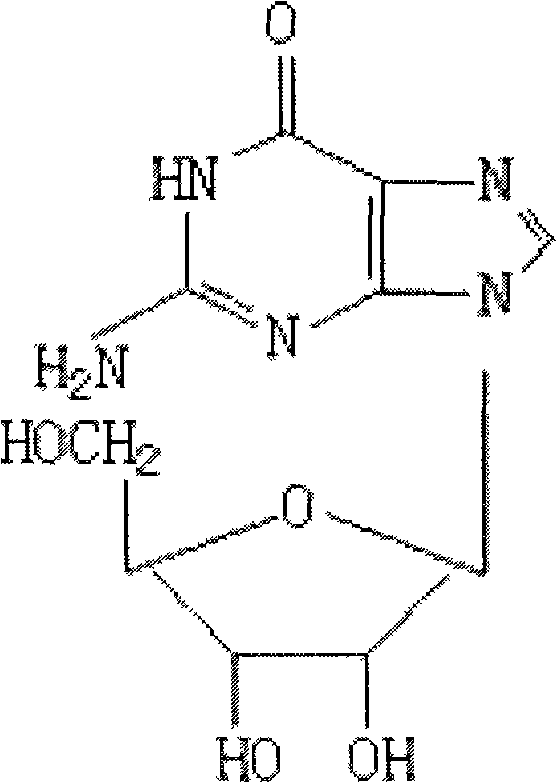
Method for increasing yield of guanosine produced by fermenting bacillus subtilis
A guanosine yield and Bacillus subtilis technology is applied in the field of improving the guanosine yield by fermentation of Bacillus subtilis, and can solve the problems of backward breeding technology, long fermentation period, low transformation rate and comprehensive extraction yield, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of high simultaneous productivity of strains, high glycoside production level, and improved transformation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0032] 1. Take 1g of glucose, 0.2g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.1g of magnesium sulfate, 0.1g of malic acid, 2g of yeast powder, 2g of agar, and 94.6g of water to prepare the primary culture medium, put it into an eggplant bottle and wait for 22min at 121°C After steam sterilization, it was left to cool down to 37°C, and the preserved strain Bacillus subtilis GDGR-1006 was inserted into it, and cultured statically at 37°C for 22 hours in a sterile state to obtain primary strains.
[0033] 2. Take 36g of glucose, 2.4g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 1.2g of magnesium sulfate, 1.2g of malic acid, 18g of yeast powder, and 1141.2g of water to make a culture medium for shake flasks, put them into shake flasks and steam at 121°C for 22min. After sterilizing, cool to 37°C, add the culture medium for primary strains obtained in step 1, and cultivate on a reciprocating shaker with an inoculum size of 0.1%, a rotation speed of 160 rpm, a temperature of 37°C, and a time period ...
example 2
[0037] 1. Take 1g of glucose, 0.2g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.1g of magnesium sulfate, 0.0g of malic acid, 2g of yeast powder, 2g of agar, and 94.7g of water, and put the prepared primary culture medium into an eggplant bottle for 22min at 121°C After steam sterilization, let it cool down to 37°C, insert the preserved strains, and culture them statically for 22 hours in a sterile state at 37°C to obtain primary strains.
[0038] 2. Take 36g of glucose, 2.4g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 1.2g of magnesium sulfate, 0.0g of malic acid, 18g of yeast powder, and 1142.4g of water. Put the prepared culture medium into the shaker flask and steam it at 121°C for 22min. After sterilizing, cool to 37°C, add the primary strain culture medium obtained in the previous step, and cultivate on a reciprocating shaker with an inoculum size of 0.1%, a rotation speed of 160 rpm, a temperature of 37°C, and a time period of 14 hours. A bottle of liquid bacteria, the resulting bacteria...
example 3
[0042] 1. Take 1g of glucose, 0.2g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 0.1g of magnesium sulfate, 0.2g of malic acid, 2g of yeast powder, 2g of agar, and 94.5g of water, and put the prepared primary culture medium into an eggplant bottle for 22min at 121°C After steam sterilization, let it cool down to 37°C, insert the preserved strains, and culture them statically for 22 hours in a sterile state at 37°C to obtain primary strains.
[0043] 2. Take 36g of glucose, 2.4g of dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, 1.2g of magnesium sulfate, 2.4g of malic acid, 18g of yeast powder, and 1140.0g of water. Put the prepared culture medium into the shaker flask and steam it at 121°C for 22min. After sterilizing, cool to 37°C, add the primary strain culture medium obtained in the previous step, and cultivate on a reciprocating shaker with an inoculum size of 0.1%, a rotation speed of 160 rpm, a temperature of 37°C, and a time period of 14 hours. Bottle of liquid bacteria, the resulting bacteria m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com