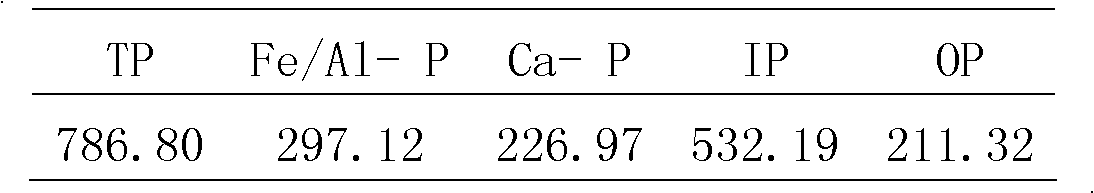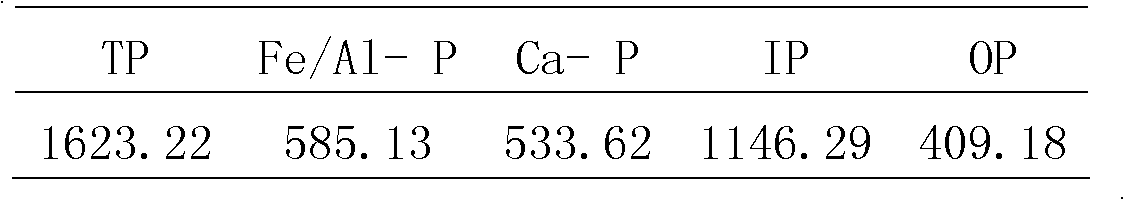Method for processing phosphorus in sediment by combining photocatalytic reduction with submerged plants
A submerged plant, combined treatment technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, light water/sewage treatment, water/sewage treatment and other directions, can solve the problem of no phosphorus and other problems, achieve low cost, solve difficult removal, and solve phosphorus stress Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0062] A method for photocatalytic reduction and submerged plant combined treatment of phosphorus in sediments, the steps are:
[0063] 1) The sediment was collected from a shallow lake in Wuhan, Hubei, and the phosphorus content of each form is shown in Table 1.
[0064] 2) The submerged plants were selected as Potamogeton crispus and Elodea nuttallii.
[0065] 3) Plant Potamogeton crispus and Elodea (quantity ratio 1:1) in a glass tank (50cmx50cmx80cm) containing sediments, the depth of which is 10cm, and a layer of nano-semiconductor photocatalyst film loaded on the sediments The magnesium slag ceramic filter ball is 2cm thick.
[0066] 4) Inject the overlying water, which is collected from the water column at the sediment sampling point, with a water depth of 60cm.
[0067] 5) Intermittent irradiation with an external light source (high-pressure mercury lamp) during the initial growth and decline period of submerged plants (irradiated for 4 hours during the day and 2 hours at night...
Embodiment 2
[0074] It is basically the same as Example 1, except that: the sediment was collected from a shallow lake in Wuhan, Hubei, and the phosphorus content of each form is shown in Table 2. The submerged plants are Potamogeton crispus and goldfish Algae (Ceratophyllum demersum L.); The nano semiconductor photocatalyst is a sulfide semiconductor (such as cadmium sulfide, etc.).
[0075] In this embodiment, after the submerged plants have grown for 180 days, the total phosphorus removal rate of the sediment can reach over 80%.
[0076] Table 2 Phosphorus content of various forms in sediments (mg / kg)
[0077]
Embodiment 3
[0079] It is basically the same as Example 1, except that: the sediment was collected from a freshwater lake in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, and the phosphorus content of each form is shown in Table 3; the submerged plants are Vallisneria spiralis and Vallisneria spiralis. Ceratophyllum demersum L.; the nano-semiconductor photocatalyst is a modified oxide semiconductor (such as modified titanium dioxide); the light source is a 250W high-pressure sodium lamp.
[0080] In this embodiment, after the submerged plants grow for 180 days, the total phosphorus removal rate of the sediment can reach more than 90%.
[0081] Table 3 Phosphorus content of various forms in sediments (mg / kg)
[0082]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com