Application of Plant Poly-adp Ribose Polymerase Inhibitors in Improving Plant Traits
A technology of ribose polymerase and plant traits, applied in the field of plant biology and agriculture, can solve the problems of slow effect, time-consuming and labor-intensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Example 1 Treatment method of Arabidopsis, tobacco, corn and other seeds
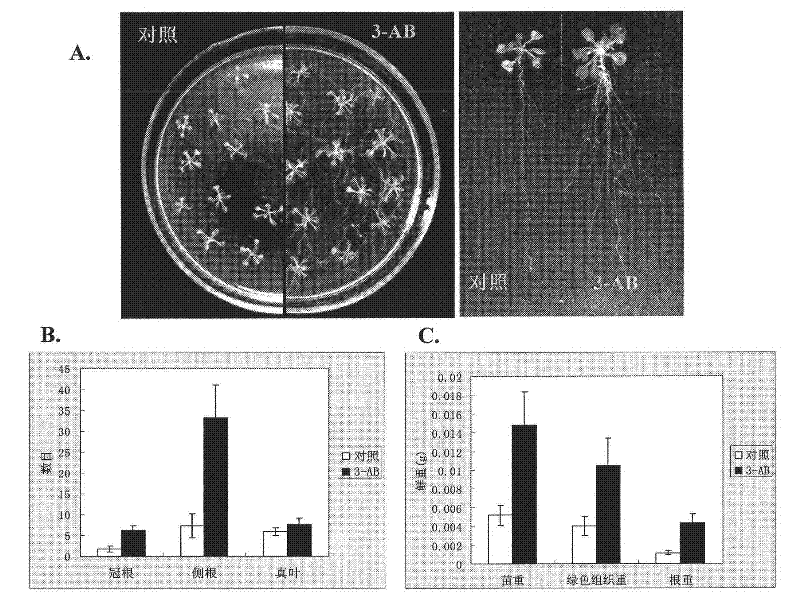
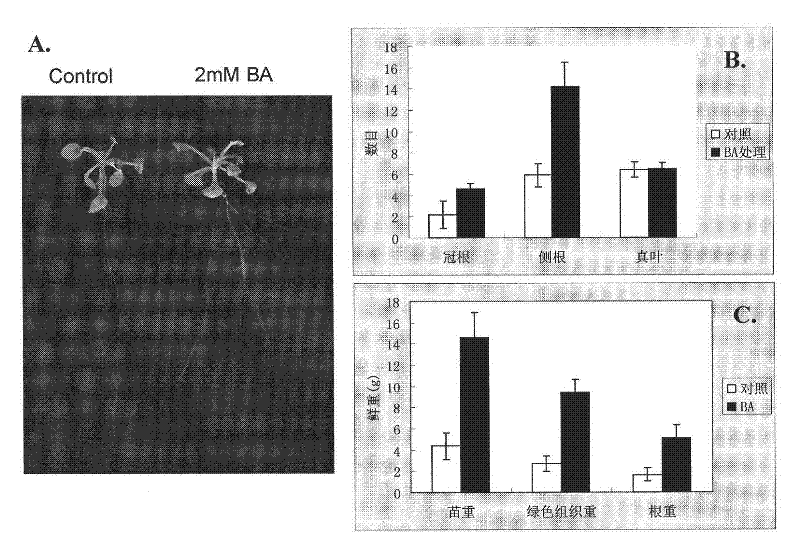
[0022] Arabidopsis thaliana and tobacco seeds: first sterilize with 70% ethanol for 10 minutes, then shake with 100% ethanol + 0.01% Triton for several times, pour it on sterilized clean filter paper, and plant it on 1 / 2MS medium with toothpicks. Put it in a light incubator for cultivation. Use the medium without 3-AB as a control to observe the growth of plants on the medium containing 1-2mM 3-AB or BA.
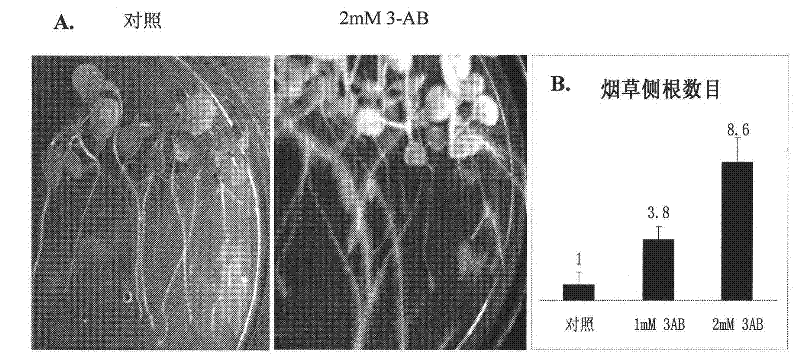
[0023] Corn seeds: Sterilize with 3% hydrogen peroxide for 30 minutes, rinse several times to wash hydrogen peroxide, soak seeds in clean pure water for 48h, 37°C for 24h, then arrange the yarn in a long test tube as a support, and place the germinated seedlings On gauze, there is 1 plant per tube, a set of ten tubes, the test tube does not contain or contains 3-AB or BA aqueous solution, and it is grown in a light incubator for one week and then photographed.
Embodiment 2
[0024] Example 2 Determination of the number of lateral roots and the fresh weight of plant parts
[0025] After 20 days of growth of Arabidopsis, take more than 15 seedlings, count the number of roots emitted from the base and the number of lateral roots of the entire root system; divide the seedlings into roots and parts above the roots, weigh the fresh weights with precision balances, compare the treatment and The number of lateral roots and the fresh weight of each part of the treated plants. The number of lateral roots of the entire root system of each plant was counted after six weeks of growth for tobacco, and the number of lateral roots that grew from the fibrous roots from the basal roots were counted for corn after one week of growth.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Example 3 Observation and Measurement of Plant Drought Resistance
[0027] When Arabidopsis germinates to the first true leaf, select robust and consistent seedlings and transplant them into pre-sterilized culture soil (the soil is first weighed to ensure the amount of soil in each pot during drought. The same, the water content is also the same). Five days after the Arabidopsis was transplanted, 3-AB was formulated into a 2mM aqueous solution, and the roots of the Arabidopsis were drip-irrigated, and each seedling should be treated with the same volume of solution as far as possible with the roots moist. Water drip irrigation was used as the control of 3-AB treatment. Repeat every 5 days for a total of 3 treatments. After the plants have grown for 30 days, let each small pot absorb water first, then stop watering, and weigh each small pot before stopping watering to ensure that the soil moisture content in each pot is consistent. After treatment for about 20 days, contr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com