Leakage protection plug
A leakage protection plug and resistor technology, applied in emergency protection circuit devices, automatic disconnection emergency protection devices, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as electric shock accidents and missing
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
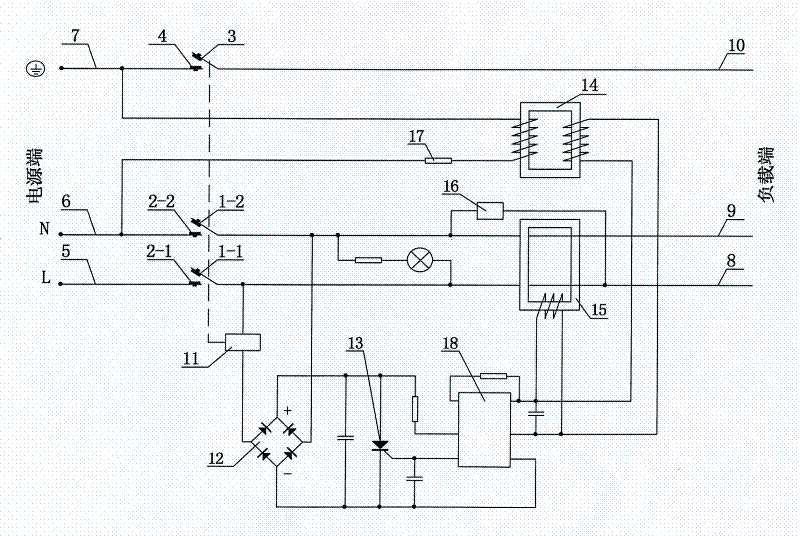
[0027] See figure 1 As shown, a leakage protection plug is mainly composed of the plug shell and the phase, zero, and ground three-pole pins, the phase line 5, the neutral line 6, the ground line 7, the rectifier circuit 12, the thyristor 13, and the zero sequence current transformer of the power terminal. 15. Test circuit 16, weak current detection inductor 14, current-limiting resistance-capacitance element 17, load end phase line 8, neutral line 9, ground line 10, amplifier circuit 18, electromagnetic trip and lock device. The electromagnetic tripping and locking device is mainly composed of the electromagnetic coil 11 and its drive circuit, the phase line contacts 1-1 and 2-1, the neutral line contacts 1-2 and 2-2, the ground line contacts 3 and 4, and the spring , Reset push rod composition. The detection circuit composed of the primary winding of the weak current detection inductor 14 and the current-limiting resistance-capacitance element 17 in series is connected betwee...
Embodiment 2
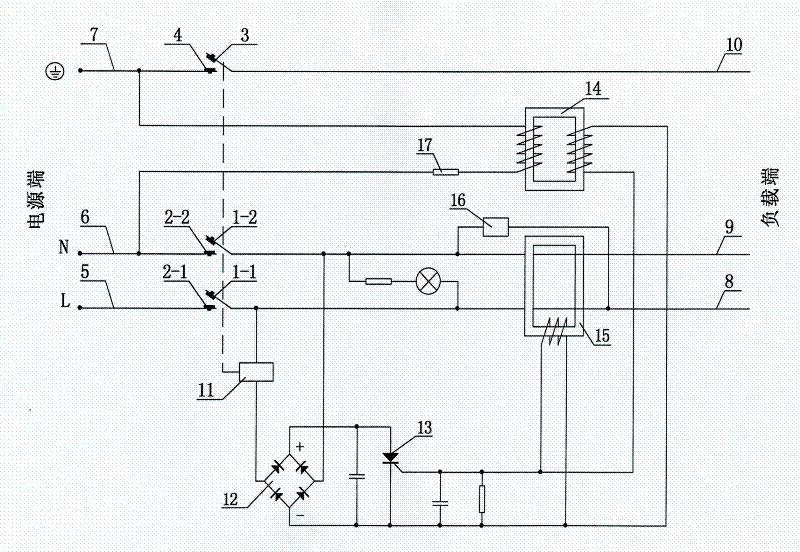
[0034] See figure 2 As shown, compared with embodiment 1, the amplifying circuit 18 described in embodiment 1 is eliminated in this embodiment, and the secondary winding output end of the zero-sequence current transformer 15 is replaced with the amplifying circuit 18 described in embodiment 1. The parallel connection of the input terminal is changed to connect in parallel with the trigger electrode and cathode of the thyristor 13 of this embodiment, and the anode and cathode of the thyristor 13 are respectively connected to the positive and negative electrodes of the output terminal of the rectifier circuit 12, so that the zero sequence current transformer is 15 times The signal output by the secondary winding directly triggers the thyristor 13. Since the signal output by the secondary winding of the zero sequence current transformer 15 is large enough, the thyristor 13 can be triggered without amplification.
[0035] In this embodiment, the current-limiting resistance-capacitanc...
Embodiment 3
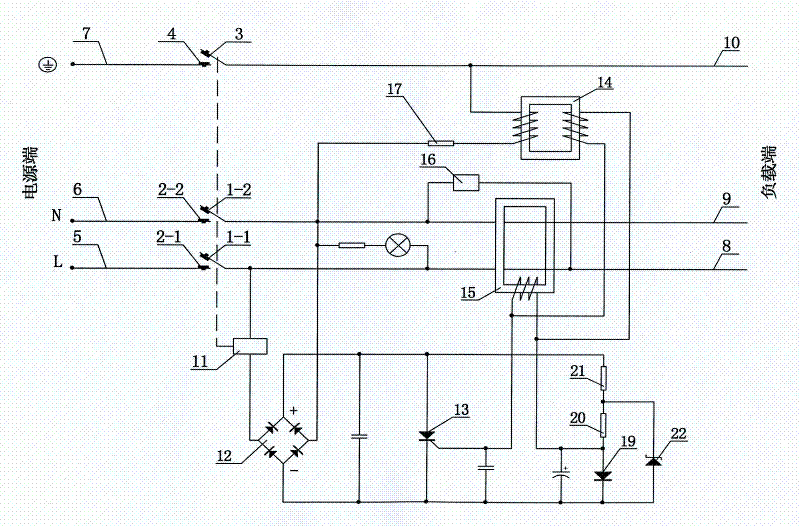
[0039] See image 3 As shown, compared with Embodiment 2, this embodiment adds a clamping diode 19 composed of a combination of a first resistor 21, a second resistor 20, a clamping diode 19, and a Zener diode 22 in the solenoid drive circuit. A positive clamp circuit. The clamp diode 19 is connected in series with the second resistor 20 and the first resistor 21 between the positive and negative terminals of the output terminal of the rectifier circuit 12. One end of the first resistor 21 is connected to the positive terminal of the output terminal of the rectifier circuit 12. The other end of the resistor 21 is connected to one end of the second resistor 20, the other end of the second resistor 20 is connected to the anode of the clamp diode 19, the cathode of the clamp diode 19 is connected to the negative electrode of the output end of the rectifier circuit 12, the other end of the first resistor 21, and the second resistor One end of 20 is also connected to the negative el...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com