Molecular marker and specific primers for assisting in test of wilt disease resistance in brassica oleracea and use thereof
A Fusarium wilt resistance and auxiliary identification technology is applied in molecular markers, special primers and application fields for auxiliary identification of Fusarium wilt resistance in cabbage, achieving the effect of early breeding and major application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
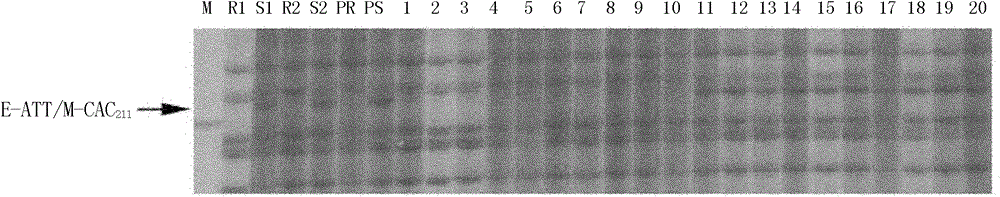
[0028] Example 1. Acquisition of AFLP Molecular Marker Closely Linked to Cabbage Fusarium Wilt Resistance Gene
[0029] Homozygous disease-resistant F2 individual plants (10 plants) and homozygous genotype susceptible F2 individual plants (10 plants) were randomly selected for 2 homozygous disease-resistant gene pools (R1, R2) and 2 Construction of homozygous susceptible gene pool (S1, S2). Two parallel BSA (Bulksegregant Analysis) resistant-susceptible pools R1 / S1 and R2 / S2 were constructed by taking the DNA of 5 homozygous resistant and 5 homozygous susceptible individuals.
[0030] AFLP molecular marker analysis: 256 pairs of AFLP primers were selected to amplify the disease-resistant gene pool, the susceptible gene pool and the parents.
[0031] Primer combinations: 16 pairs of EcoRI+ANN (N: A, G, C and T) and 16 pairs of MseI+ANN primer combinations, a total of 256 pairs of AFLP primers.
[0032]Pre-amplification program: 94°C for 5min; 94°C for 30s, 56°C for 30s, 72°C ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2. Obtaining the Sequence of a Specific Detection Gene Fragment Closely Linked to the Cabbage Fusarium Wilt Resistance Gene
[0039] After recovering and purifying the 2-item AFLP bands from the polypropylene gel, they were ligated with the pEASY-T1 vector. The ligation system: PCR products 4 μl, pMD-T vector 1 μl, solution I 5 μl, total volume 10 μl. Add the above reagents into a 0.5 centrifuge tube in an ice bath, flick to mix well, centrifuge briefly, and connect overnight (4°C). Take out the centrifuge tube of 50 μl of competent bacterial suspension from an 80°C refrigerator, put it on the ice box to thaw slowly, add about 10 μl of all the ligation products, flick the tube wall to mix well, and place it on the ice-water mixture for 30 minutes; Quickly heat-shock in a water bath at 42°C for 90s; quickly place it on ice for 3-5 minutes, do not shake the centrifuge tube during this period; add 700 μl LB liquid medium without AmP, transfer to 37°C, and culture o...
Embodiment 3
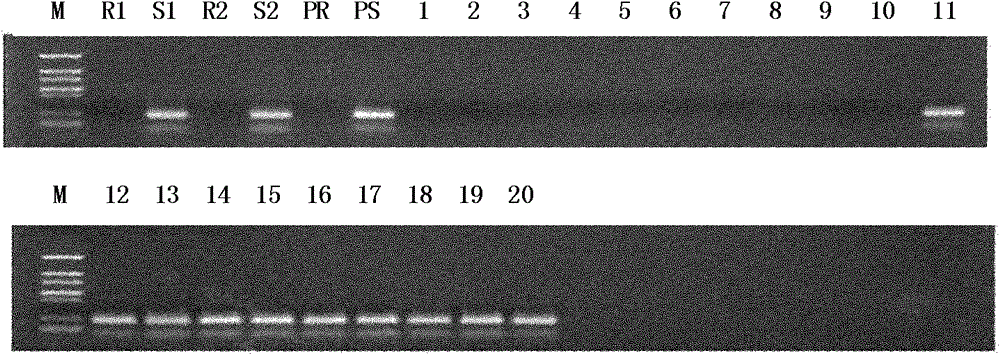
[0040] Example 3, Development and identification of SCAR primers for cabbage wilt resistance by specific gene fragment sequences
[0041] According to the sequencing results, the vector and linker sequences were removed, and SCAR primers were designed by using the remaining sequences combined with restriction sites. According to the AFLP primer numbering rules, this newly developed marker was named S46M48 198 , wherein S represents the SCAR marker, 46 represents E46 (E-ATT), 48 represents M48 (M-CAC), subscript 198 represents the length of the amplified fragment of the SCAR marker, and the primer sequence is:
[0042] S46M48 198 -F: 5'-ATTGGTGGCCTGCACTTTGAGCATC-3' (sequence 2 of the sequence listing);
[0043] S46M48 198 -R: 5'-ACAACAAACTAATCTCAAACATGTC-3' (SEQ ID NO: 3 of the Sequence Listing).
[0044] Using the resistant gene pool, the susceptible gene pool, the parental DNA and the DNA of individual plants that make up the resistant-susceptible pool, use the newly synth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com