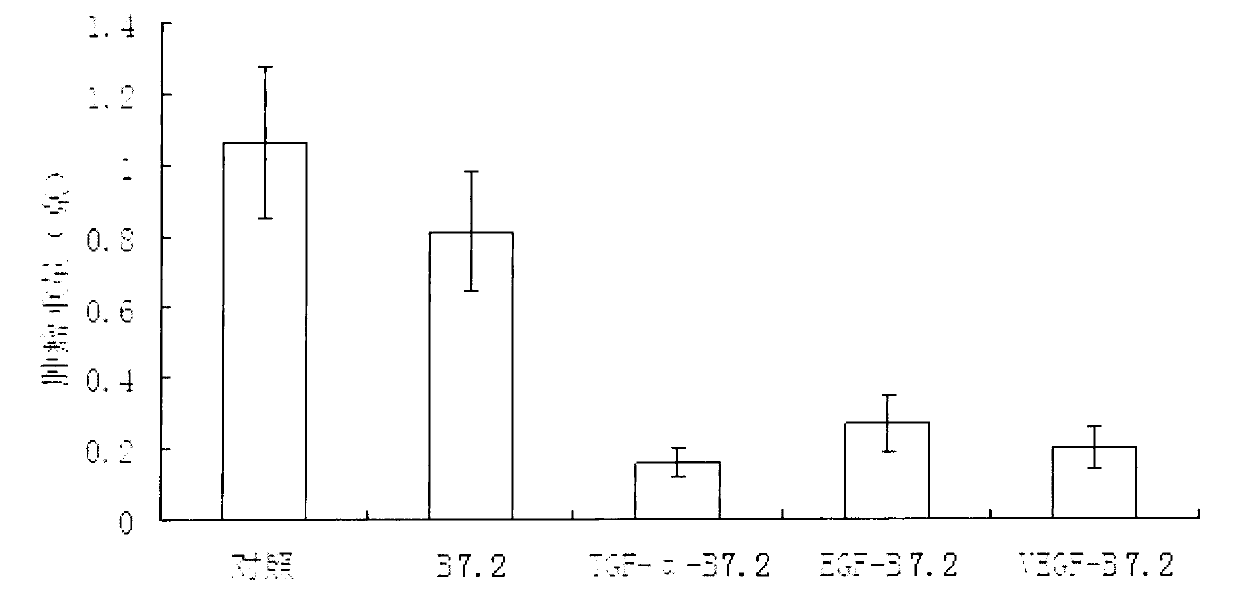
Fusion protein capable of inducing and activating cancer-targeted T cells, preparation method and use thereof
A fusion protein and cancer cell technology, applied in the field of biomedicine, to achieve the effect of inhibiting tumor growth
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031]Example 1 Construction of B7.2 (CD86) expression vector
[0032] According to the information of the human-derived B7.2 gene (aka CD86) in the GenBank database (NM_175862 and L25259), TAKARA was commissioned to synthesize a nucleic acid sequence fragment including a linker peptide and a B7.2 gene (222 encoding the extracellular part) amino acid) and a few bases of the restriction enzyme cleavage point HindIII in front of the whole fragment and XhoI at the back, insert this synthesized nucleic acid fragment into the T vector and carry out DNA sequencing identification, and then use the double digestion method to use HindIII and XhoI After treatment, this fragment was inserted into the pET22b plasmid, thus producing the expression vector pET22b-B7.2, which expresses the B7.2 protein. The sequence listing (SEQ ID NO. 2) is only the B7.2 protein, and another sequence listing (SEQ ID NO. 14) can be found in the preceding linker peptide.
Embodiment 2
[0033] Example 2 Construction of TGF-α-B7.2 expression vector
[0034] According to the information of human-derived TGF-α gene (NM_003236) in the GenBank database, TAKARA was commissioned to synthesize a nucleic acid sequence fragment including TGF-α gene and several restriction endonuclease sites BamHI and EcoRI added in front of TGF-α base, containing restriction endonuclease sites for SalI and HindIII at the end of the fragment. The synthesized nucleic acid fragment was inserted into the T vector and identified by DNA sequencing. Then, after treatment with BamHI and HindIII by double digestion method, the fragment was inserted into the pET22b-B7.2 plasmid, thus producing the expression vector pET22b. -TGF-α-B7.2, which can express a TGF-α-B7.2 fusion protein (see SEQ ID NO. 4 of the Sequence Listing).
Embodiment 3
[0035] Example 3 Construction of EGF-B7.2 expression vector
[0036] According to the human-derived EGF gene information (NM_001963 and NM_001178130) in the GenBank database, TAKARA was commissioned to synthesize a nucleic acid sequence fragment including the EGF gene and a few bases of restriction endonuclease sites BamHI and EcoRI in front of EGF. Following the fragment contains restriction enzyme sites for SalI and HindIII. The synthesized nucleic acid fragment was inserted into the T vector and identified by DNA sequencing. Then, after treatment with BamHI and HindIII by double digestion method, the fragment was inserted into the pET22b-B7.2 plasmid, thus producing the expression vector pET22b. -EGF-B7.2, which can express the EGF-B7.2 fusion protein (see SEQ ID NO. 6 of the sequence listing).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com