Marking method for ingot casting polycrystalline silicon slice head and tail sequencing
A polysilicon and marking technology, which is applied in the direction of electrical components, circuits, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of a large number of fragments of silicon wafers and the inability to distinguish the exact position, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The present invention will now be described in further detail in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and preferred embodiments. These drawings are all simplified schematic diagrams, which only illustrate the basic structure of the present invention in a schematic manner, so they only show the configurations related to the present invention.
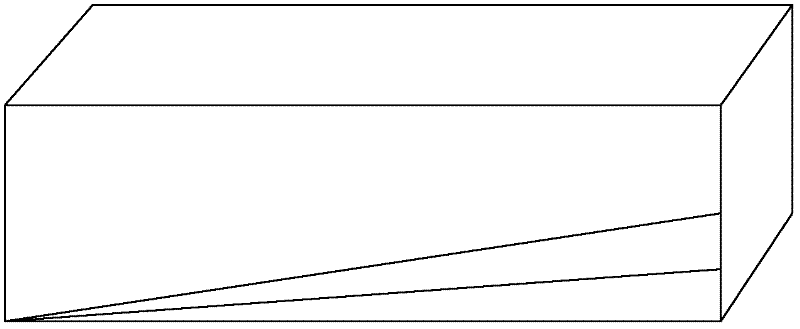
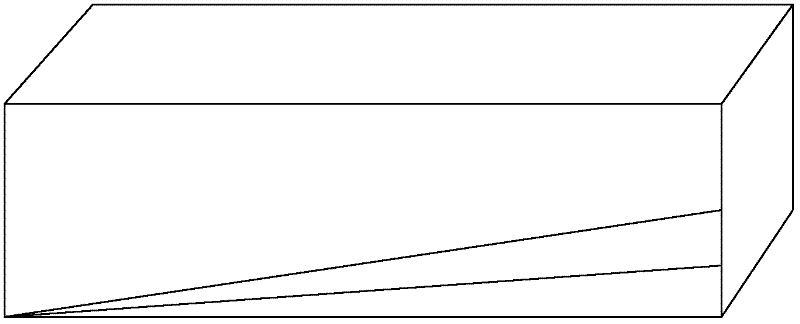
[0020] Firstly, the ingot polysilicon ingot after squaring is tested by infrared and minority carrier lifetime, and the truncation position is determined based on the infrared and minority carrier lifetime detection results, and the truncation process is carried out. Then use a laser to draw a line mark on the surface of the truncated ingot.
[0021] Specific identification methods such as figure 1 As shown in FIG. 1 , one surface of the truncated polysilicon rod is selected for laser line drawing. Draw a line from a vertex of the ingot head to its opposite side, the intersection point of the first line and the opposite si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com