Reaction device for producing light olefins from oxygenated compounds
A low-carbon olefin and reaction device technology, which is applied to the production of hydrocarbons from oxygen-containing organic compounds, ethylene production, condensation between hydrocarbons and non-hydrocarbons, etc., can solve the problem of low yield of low-carbon olefins
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
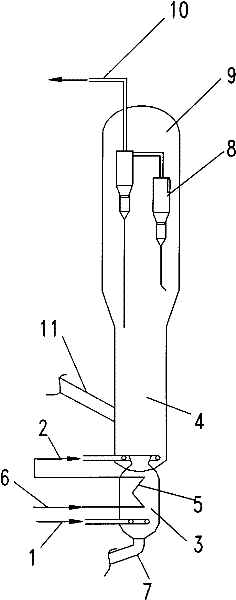
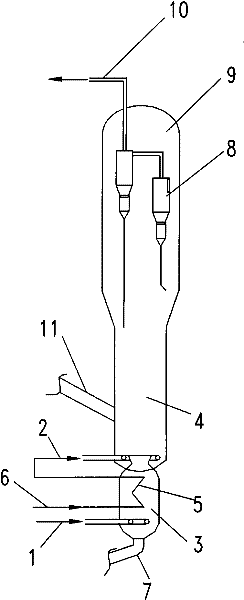
[0020] in such as figure 1 In the reaction device shown, the catalyst is SAPO-34, the main reactor and the auxiliary reactor are fluidized beds, the main reactor is fed with methanol with a purity of 99.5%, and the feed temperature is 210 ° C, and the distribution plate is set to enter the reaction Zone, the reaction conditions of the main reactor are: the reaction temperature is 450°C, the reaction pressure is 0.01MPa in terms of gauge pressure, and the gas phase velocity in the reactor is 0.7 m / s; the auxiliary reactor is fed with pure ethanol, and the feed is liquid Phase nozzle feeding mode, reaction conditions in the auxiliary reactor: the mass ratio of ethanol feed to methanol feed is 0.2, the reaction temperature is 350° C., and the gas phase linear velocity is 0.5 m / s. The carbon deposition amount of the carbon deposition catalyst is 2.5%, and the carbon deposition amount of the raw catalyst is 2.97%. The outlet of the main reactor adopts gas chromatography to analyze ...
Embodiment 2
[0022] According to the conditions described in Example 1, the main reactor adopts methanol feed with a purity of 99.5%, and the feed temperature is 180°C. The reaction conditions of the main reactor are: the reaction temperature is 400°C, and the reaction pressure is 0.1 in gauge pressure. MPa, the linear velocity of the gas phase in the reactor is 0.67 m / s; the auxiliary reactor adopts the mixed feed of ethanol and methanol, and the feed adopts the liquid phase nozzle feeding mode, and the mass ratio of ethanol and methanol feed in the auxiliary reactor feed is 5.2. The mass ratio of ethanol to methanol in the total feed is 0.6, and the reaction conditions in the auxiliary reactor are: the reaction temperature is 420°C, and the gas phase velocity is 0.8 m / s. The carbon deposition amount of the carbon-deposited catalyst is 3.17%, and the carbon deposition amount of the waiting catalyst is 3.51%. The experimental results are: the methanol conversion rate is 98.31% (weight), the...
Embodiment 3
[0024] According to the conditions described in Example 1, the main reactor adopts methanol feed with a purity of 99.5%, and the feed temperature is 300°C. The reaction conditions of the main reactor are: the reaction temperature is 500°C, and the reaction pressure is 0.3 in gauge pressure. MPa, the gas phase linear velocity in the reactor is 0.5 m / s; the reaction conditions in the auxiliary reactor: the mass ratio of ethanol feed to methanol feed is 0.1, the reaction temperature is 300 ° C, and the gas phase linear velocity is 0.3 m / s. The carbon deposition amount of the carbon deposition catalyst is 4.98%, and the carbon deposition amount of the waiting catalyst is 5.94%. The experimental results are: the methanol conversion rate is 99.76% (weight), the ethanol conversion rate is 100% (weight), and the ethylene yield is 15.23%. (weight), the propylene yield was 15.61% (weight).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com