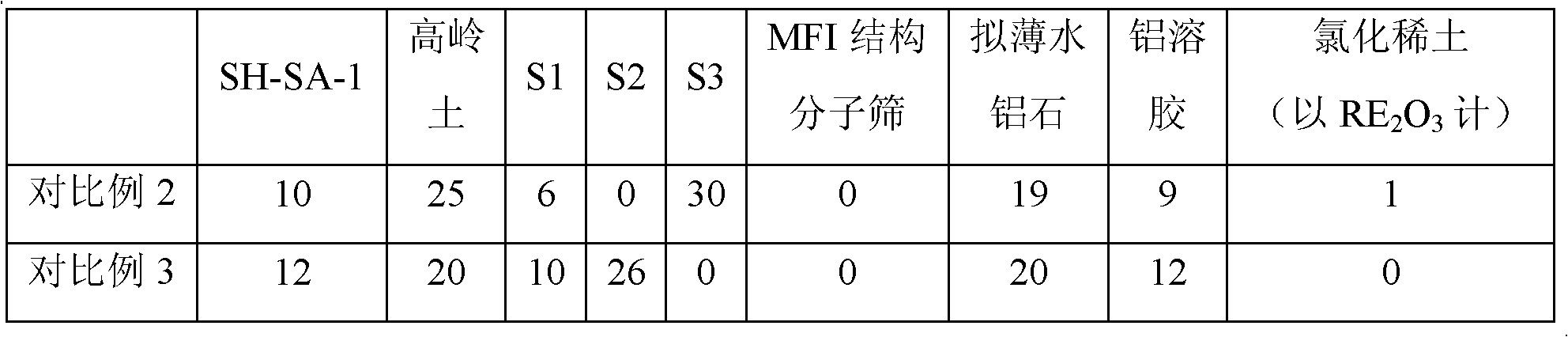
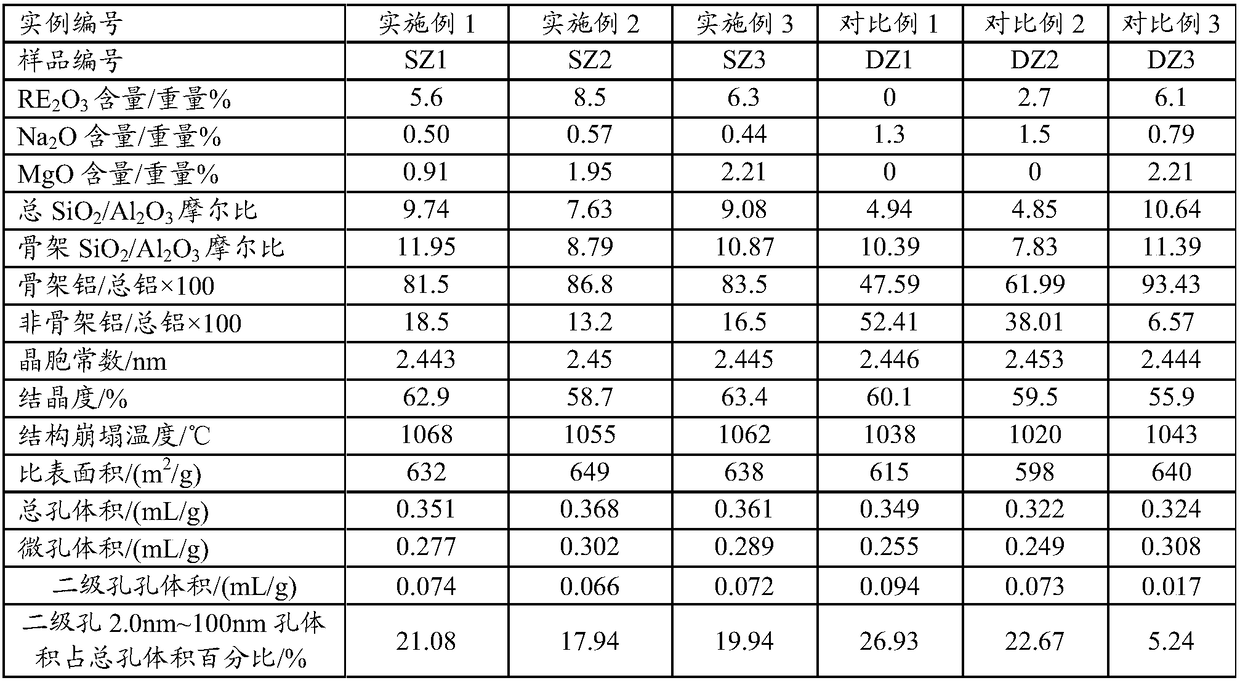
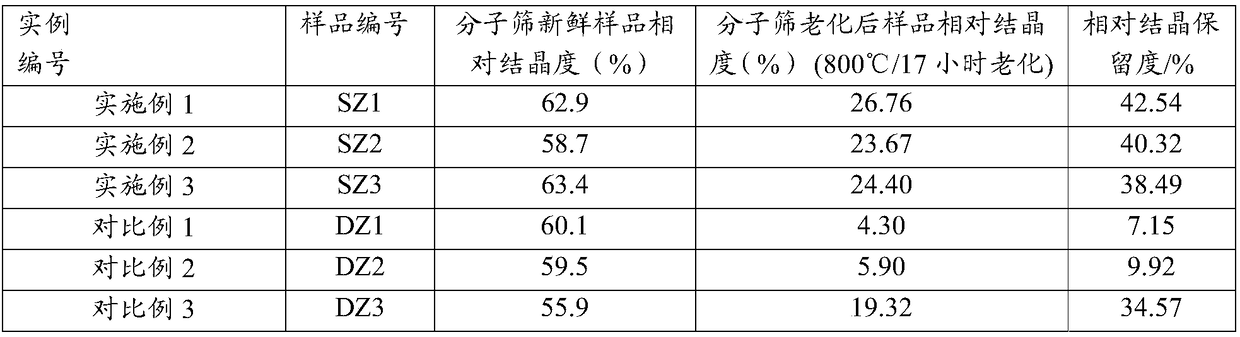
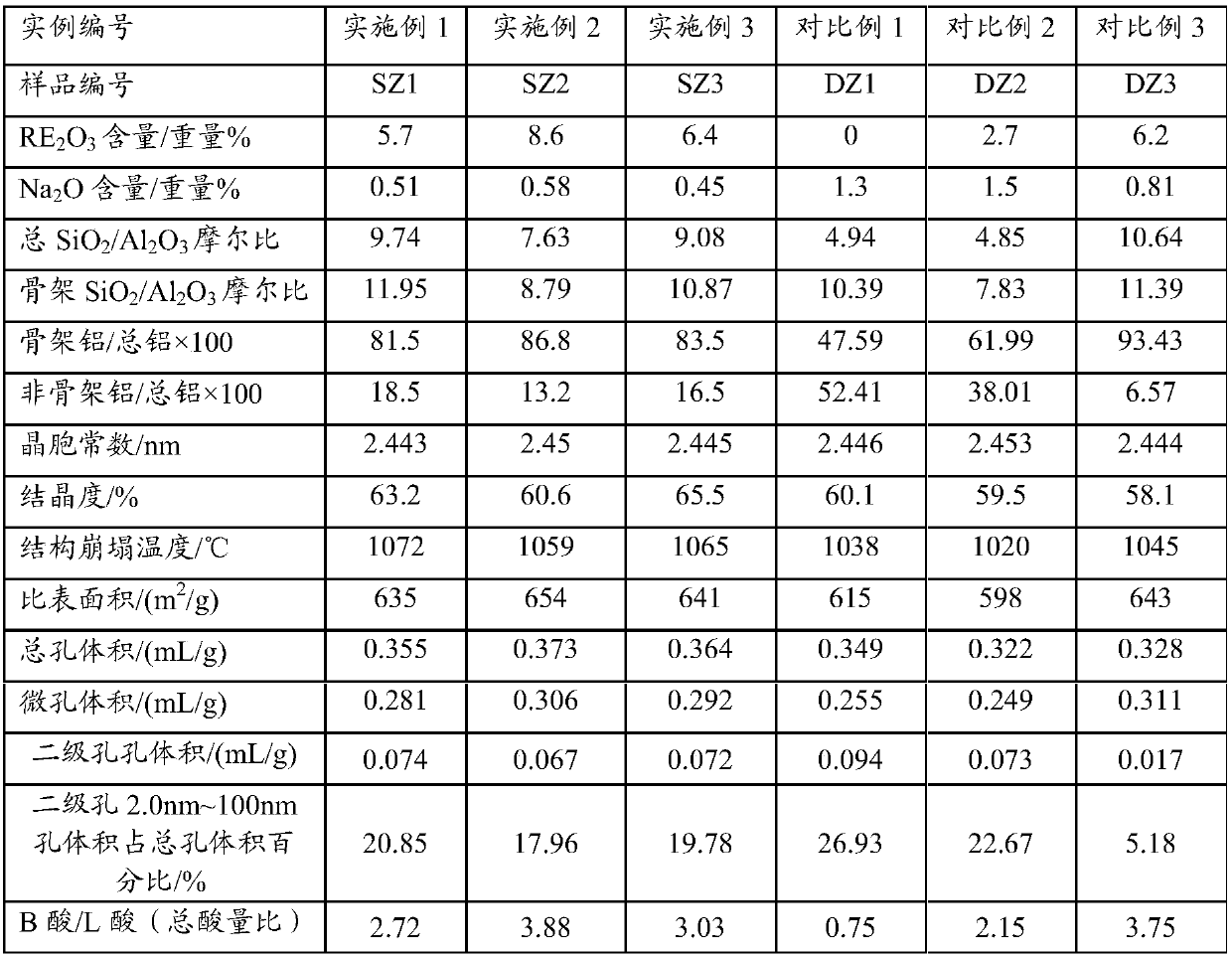
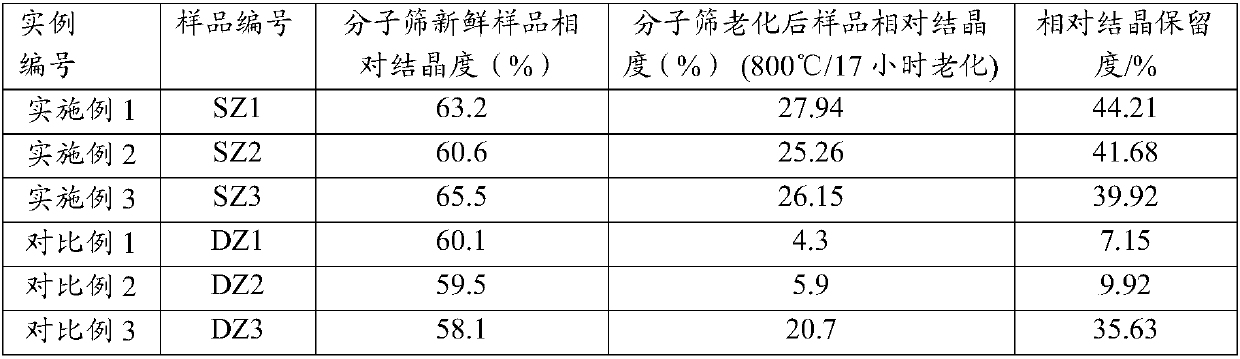
The invention provides a catalytic cracking catalyst. The catalytic cracking catalyst contains a modified Y type molecular sieve containing phosphorus and rare earth, an alumina binder containing an additive and clay. In the modified Y type molecular sieve containing phosphorus and rare earth, the content of rare earth oxide is 4 to 11 wt%; the content of phosphorus is 0.05 to 10 wt%; the contentof sodium oxide is no more than 0.5 wt%; a total pore volume is 0.4 to 0.48 mL / g; the pore volume of secondary pores accounts for 20 to 38% of the total pore volume; a lattice constant is 2.440 nm to2.455 nm; the content of non-framework aluminum is no more than 10% of total aluminum content; lattice collapse temperature is no less than 1060 DEG C; and a ratio of the amount of acid B to the amount of acid L is no less than 3.50. The catalyst has higher heavy oil conversion activity, low coke selectivity, and higher gasoline yield, liquefied gas yield, light oil yield and total liquid yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking auxiliary agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102974331AHeavy oil cracking ability is strongGood choiceCatalytic crackingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRoom temperatureSpinel
The invention provides a catalytic cracking auxiliary agent and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking auxiliary agent contains a mesoporous silica alumina material, spinel and / or precursors of the spinel and clay and / or heat-resistant inorganic oxide, wherein the mesoporous silica alumina material is obtained by the following steps of mix-pulping the mesoporous silica alumina material without ion exchange with water to obtain a slurry liquid; and contacting the slurry liquid with an inorganic acid for at least 0.2 hour at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 DEG C, so as to make the sodium oxide content in the mesoporous silica alumina material no higher than 0.2 wt%, wherein the weight ratio of the mesoporous silica alumina material without ion exchange, water and the inorganic acid is 1 : 5-30 : 0.03-0.3. The catalytic cracking auxiliary agent has relatively strong heavy oil cracking ability, high light oil yield and good coke selectivity when being used for the catalytic cracking of the heavy oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing catalytic cracking catalyst
ActiveCN102794191AReduce sodium oxide contentReduce water consumptionMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationMolecular sieveOrganic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing a catalytic cracking catalyst. The method comprises the following steps of: performing molecular sieve exchange, preparing the catalyst, and washing the catalyst and is characterized in that the step of performing molecular sieve exchange comprises the following substeps of: contacting a molecular sieve and an aqueous solution containing organic acid and inorganic acid at the temperature of between 0 and 5 DEG C for 0.5 to 3 hours, wherein the weight ratio of H2O to the molecular sieve is (11-18):1; the step of washing the catalyst comprises the following substeps of: contacting the catalyst and the aqueous solution containing the organic acid and the inorganic acid at the temperature of between 0 and 5 DEG C for 10 to 30 minutes, wherein the weight ratio of H2O to the catalyst is (7-9):1; and based on the amount of H<+>, the concentration of the organic acid in the aqueous solution is 0.0001 to 0.2 mol / L, and the concentration of the inorganic acid is 0.0001 to 0.1 mol / L. According to the method, ammonium salt is not completely used in the preparation process of the catalyst, the problem of ammoniac nitrogen pollution can be solved from the source, and water consumption and the discharge of wastewater in the preparation process are reduced obviously.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102974384AHigh FCC activityImprove conversion rateCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsIon exchangeRare earth
The invention relates to a catalytic cracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking catalyst comprises a cracking-active component, a mesoporous silica-alumina material, clay, and a binder. The preparation method of the mesoporous silica-alumina material comprises the steps that: a mesoporous silica-alumina material without ion exchange is mixed with water, and the mixture is beaten into slurry; and the obtained slurry contacts an inorganic acid under room temperature to 100 DEG C for at least 0.2h, such that the sodium oxide content in the mesoporous silica-alumina material is no higher than 0.2wt%, wherein a weight ratio of the mesoporous silica-alumina material without ion exchange to water to inorganic acid is 1:5-30:0.03-0.3. The cracking-active component comprises 90-100wt% of rare-earth-containing Y-type molecular sieve. During a catalytic cracking treatment process upon raw oil with relatively high basic nitrogen content, the catalytic cracking catalyst shows relatively high catalytic cracking activity, and assists in achieving relatively high conversion rate and especially relatively high gasoline yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking catalyst
ActiveCN108452835AReduce sodium oxide contentLow non-framework aluminum contentCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveRare earth
The invention provides a catalytic cracking catalyst. The catalytic cracking catalyst contains a modified Y type molecular sieve containing magnesium, alumina containing an additive and clay. In the modified Y type molecular sieve containing magnesium, the content of rare earth oxide is 4 to 10 wt%; the content of magnesium oxide is 0.1 to 4 wt%; the content of sodium oxide is 0.3 to 0.8 wt%; a total pore volume is 0.33 to 0.39 mL / g; the pore volume of secondary pores with pore diameters of 2 to 100 nm in the modified Y type molecular sieve accounts for 10 to 30% of the total pore volume; a lattice constant is 2.440 nm to 2.455 nm; the content of non-framework aluminum in the modified Y type molecular sieve is no more than 20% of total aluminum content; and lattice collapse temperature isno less than 1045 DEG C. The modified Y type molecular sieve has higher heavy oil conversion activity, low coke selectivity, and higher diesel oil yield, light oil yield and total liquid yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking catalyst
ActiveCN108452829AHigh hydrothermal stabilityHigh conversion activity of heavy oilMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveRare earth
The invention relates to a catalytic cracking catalyst, which contains a modified Y-type molecular sieve, an alumina binder and clay, wherein the modified Y-type molecular sieve contains 5-12 wt% of oxidized rare earth and 0.1-0.7 wt% of sodium oxide, and has the total pore volume of 0.33-0.39 mL / g, the pore volume of the secondary pores with the pore size of 2-100 nm in the modified Y-type molecular sieve accounts for 10-25% of the total pore volume, the unit cell constant is 2.440-2.455 nm, the non-framework aluminum content in the modified Y-type molecular sieve is not more than 20% of thetotal aluminum content, the lattice collapse temperature is not below 1050 DEG C, and a ratio of the amount of B acid to the amount of L acid is not less than 2.50. According to the present invention,the catalytic cracking catalyst has advantages of high heavy oil conversion activity, low coke selectivity, high diesel yield, high liquefied gas yield, high light-oil yield and high total liquid recovery.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102974389AThe preparation process is environmentally friendlyLow costCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsIon exchangeSlurry
The invention relates to a catalytic cracking catalyst and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking catalyst comprises a cracking-active component, a mesoporous silica-alumina material, clay, and a binder. The preparation method of the mesoporous silica-alumina material comprises the steps that: a mesoporous silica-alumina material without ion exchange is mixed with water, and the mixture is beaten into slurry; and the obtained slurry contacts an inorganic acid under room temperature to 100 DEG C for at least 0.2h, such that the sodium oxide content in the mesoporous silica-alumina material is no higher than 0.2wt%, wherein a weight ratio of the mesoporous silica-alumina material without ion exchange to water to inorganic acid is 1:5-30:0.03-0.3. The cracking-active component comprises 50-95wt% of a Y-type molecular sieve component and 5-50wt% of an MFI-structured molecular sieve component. During a catalytic cracking treatment process upon raw oil with relatively high basic nitrogen content, the catalytic cracking catalyst shows relatively high catalytic cracking activity, and assists in achieving relatively high conversion rate and especially relatively high liquefied gas yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Ammonium stabilized silica sol, its production and use thereof
An ammonium stabilized silica sol consists of silica 10-36%, sodium oxide 0.01-0.2% and ammonia 0.05-0.5%, with the pH value of 8.0-10.0. The silica with colloidal particle exists in water, the average particle size is 8-20 nanometer, sodium oxide with Na+ exists in silica sol solution, the ammonia with NH3.H2O and NH4 stable state exist in silica sol solution. Production is carried out by taking basic sodium silica sol as material, ionic exchange reacting by cation exchange resin with ammonia water of ammonium bicarbonate pretreated, and obtaining ammonium stabilized silica sol. It is prepared for polycrystal mullite fire-proof fiber. It achieves higher temperature resistant performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG YUDA CHEM IND
Catalytic cracking auxiliary agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102974335AHeavy oil cracking ability is strongGood choiceCatalytic crackingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsIon exchangeRoom temperature
The invention relates to a catalytic cracking auxiliary agent and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking auxiliary agent comprises a mesoporous silica-alumina material and clay and / or a heat-resistant inorganic oxide. The preparation method of the mesoporous silica-alumina material comprises the steps that: a mesoporous silica-alumina material without ion exchange is mixed with water, and the mixture is beaten into slurry; and the obtained slurry contacts an inorganic acid under room temperature to 100 DEG C for at least 0.2h, such that the sodium oxide content in the mesoporous silica-alumina material is no higher than 0.2wt%, wherein a weight ratio of the mesoporous silica-alumina material without ion exchange to water to inorganic acid is 1:5-30:0.03-0.3. When the catalytic cracking auxiliary agent is used in heavy oil catalytic cracking, the catalytic cracking auxiliary agent has relatively high heavy oil cracking capacity, higher light oil yield, and better coke selectivity.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Catalytic cracking catalyst
ActiveCN108452834AReduce sodium oxide contentHigh crystallinity valueCatalytic crackingMolecular sieve catalystsMolecular sieveAluminium
The invention provides a catalytic cracking catalyst. The catalytic cracking catalyst contains a modified Y type molecular sieve containing phosphorus and rare earth, alumina containing an additive and clay. The modified Y type molecular sieve containing phosphorus and rare earth comprises 4 to 11 wt% of rare earth, 0.05 to 10 wt% of phosphorus and 0.1 to 0.7 wt% of sodium oxide, and has a pore volume is 0.33 to 0.39 mL / g; the volume of pores with pore diameters of 2 to 100 nm accounts for 15 to 30% of a total pore volume; a lattice constant is 2.440 nm to 2.455 nm; the content of non-framework aluminum is no more than 20% of total aluminum content; lattice collapse temperature is more than 1050 DEG C; and a ratio of the amount of acid B to the amount of acid L is no less than 2.50. The catalyst has higher heavy oil cracking activity, good coke selectivity, and high gasoline yield, liquefied gas yield and total liquid yield.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for reducing ammonium and nitrogen consumption in FCC (Fluid Catalytic Cracking) catalyst production process
ActiveCN102078820AReduce sodium oxide contentReduce the amount of ammonium nitrogenMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationOrganic acidMolecular sieve
The invention discloses a method for preparing a FCC (Fluid Catalytic Cracking) catalyst, which comprises the steps of exchanging molecular sieves, preparing catalyst granules containing the exchanged molecular sieves and washing the catalyst, wherein the step of exchanging the molecular sieves comprises that the molecular sieves are contacted with low-concentration aqueous solution of inorganic acid and organic acid for 0.5 to 3 hours at the temperature of between 0 and 5 DEG C and separation is performed; and the step of washing the catalyst comprises that the catalyst is contacted with thediluted solution of the organic acid and the inorganic acid for 10 to 60 minutes at the temperature of between 0 and 5 DEG C. The method can be used for preparing the high-performance cracking catalyst and reduce the ammonium and nitrogen consumption in the catalyst preparation process.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for recycling alumina and sodium oxide from bayer process red mud
ActiveCN103030160BHigh dissolution rateEfficient cycleAlkali metal oxidesAluminium oxides/hydroxidesBrickRed mud
The invention relates to a method for recycling alumina and sodium oxide from bayer process red mud. In the method, by adopting a high molecular ratio and high alkali concentration sodium aluminate solution, aluminum extracting reaction can be rapidly carried out under mild operating conditions, so that the recovery rate of alumina in the red mud reaches more than 85%, and the defects, such as equipment scabbing and the like can be effectively prevented and even eliminated; by implementing an efficient crystallization process of an intermediate product of hydrated sodium aluminate, the cycle efficiency of a dissolution medium is greatly improved; due to complete transformation of a phase in the aluminum extracting reaction, a reaction process of recycling sodium oxide can be performed at low temperature and normal pressure; and after secondary sodium removal reaction, the sodium oxide content in final red mud is not more than 1% and is far less than 6-8% of the bayer process red mud. Therefore, the red mud can be doped in large proportion for preparing cement, brick and roadbed materials, concrete additives, environmental remediation materials and other fillers, and the problems such as resource utilization of the red mud, potential environment hazard and the like are hopefully solved.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalytic cracking auxiliary agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102974337AHeavy oil cracking ability is strongGood choiceCatalytic crackingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsIon exchangeRoom temperature
The invention provides a catalytic cracking auxiliary agent and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking auxiliary agent contains a mesoporous silica alumina material, a metal trapping agent and clay and / or heat-resistant inorganic oxide, wherein the mesoporous silica alumina material is obtained by the following steps of mix-pulping the mesoporous silica alumina material without ion exchange with water to obtain a slurry liquid; and contacting the slurry liquid with an inorganic acid for at least 0.2 hour at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 DEG C, so as to make the sodium oxide content in the mesoporous silica alumina material no higher than 0.2 wt%, wherein the weight ratio of the mesoporous silica alumina material without ion exchange, water and the inorganic acid is 1 : 5-30 : 0.03-0.3. The catalytic cracking auxiliary agent has relatively strong heavy oil cracking ability, high light oil yield and good coke selectivity when being used for the catalytic cracking of the heavy oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
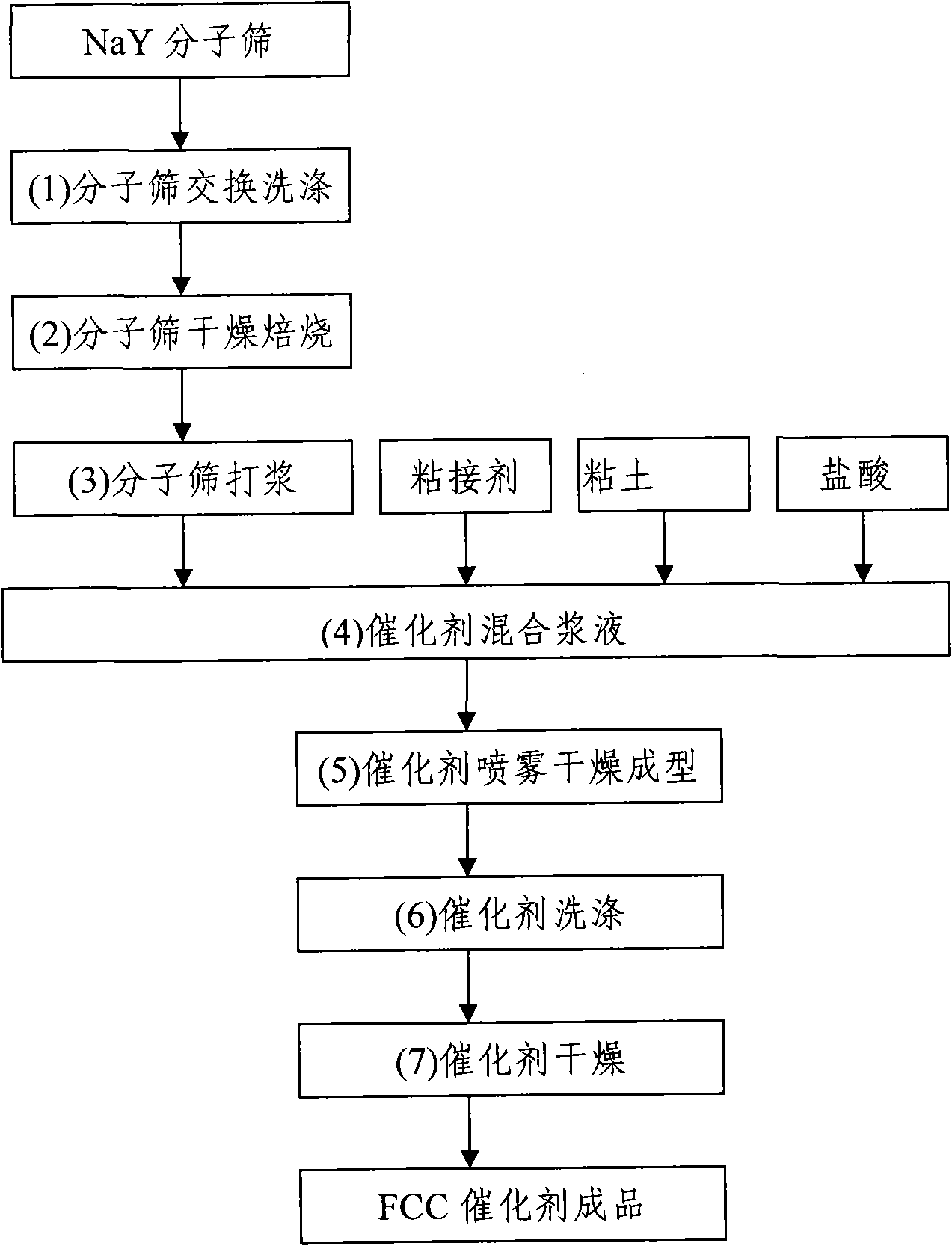
Exchange modification method for reducing content of sodium oxide in Y-type molecular sieve
ActiveCN102795636AEliminate the problem of ammonia nitrogen pollutionReduce water consumption and waste water dischargeFaujasite aluminosilicate zeoliteMolecular sieveOrganic acid
The invention discloses an exchange modification method for reducing the content of sodium oxide in a Y-type molecular sieve. The exchange modification method is characterized by comprising the following steps of contacting the Y-type molecular sieve of which the content of Na is relatively high and an aqueous solution containing inorganic acid and organic acid at the temperature of 0 to 5 DEG C for 0.5 to 3 hours; and separating, washing and drying to obtain a Y-type molecular sieve of which the content of the sodium oxide is relatively low, wherein the weight ratio of H2O to the molecular sieve is (11-18):1. By the exchange modification method, ammonium salt is not required in the process of reducing the content of the sodium oxide in the Y-type molecular sieve, so that pollution caused by ammonia nitrogen can be eliminated at the source, and water consumption and waste water emission are obviously reduced in the Y-type molecular sieve exchange process.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing catalytic cracking aid
ActiveCN102794194AReduce sodium oxide contentReduce water consumptionMolecular sieve catalystsBulk chemical productionMolecular sieveOrganic acid
The invention discloses a method for preparing a catalytic cracking aid. The method comprises the following steps of performing molecular sieve exchange, preparing a propylene aid and washing the propylene aid and is characterized in that the step of performing molecular sieve exchange comprises the following substeps of: contacting a molecular sieve and an aqueous solution containing inorganic acid and organic acid at the temperature of between 0 and 5 DEG C for 0.5 to 2 hours, wherein the weight ratio of H2O to the molecular sieve is (5-10):1, and based on the amount of H<+>, the concentration of the organic acid in the aqueous solution is 0.009 to 0.9 mol / L, and the concentration of the inorganic acid is 0.001 to 0.1 mol / L; the step of washing the propylene aid comprises the following substeps of: contacting the propylene aid and the aqueous solution containing the inorganic acid and the organic acid at the temperature of between 0 and 5 DEG C for 10 to 100 minutes, wherein the weight ratio of H2O to the propylene aid is (5-9):1; and based on the amount of H<+>, the concentration of the organic acid in the aqueous solution is 0.0001 to 0.2 mol / L, and the concentration of the inorganic acid is 0.0001 to 0.1 mol / L. According to the method, ammonium salt is not used in the preparation process of the propylene aid, the problem of ammoniac nitrogen pollution can be solved from the source, and water consumption and the discharge of wastewater in the preparation process are reduced obviously.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
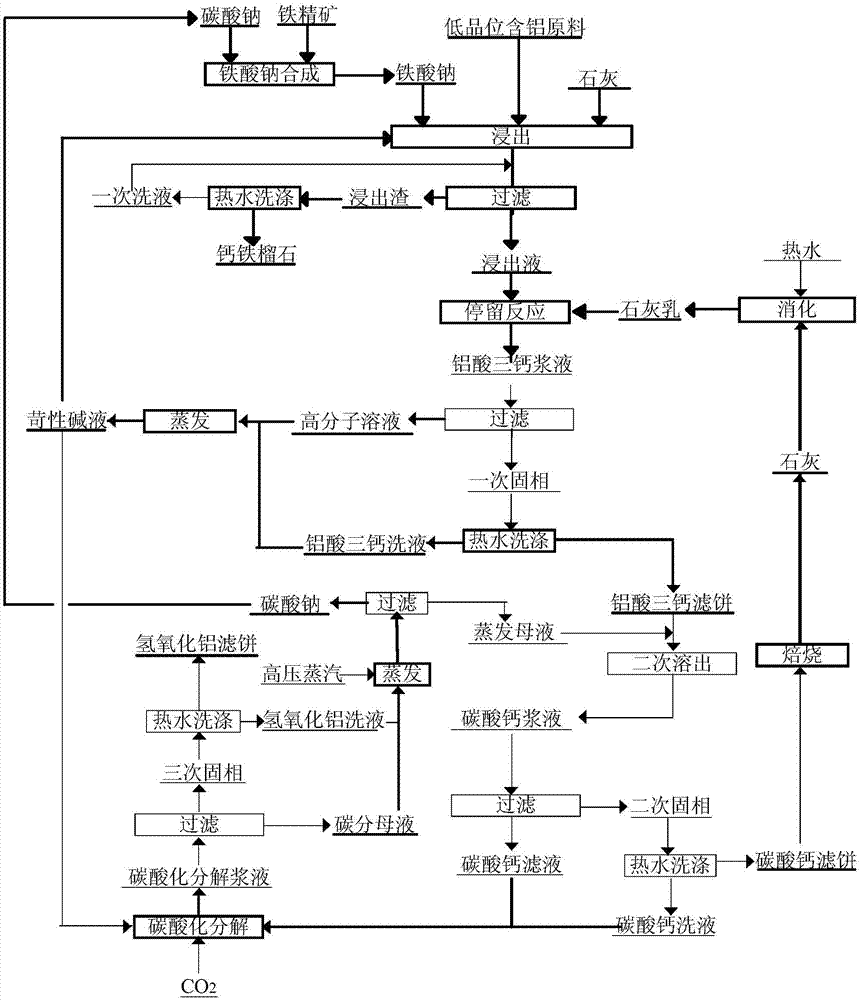
Comprehensive utilization method for low-grade aluminum-containing raw material
InactiveCN107963645ARealize the internal recycling of the processAchieve emissionsProductsReagentsDecompositionAluminium hydroxide
A comprehensive utilization method for a low-grade aluminum-containing raw material is carried out according to the steps of: 1) mixing sodium ferrite, the low-grade aluminum-containing raw material and lime and leaching the mixture with a caustic alkali solution, adding lime milk or lime to the leachate to perform a retention reaction, and filtering produced tricalcium aluminate slurry to preparea high-molecular solution; 2) heating and evaporating the high-molecular solution to prepare a caustic alkali solution; 3) performing mixing and secondary dissolution to the tricalcium aluminate filter cake and evaporation mother liquid to prepare calcium carbonate slurry; 4) filtering the calcium carbonate slurry to prepare a secondary solid phase and a secondary filtrate, feeding CO2 to the calcium carbonate filtrate for carbonation decomposition, thus producing carbonation decomposition slurry; 5) respectively processing the carbonation decomposition slurry to obtain aluminum hydroxide andlime; 6) processing leaching residue to prepare andradite. The method forms a closed loop of novel technology for comprehensive utilization of the low-grade aluminum-containing raw material, whereinthe ultra-white aluminum hydroxide and andradite are produced, while other materials are circulated internally in the process.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV ENG & RES INST CO LTD
Exchange modification method for reducing content of sodium oxide in beta-type molecular sieve
ActiveCN102795634AEliminate pollutionReduce sodium oxide contentCrystalline aluminosilicate zeolitesMolecular sieveOrganic acid
The invention discloses an exchange modification method for reducing the content of sodium oxide in a beta-type molecular sieve. The exchange modification method is characterized by comprising the following steps of contacting the molecular sieve of which the content of Na is relatively high and an aqueous solution containing inorganic acid and organic acid at the temperature of 0 to 5 DEG C for 0.5 to 2 hours; and separating, washing and drying to obtain the exchanged molecular sieve, wherein the weight ratio of H2O to the molecular sieve is (2.5-7.5):1. By the exchange modification method, the content of Na2O in the beta-type molecular sieve of which the content of the Na is relatively high can be reduced from 2.6 weight percent to less than 0.4 weight percent at one time, so that the actual requirement of industrial production is met; the relative crystallinity of the molecular sieve is not increased; the nitrogen-ammonia pollution is eliminated at the source; and water consumption in the molecular sieve exchange process is obviously reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A kind of catalytic cracking auxiliary agent and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102974331BHeavy oil cracking ability is strongGood choiceCatalytic crackingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRoom temperatureSpinel
The invention provides a catalytic cracking auxiliary agent and a preparation method thereof. The catalytic cracking auxiliary agent contains a mesoporous silica alumina material, spinel and / or precursors of the spinel and clay and / or heat-resistant inorganic oxide, wherein the mesoporous silica alumina material is obtained by the following steps of mix-pulping the mesoporous silica alumina material without ion exchange with water to obtain a slurry liquid; and contacting the slurry liquid with an inorganic acid for at least 0.2 hour at a temperature ranging from room temperature to 100 DEG C, so as to make the sodium oxide content in the mesoporous silica alumina material no higher than 0.2 wt%, wherein the weight ratio of the mesoporous silica alumina material without ion exchange, water and the inorganic acid is 1 : 5-30 : 0.03-0.3. The catalytic cracking auxiliary agent has relatively strong heavy oil cracking ability, high light oil yield and good coke selectivity when being used for the catalytic cracking of the heavy oil.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
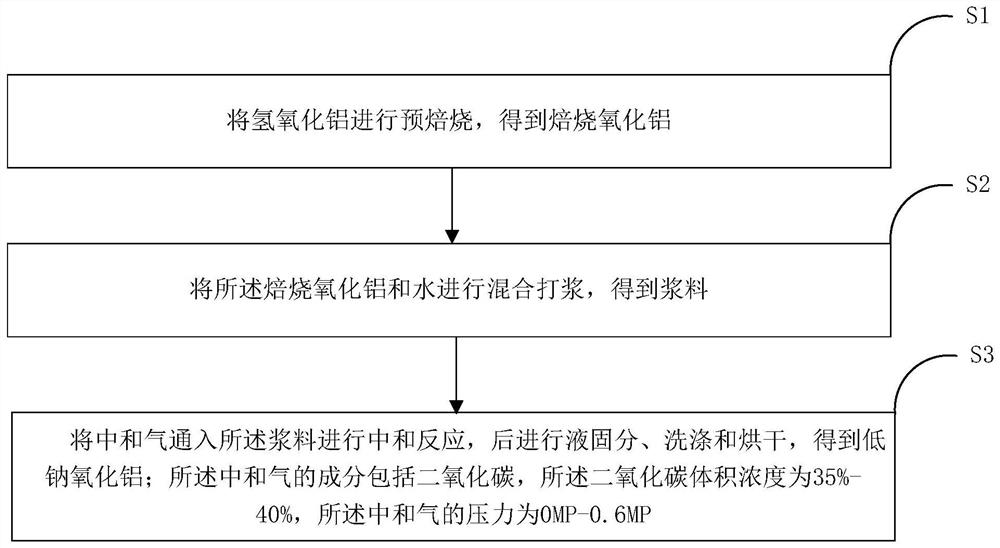
Low-sodium aluminum oxide and preparation method thereof
The invention particularly relates to low-sodium aluminum oxide and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of aluminum oxide preparation, and the method comprises the following steps: pre-roasting aluminum hydroxide to obtain roasted aluminum oxide; mixing and pulping the roasted aluminum oxide and water to obtain slurry; introducing neutralized gas into the slurry to carry out neutralization reaction, and then carrying out liquid-solid separation, washing and drying to obtain low-sodium aluminum oxide; wherein the component of the middle gas comprises carbon dioxide, the volume concentration of the carbon dioxide is 35%-40%, and the pressure of the middle gas is 0 MP-0. 6 MP; cO2 gas is introduced under the pressurization condition for sodium removal, the content of sodium oxide in the product is low, washing liquid can be recycled, and the method is environmentally friendly.
Owner:GUIZHOU BRANCH CHINA ALUMINUM IND
A modification method of in-situ crystallization type catalytic cracking catalyst
ActiveCN104209137BLow modification costReduce sodium oxide contentMolecular sieve catalystsReaction temperatureCalcination
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
A novel desulfurization adsorbent and its preparation method
ActiveCN105797674BImprove desulfurization effectUniform loadOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesPhosphatePhysical chemistry
Owner:QINGDAO HUICHENG PETROCHEM TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com