Single-stage boost inverter
An inverter, single-stage technology, applied in the field of new energy power generation inverter, can solve the problems of reducing conversion efficiency, increasing system cost, and devices cannot be turned on at the same time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
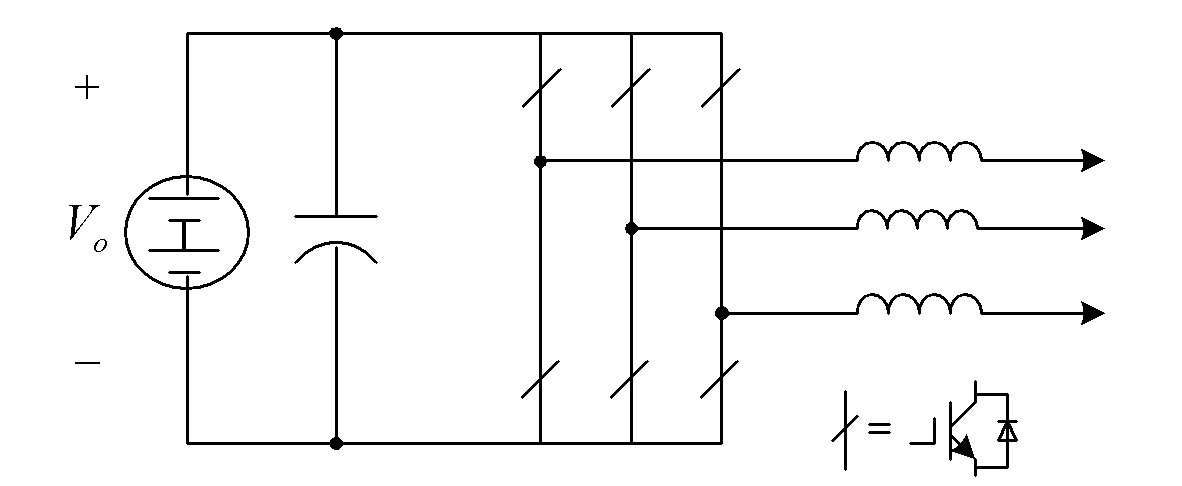
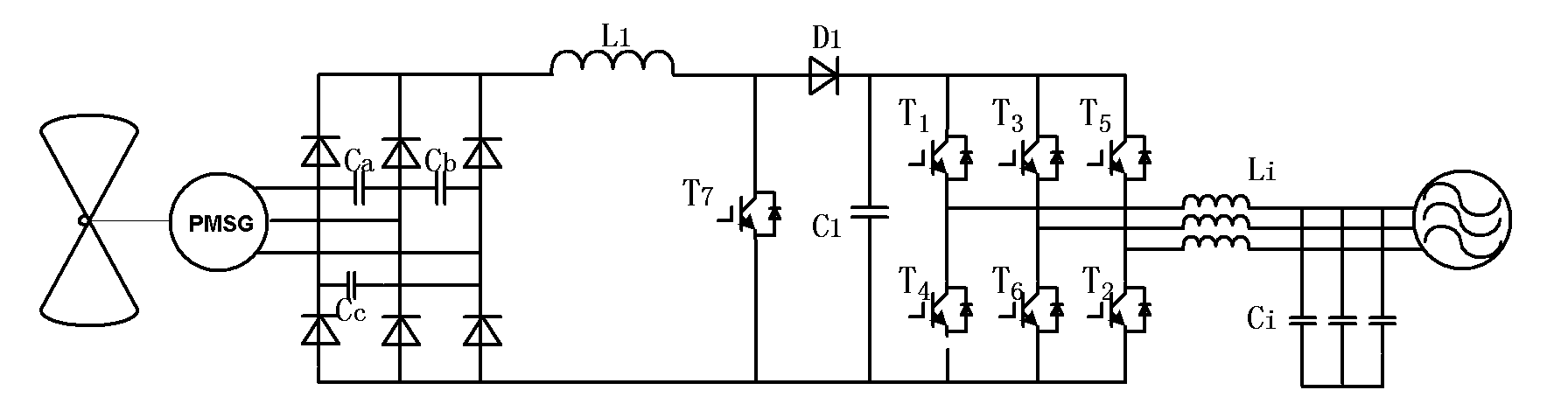
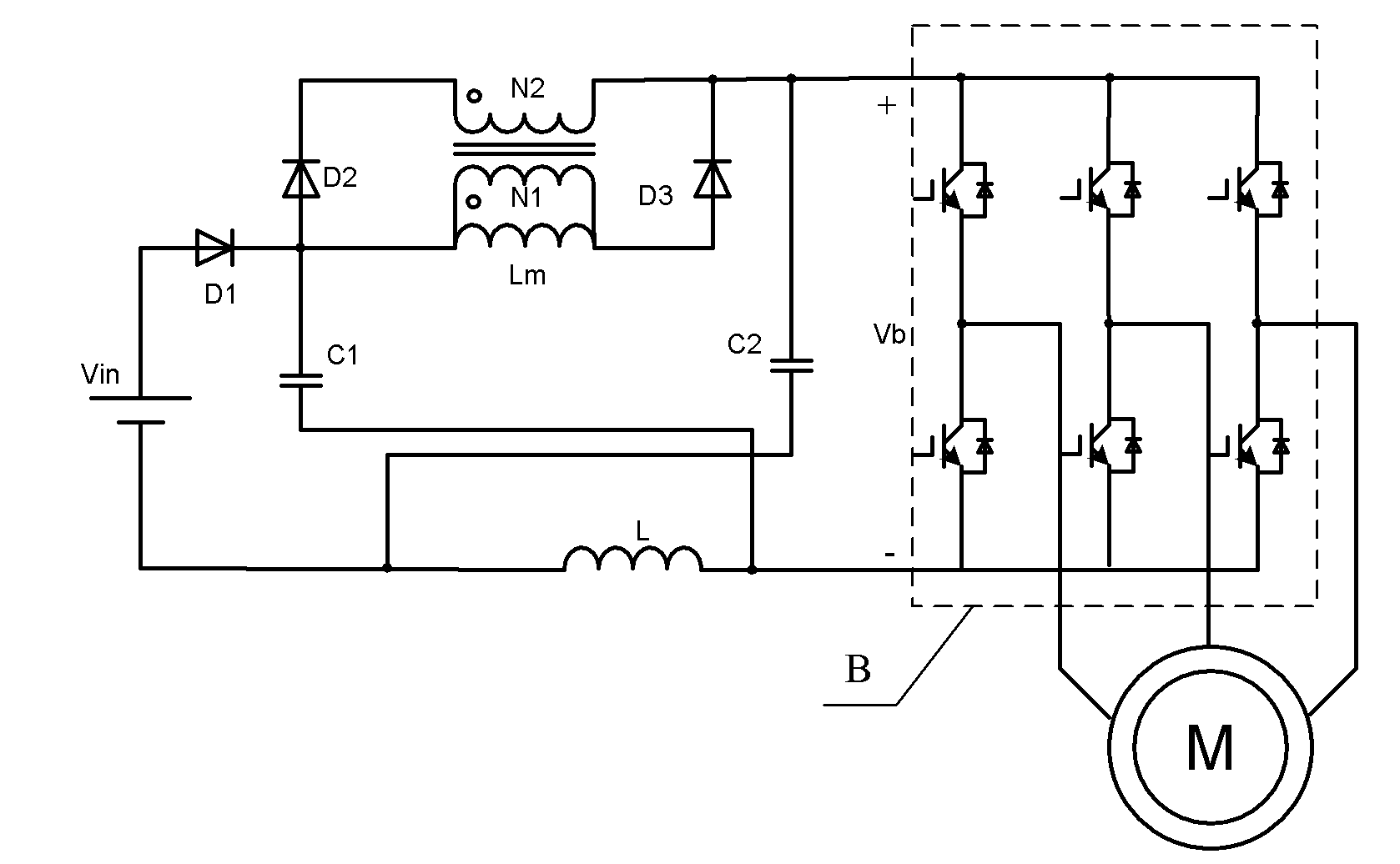
[0023] as attached image 3 As shown, the single-stage boost inverter topology of the present invention adds a boost network composed of passive devices before the three-phase switching bridge B of the traditional voltage-type inverter: a primary and secondary windings are tightly coupled and N1 <N2 coupled inductance, its equivalent model is the parallel connection of ideal transformer and excitation inductance, one end of excitation inductance Lm is connected to the cathode of the first diode D1, and connected to the anode of the second diode D2 and the first capacitor C1 at the same time The other end is connected to the anode of the third diode D3, the anode of the first diode D1 is connected to the positive pole of the power supply, the cathode of the second diode D2 is connected to one end of the secondary winding N2 of the coupled inductor, and the secondary The other end of the winding N2 is connected to the cathode of the third diode D3, and is connected to the positi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com