Method for culturing human embryo stem cell by using umbilical cord source mesenchymal stem cell
A technology of human embryonic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells, applied in the field of culturing human embryonic stem cells using umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells, can solve problems such as difficulties in clinical research and application, achieve small complications and risks, maintain stability, and maintain undifferentiated growth Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Embodiment 1, the preparation of experimental cell
[0080] 1. Primary culture, passage, cryopreservation and recovery of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (HUCMSCs)
[0081] 1. Primary culture of HUCMSCs
[0082] (1) Aseptically take the isolated umbilical cord 10cm of healthy (no infectious disease, serological examination is negative for HBV, HCV, HIV and syphilis) caesarean section fetus, and place it in a 50ml centrifuge tube, which is put into sterile PBS in advance; the umbilical cord The acquisition was obtained with the informed consent of the pregnant woman and her family members.
[0083] (2) In the ultra-clean bench, fully rinse the outer surface of the umbilical cord with PBS containing 1× penicillin-streptomycin, fully wash off the blood, and then put the umbilical cord into a glass dish for operation;
[0084] (3) Use tissue scissors to carefully remove two umbilical veins and one umbilical artery, and cut the remaining umbilical cord intersti...
Embodiment 2
[0163] Example 2, Proliferation and Culture of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
[0164] 1. Proliferation and culture of human embryonic stem cells by the method of the present invention
[0165] (1) Preparation of HUCMSCs feeder layer
[0166] (1) Take HUCMSCs from P3 to P13, wait until they reach the logarithmic growth phase, discard the medium, and add a medium containing 10 μg / ml mitomycin C (that is, the concentration of mitomycin C in the medium is 10 μg / ml), placed in the incubator for 3 hours;
[0167] (2) Treat the petri dish with 0.1% gelatin (add gelatin, shake to cover the bottom of the dish with gelatin, then place at 37°C for half an hour), discard the gelatin, and place at room temperature until the gelatin at the bottom of the dish is dry.
[0168] (3) Discard the medium containing mitomycin C, add 2-3mL PBS, shake gently, discard the PBS, and wash 3-5 times in this way (must be washed more than 3 times to completely wash away the remaining mitomycin Mitomycin C, ...
Embodiment 3
[0186] Example 3. Identification of hESCs using HUCMSCs and MEFs as feeder cells
[0187] 1. Alkaline phosphatase (AKP) staining
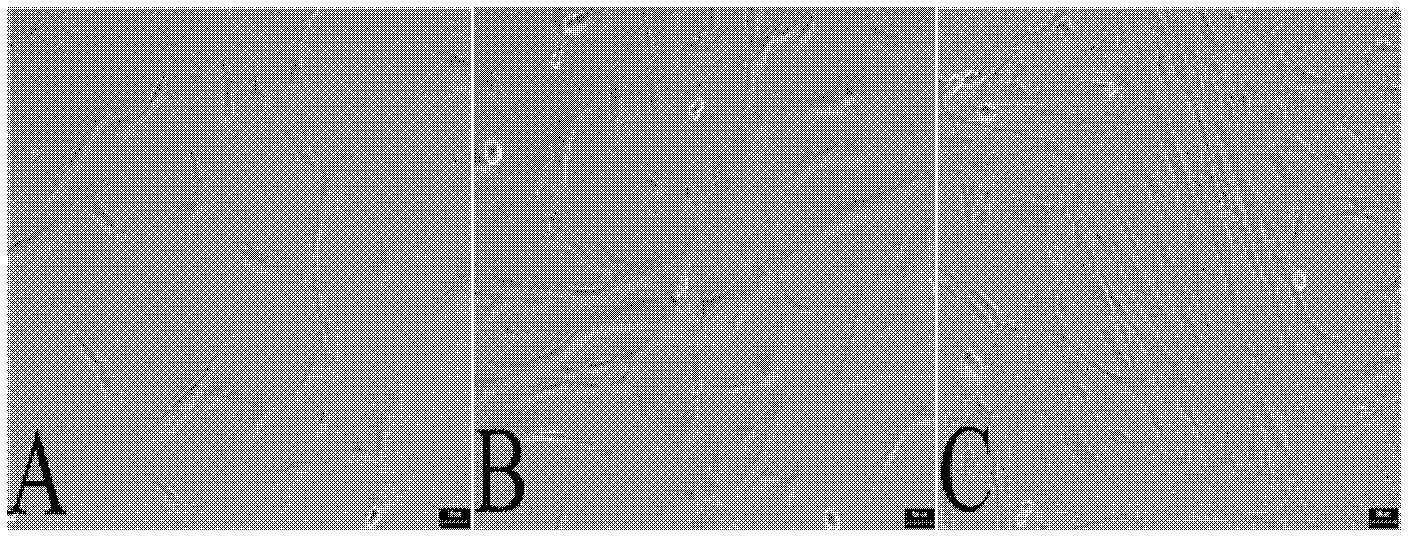
[0188] Positive alkaline phosphatase staining is one of the indicators of hESCs pluripotency. hESCs at passage 30 were stained and observed using the Millipore Alkaline Phosphatase Detection Kit. Refer to the manual for specific steps. Observation and photography under a microscope.
[0189] Identified by alkaline phosphatase staining, hESCs alkaline phosphatase staining on the HUCMSCs feeder layer ( Figure 7 A) The alkaline phosphatase staining of hESCs with MEF as the feeder layer was positive ( Figure 7 B).
[0190] 2. Immunofluorescence detection of specific antigen expression
[0191] (1) After hESCs were cultured on HUCMSCs feeder layer and MEF feeder layer for 30 passages, appropriate amount of cells were digested and inoculated in a 24-well plate with feeder layer cells.
[0192] (2) After 3 days, fix with 4% paraformaldehyde at ro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com