Method for producing liquefied natural gas
A technology for liquefied natural gas and products, which is applied in the direction of refrigeration and liquefaction, gas fuel, and irreversible cycle compressors, etc. It can solve the problems of complex structure of pre-cooling compressors, complex structures of propane compressors, and difficult implementation of domestic equipment, etc., to achieve The effect of simple structure, simple design and manufacture, and reduced equipment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
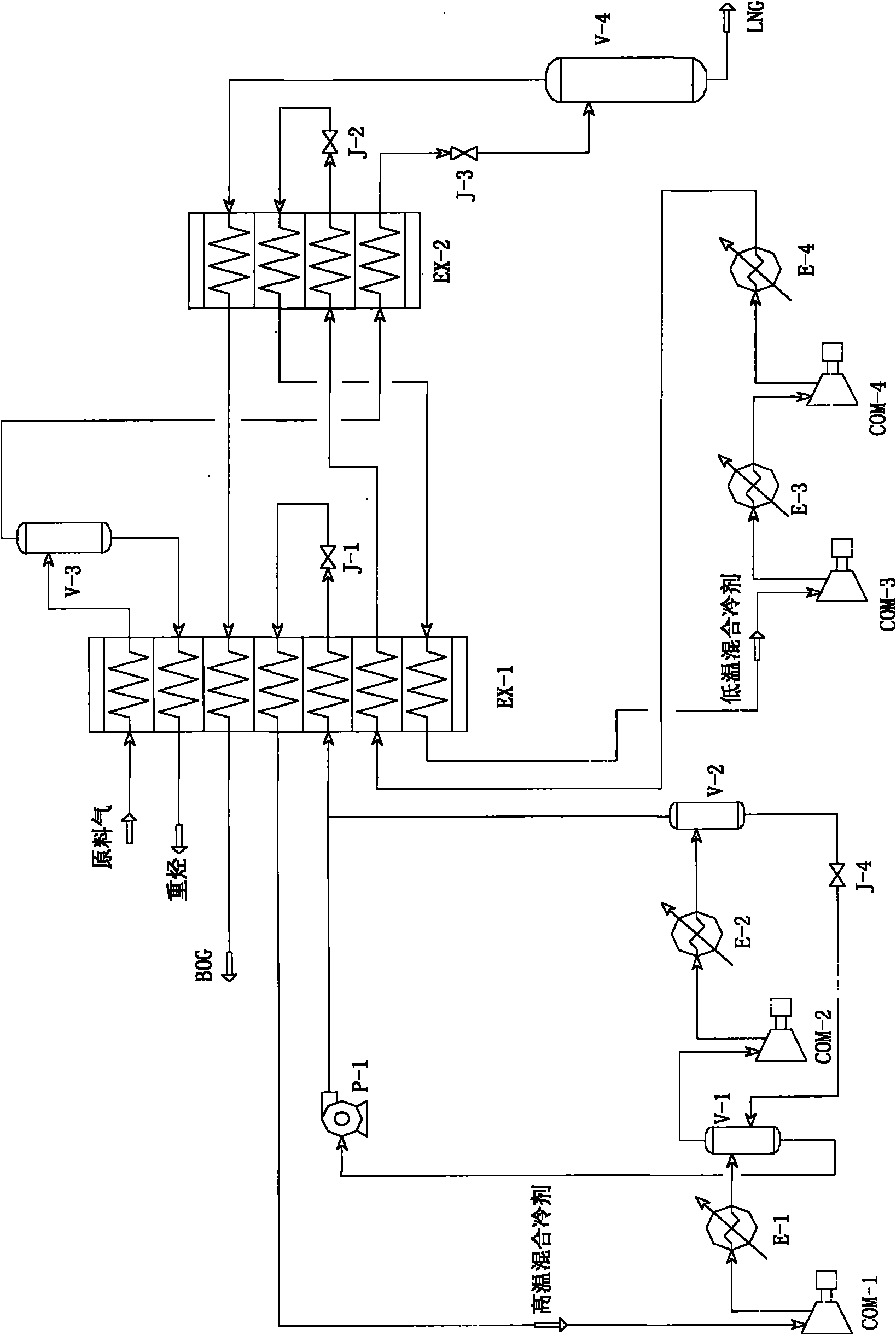
[0041] like figure 1 As shown, the raw material gas with a pressure of 4.0Mpa after purification enters the first heat exchanger EX-1 (also known as the first-stage plate-fin heat exchanger or precooler), and is cooled with other cold fluids in the first heat exchanger. After heat exchange, the temperature is cooled to about -50°C, and it exits the first heat exchanger and enters the heavy hydrocarbon separator V-3. The temperature entering the heavy hydrocarbon separator is related to the pressure of the raw gas. The higher the pressure of the raw gas, the easier it is for the heavy components in the raw gas to be liquefied; the lower the pressure, the lower the temperature required for the liquefaction of the heavy components. Therefore, the temperature entering the heavy hydrocarbon separator can be adjusted according to the feed gas pressure, but it should not be too low. In principle, the lower the temperature, the more heavy components will be liquefied, and the smaller...
Embodiment 2
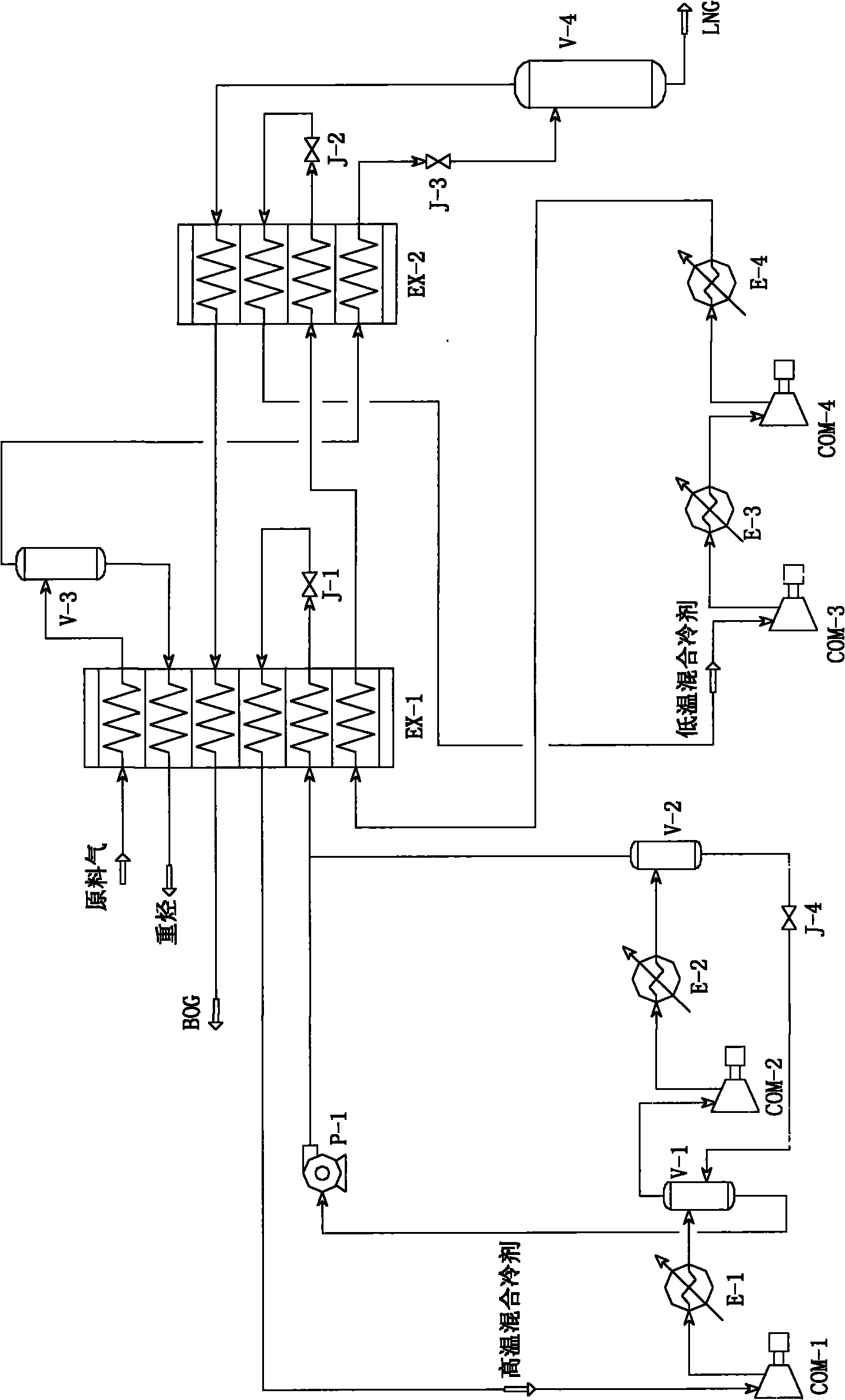
[0052] like figure 2 As shown, the difference between Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is that the low-temperature mixed refrigerant enters the cold end of the second heat exchanger EX-2 through the second throttle valve J-2 to depressurize and throttling, and from the second heat exchange After the hot end of the heat exchanger EX-2 comes out, it does not enter the cold end of the first heat exchanger EX-1 as in Embodiment 1, but directly returns to the inlet of the first compressor COM-1 for compression.
[0053] Since the mixed refrigerant coming out from the hot end of the second heat exchanger EX-2 is a low-temperature fluid, generally -40°C to -70°C, the low-temperature mixed refrigerant compressor in embodiment 2 must use a low-temperature compressor; and the implementation The low-temperature mixed refrigerant compressor of Example 1 can be a normal-temperature compressor.
Embodiment 3
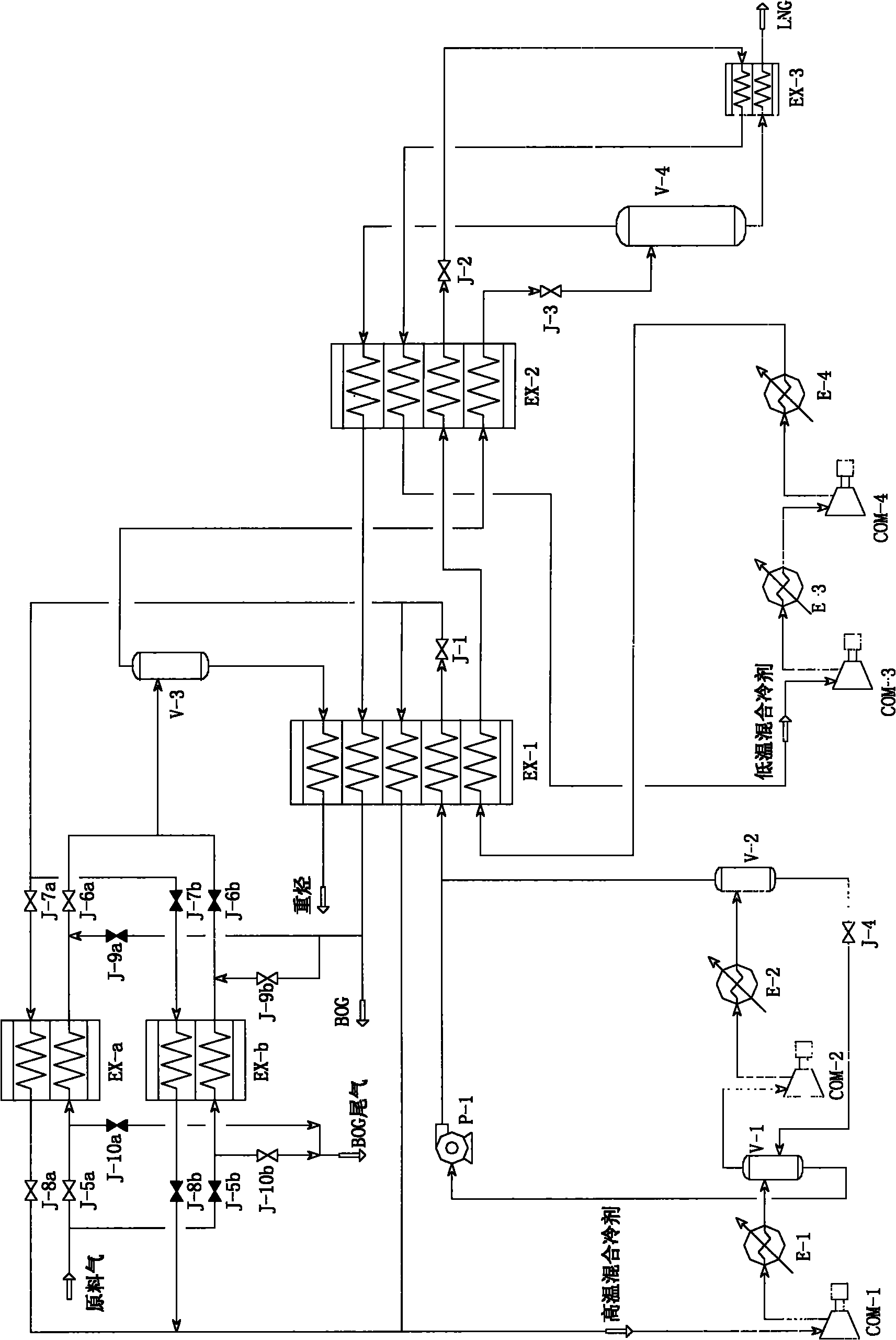
[0055] like image 3 As shown, the difference between embodiment 3 and embodiment 2 is that the switch heat exchangers EX-a and EX-b are adopted, and the subcooler EX-3 is adopted.
[0056] The purified raw material gas is selected to enter the switchable heat exchanger EX-a or EX-b through the opening and closing of switching valves J-5a and J-5b. In Example 3, take the switchable heat exchanger EX-a selected as an example (the valve J-5b is blacked out to indicate the closed state, and other blackened valves are also the same), the raw material gas exchanges heat with the cold fluid, the temperature drops, and then enters Heavy hydrocarbon separator. The cold fluid comes from the high-temperature mixed refrigerant, which is decompressed by the first throttle valve J-1, and is divided into two paths, one path provides cooling capacity for the switchable heat exchanger EX-a or EX-b, and the other path is the first heat exchanger EX-1 provides cooling capacity. The two high-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com