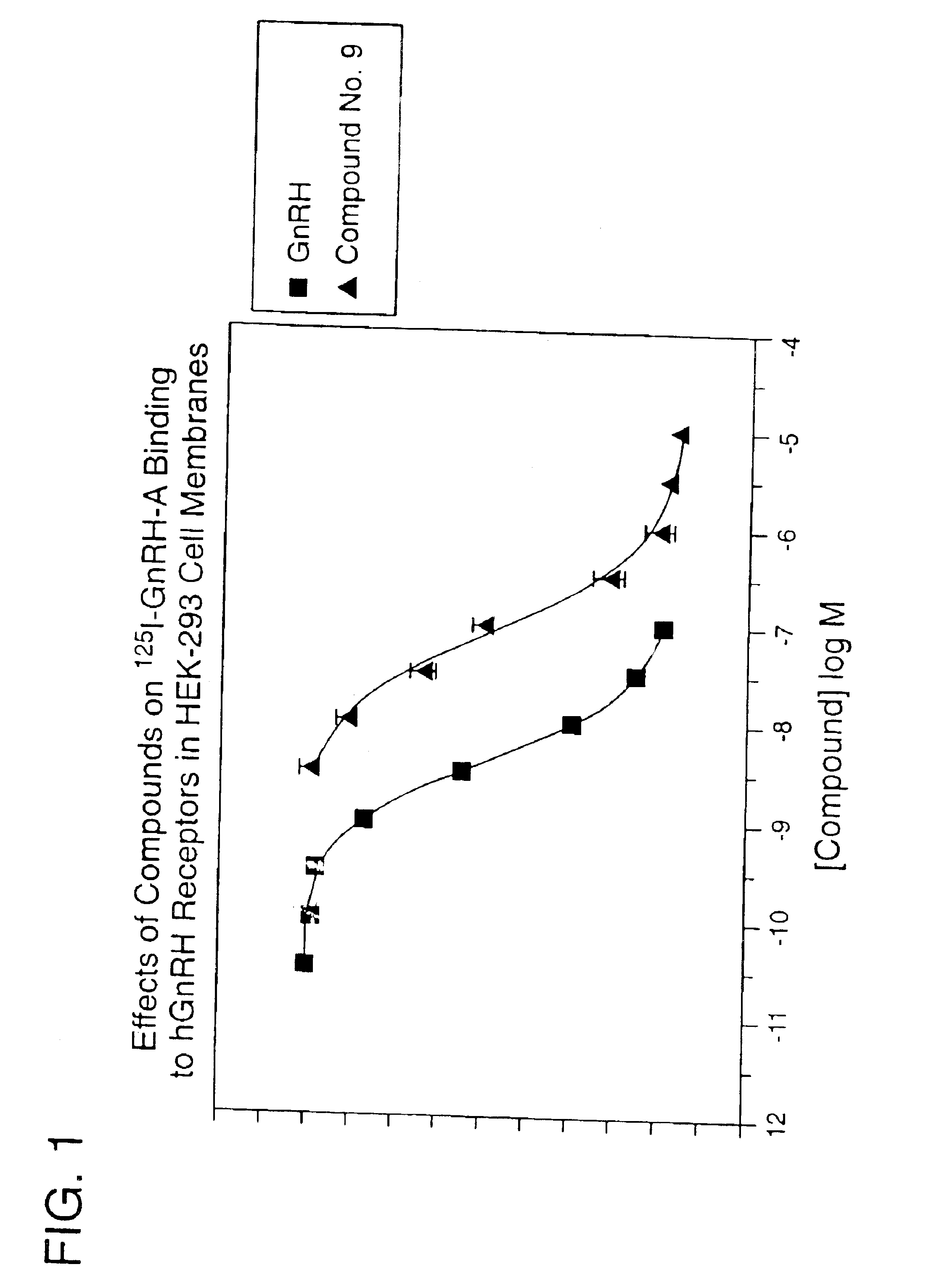
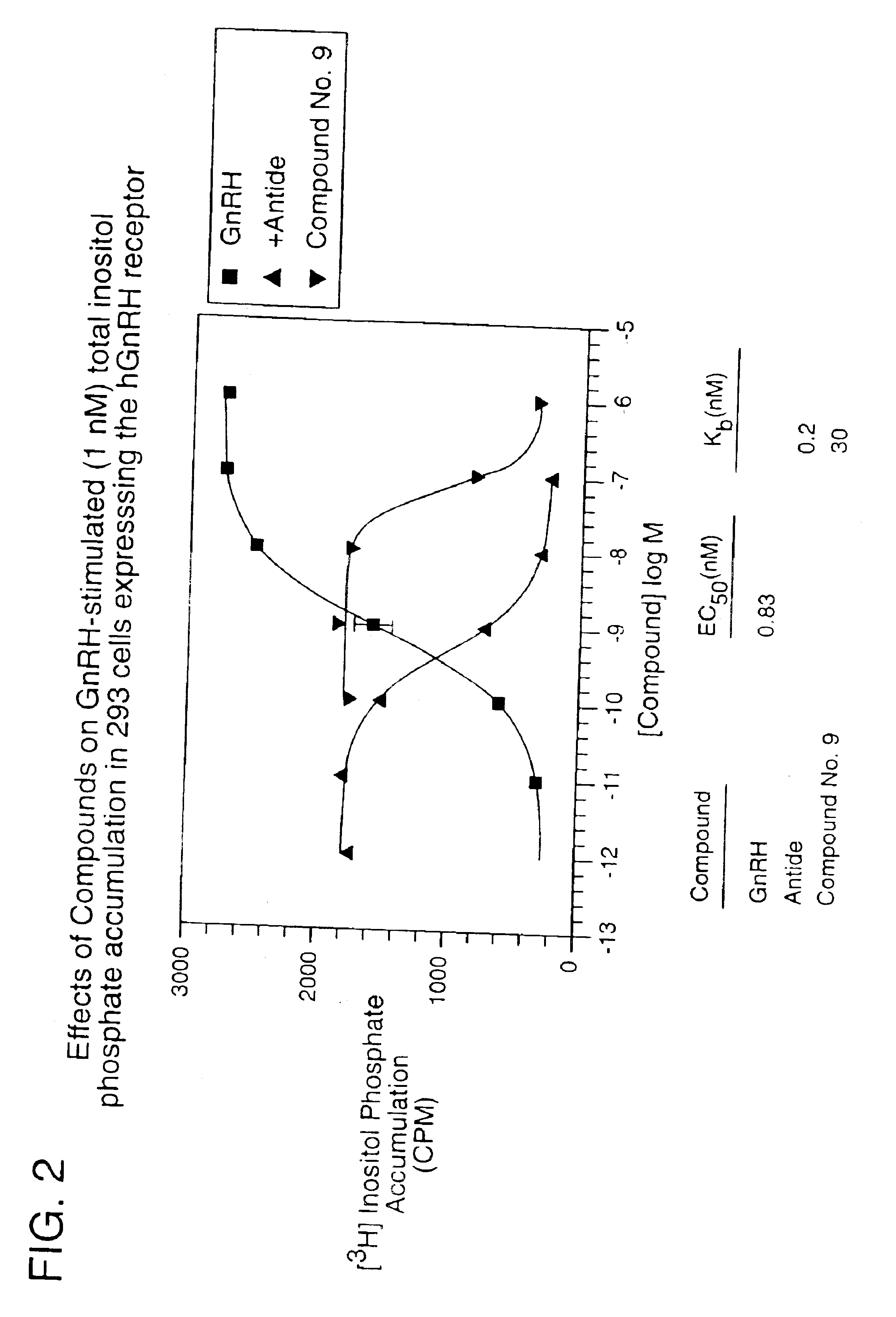
Patents
Literature
117 results about "Gonadotropin-releasing hormone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) is a releasing hormone responsible for the release of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary. GnRH is a tropic peptide hormone synthesized and released from GnRH neurons within the hypothalamus. The peptide belongs to gonadotropin-releasing hormone family. It constitutes the initial step in the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis.
Ligand/lytic peptide compositions and methods of use
InactiveUS6635740B1Prevents sexual maturationInhibition of maturationHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsLytic peptideAbnormal tissue growth
Amphipathic lytic peptides are ideally suited to use in a ligand / cytotoxin combination to specifically inhibit cells that are driven by or are dependent upon a specific ligand interaction; for example, to induce sterility or long-term contraception, or to attack tumor cells, or to selectively lyse virally-infected cells, or to attack lymphocytes responsible for autoimmune diseases. The peptides act directly on cell membranes, and need not be internalized. Administering a combination of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) (or a GnRH agonist) and a membrane-active lytic peptide produces long-term contraception or sterilization in animals in vivo. Administering in vivo a combination of a ligand and a membrane-active lytic peptide kills cells with a receptor for the ligand. The compounds are relatively small, and are not antigenic. Lysis of gonadotropes has been observed to be very rapid (on the order of ten minutes.) Lysis of tumor cells is rapid. The two components-the ligand and the lytic peptide-may optionally be administered as a fusion peptide, or they may be administered separately, with the ligand administered slightly before the lytic peptide, to activate cells with receptors for the ligand, and thereby make those cells susceptible to lysis by the lytic peptide. The compounds may be used in gene therapy to treat malignant or non-malignant tumors, and other diseases caused by clones or populations of "normal" host cells bearing specific receptors (such as lymphocytes), because genes encoding a lytic peptide or encoding a lytic peptide / peptide hormone fusion may readily be inserted into hematopoietic stem cells or myeloid precursor cells.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
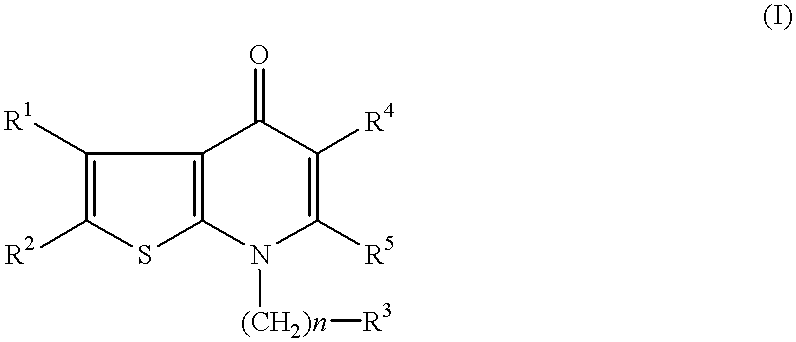
Thienopyrimidine compounds and use thereof
ActiveUS7300935B2Excellent gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonizing activityPromote oral absorptionBiocideNervous disorderHalogenHydroxy group
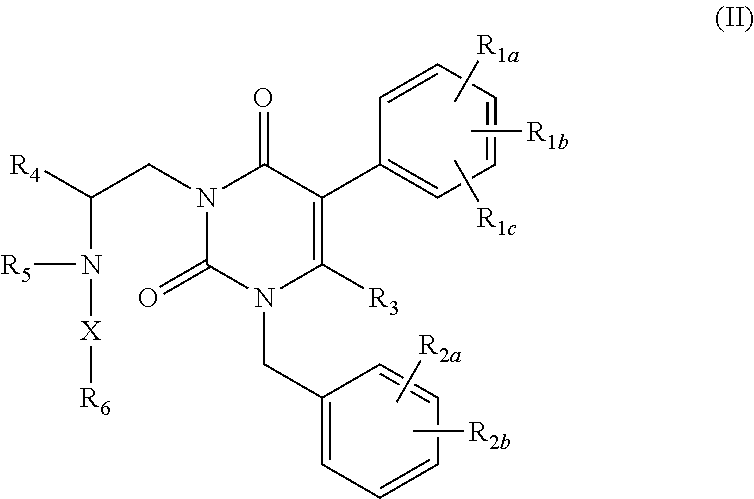
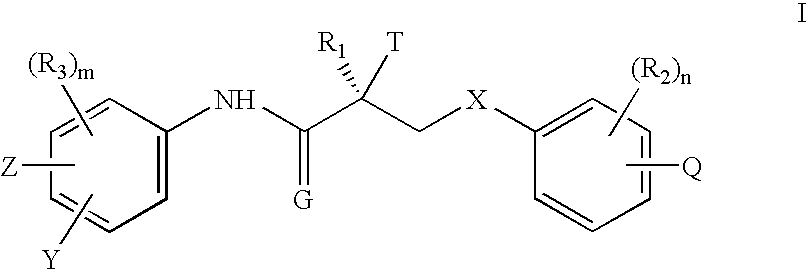
The present invention provides a compound represented by the formula:wherein R1 is a C1-4alkyl; R2 is (1) a 5- to 7-membered nitrogen-containing heterocyclic group which may have a substituent selected from the group consisting of (1′) a halogen, (2′) a hydroxy group, (3′) a C1-4alkyl and (4′) a C1-4alkoxy, (2) a phenyl which may have a substituent selected from the group consisting of (1′) a halogen, (2′) a C1-4alkoxy-C1-4alkyl, (3′) a mono-C1-4alkyl-carbamoyl-C1-4alkyl, (4′) a C1-4alkoxy and (5′) a mono-C1-4alkylcarbamoyl-C1-4alkoxy, or the like; R3 is a C1-4alkyl; R4 is a C1-4alkoxy, or the like; n is an integer of 1 to 4; or a salt thereof, as a thienopyrimidine compound having gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonistic activity.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Methods and compositions for treating benign gynecological disorders
InactiveUS6960337B2Increased riskPrevent endometrial hyperplasiaOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseGynecology
An improvement in a method of treating benign gynecological disorders is described. In the method, treatment of a benign gynecological disorder with a composition comprised of a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) compound and an estrogenic compound, and optionally, an androgenic compound, is extended to premenopausal women who are not receiving an exogenously supplied progestin on a regular or periodic basis. Treatment in accord with the invention does not increase significantly the risk of endometrial hyperplasia. The method is also suitable for contraception.
Owner:BALANCE PHARMA
Prevention of diabetes and prolongation of the honeymoon phase of diabetes by administration of GnRH antagonists
InactiveUS6875843B2Reduce morbidityProlong honeymoon phase of diabetesPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiabetes mellitusMammal
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
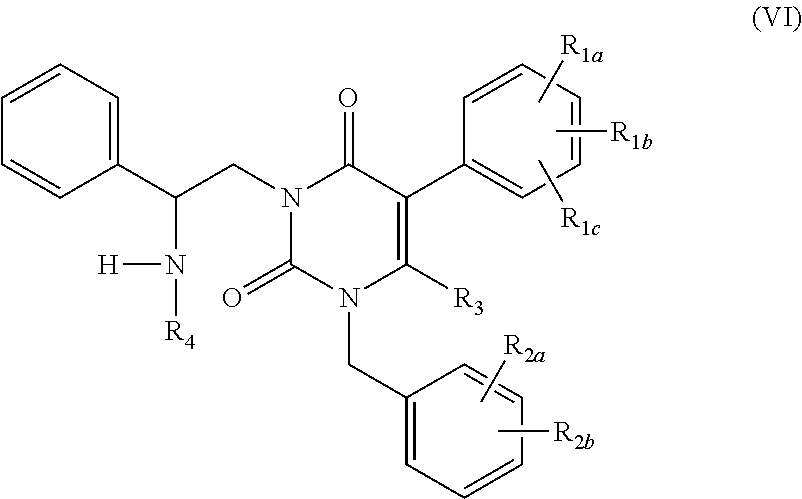
Processes for the preparation of uracil derivatives
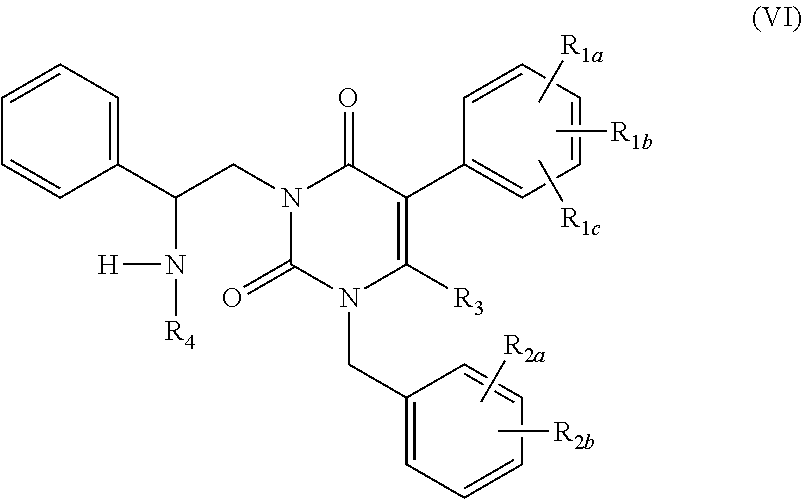
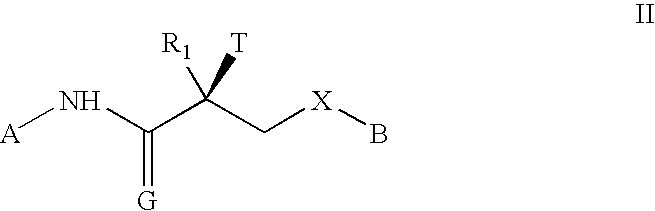
The present invention relates to processes and intermediates for preparing Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) receptor antagonists of structure (VI); and stereoisomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Owner:NEUROCRINE BIOSCI INC
Non-peptide GNRH agents, methods and intermediates for their preparation
InactiveUS7101878B1Modulate activityGood biodistributionBiocideOrganic chemistrySteroidal hormonesGonadotropin-releasing hormone
Non-peptide GnRH agents capable of inhibiting the effect of gonadotropin-releasing hormone are described. Such compounds and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts, multimers, prodrugs, and active metabolites are suitable for treating mammalian reproductive disorders and steroid hormone-dependent tumors as well as for regulating fertility, where suppression of gonadotropin release is indicated. Methods for synthesizing the compounds and intermediates useful in their preparation are also described.
Owner:AGOURON PHARMA INC
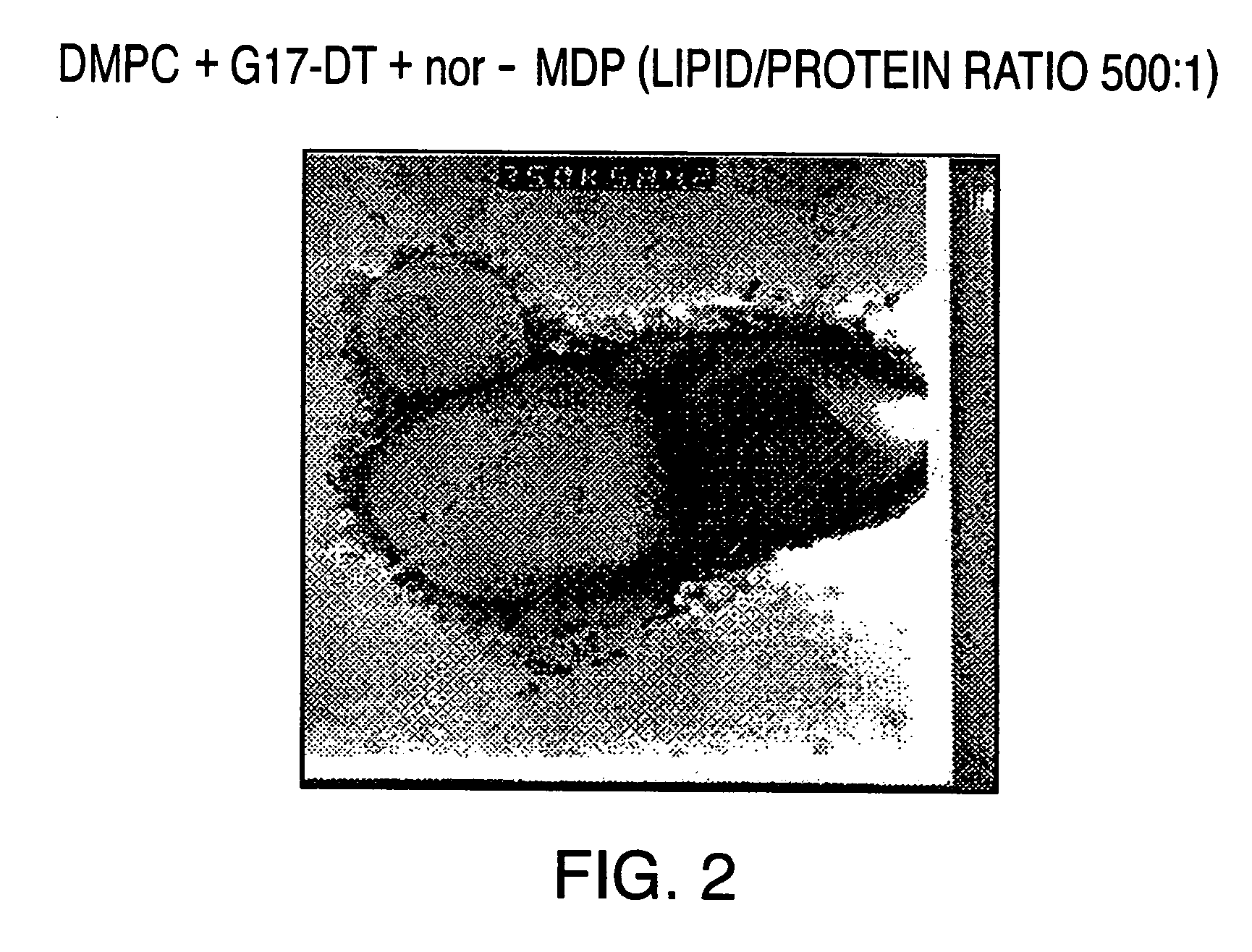
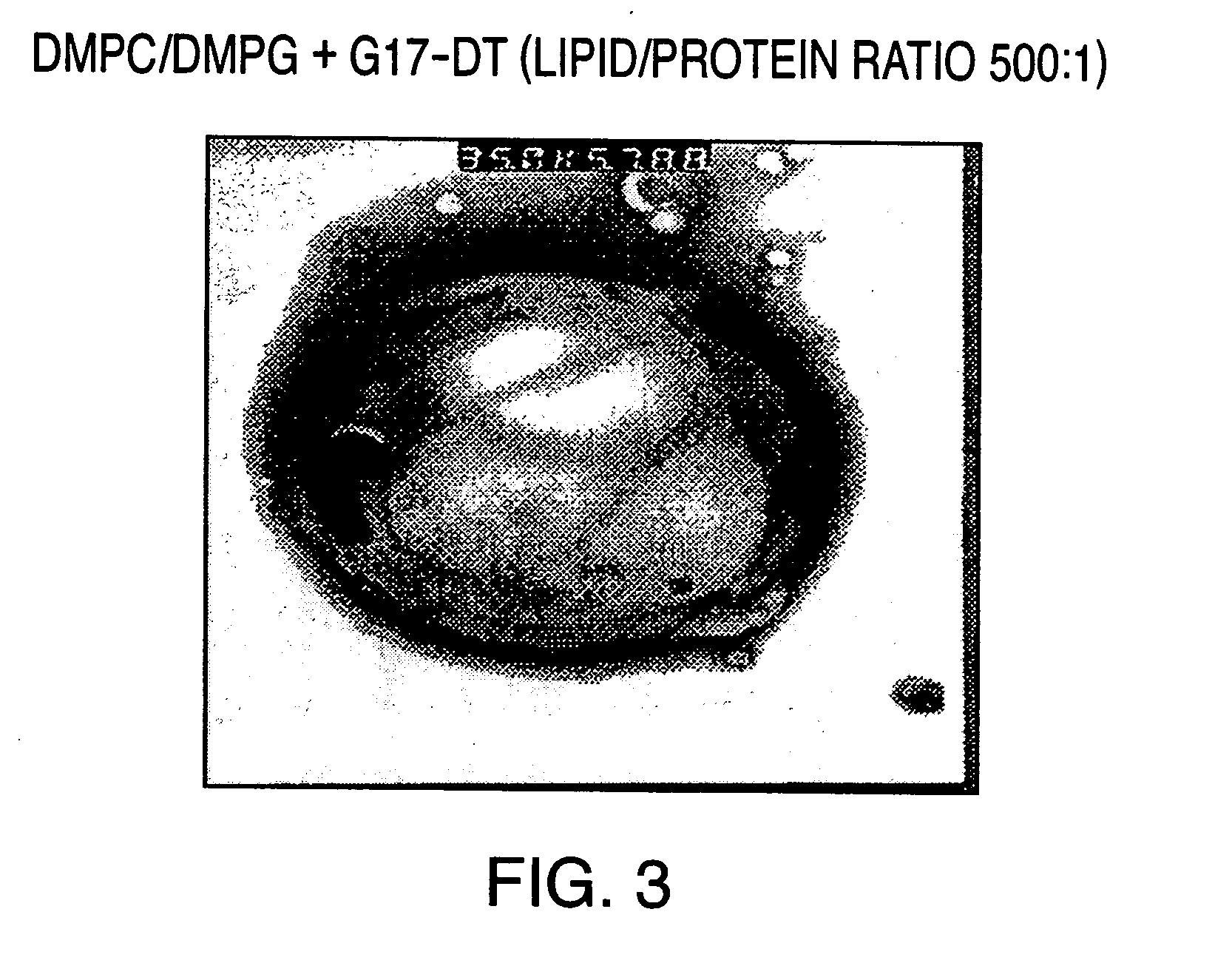
Liposomal vaccine
InactiveUS20050169979A1High weight ratioHigh encapsulation efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedHormones regulationLiposome
The invention provides liposomal vehicles for encapsulating relatively high levels of immunogenic protein substances including immunogens directed against hormones and hormone receptors, such as gastrin and gonadotropin releasing hormone and their receptors. The liposome encapsulating large amounts of immunogens can be injected parenterally to induce effective immune responses without exhibiting significant adverse tissue reactogenicity. Methods for production of the liposomal vaccines and methods of their administration for treatment of diseases and conditions associated with the cognate hormones are also provided.
Owner:RECEPTOR BIOLOGIX +1
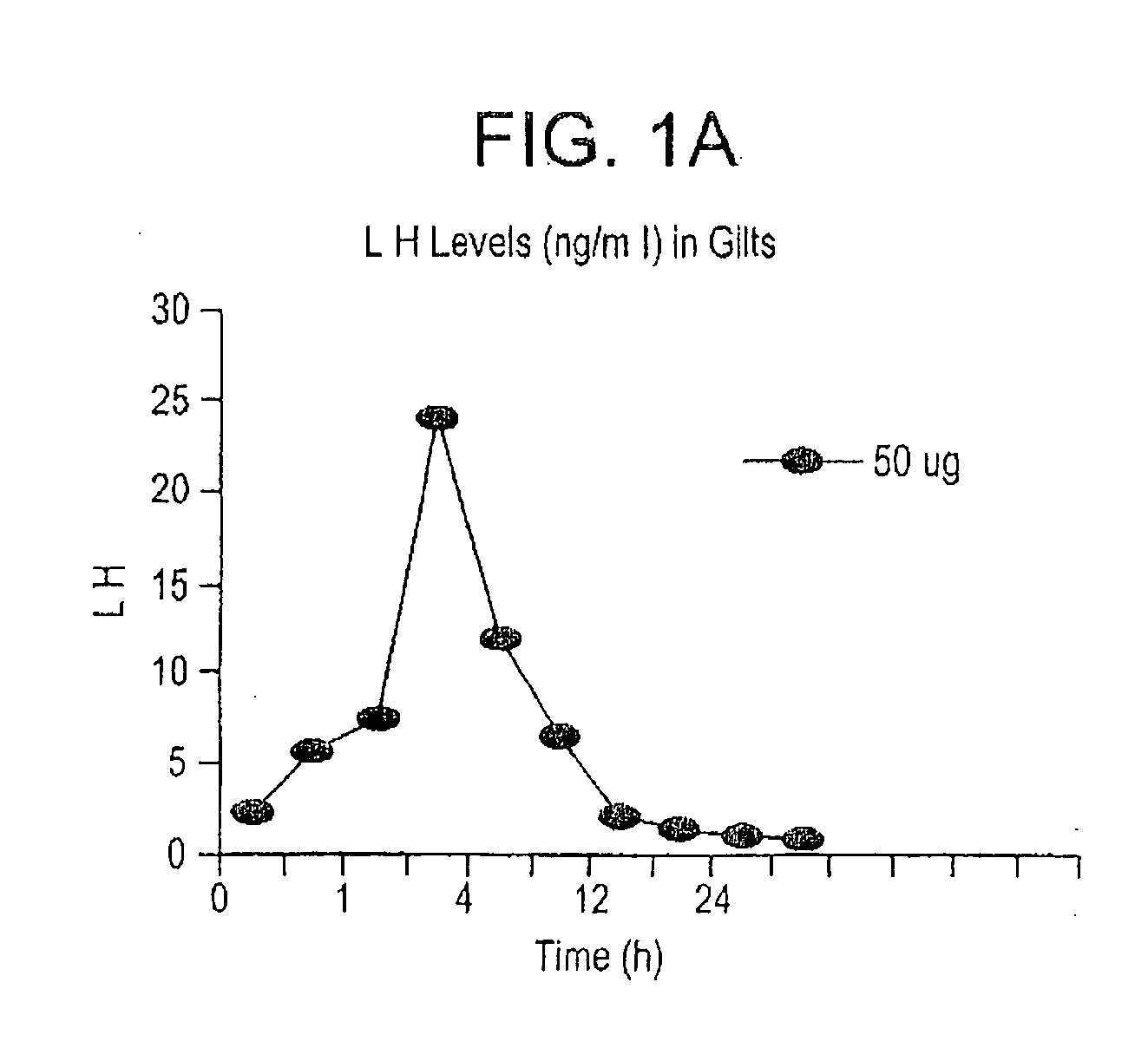
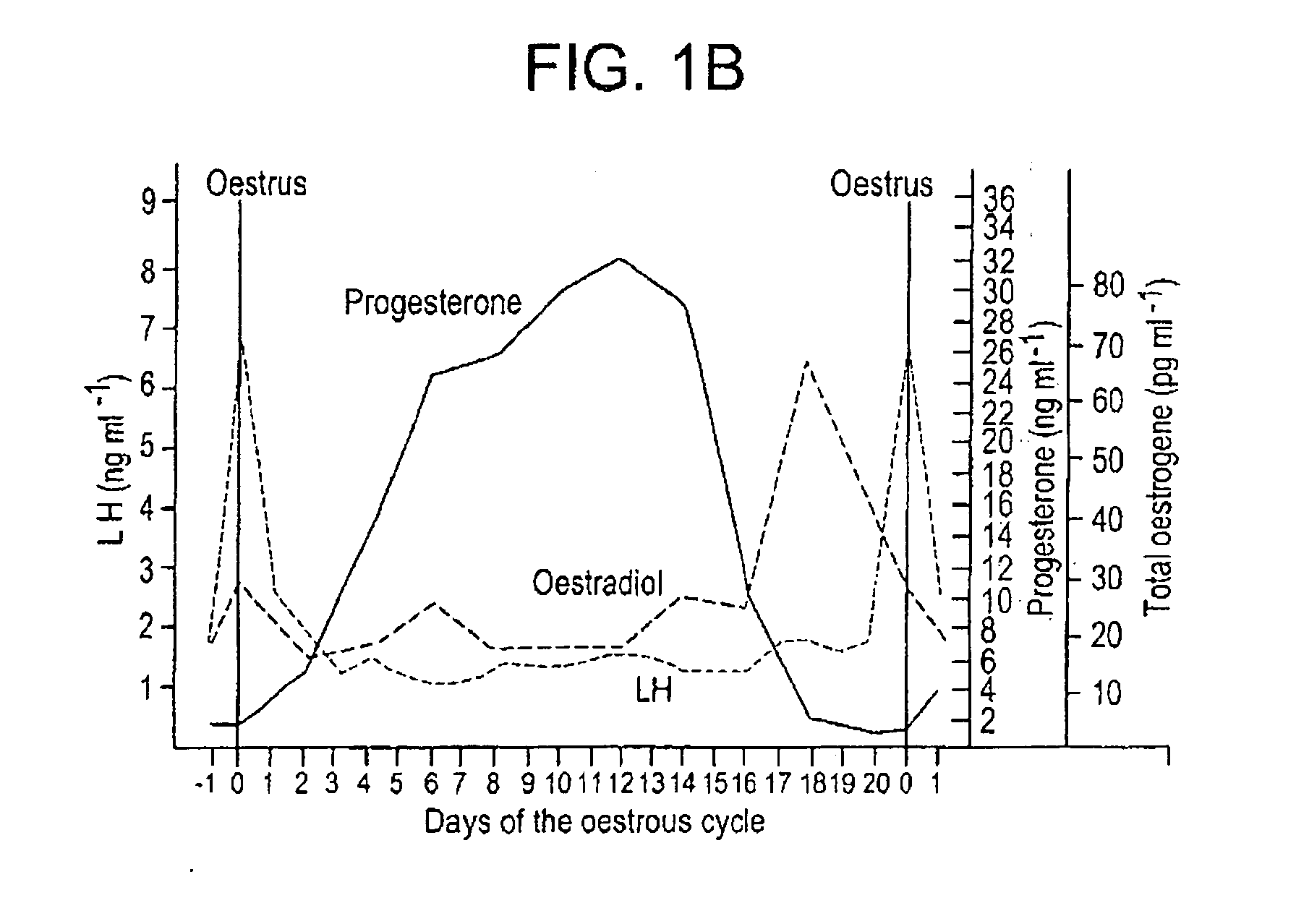
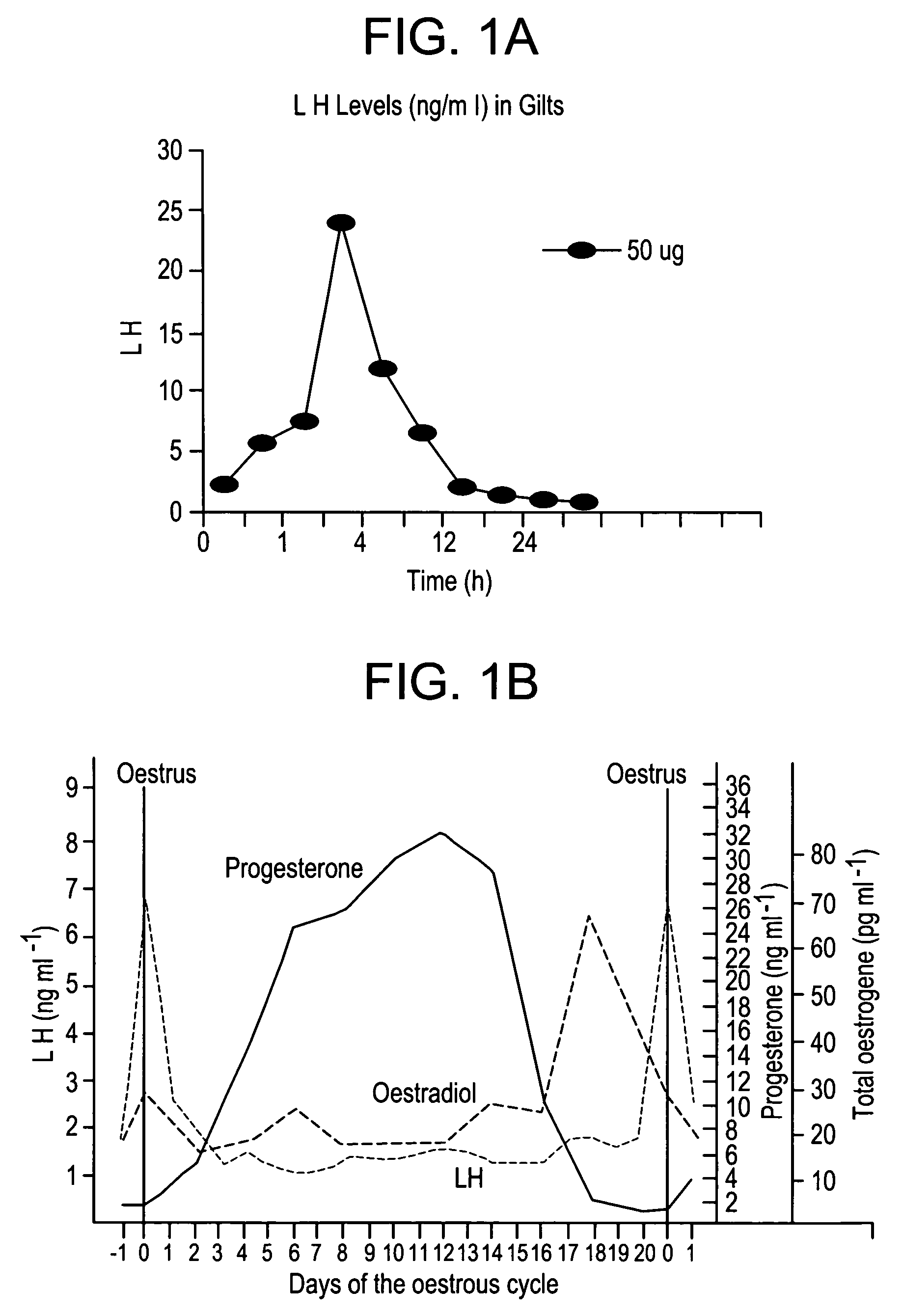
Process for the synchronization of ovulation for timed breeding without heat detection
InactiveUS20070197435A1Efficient methodPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesSingle injectionBiology
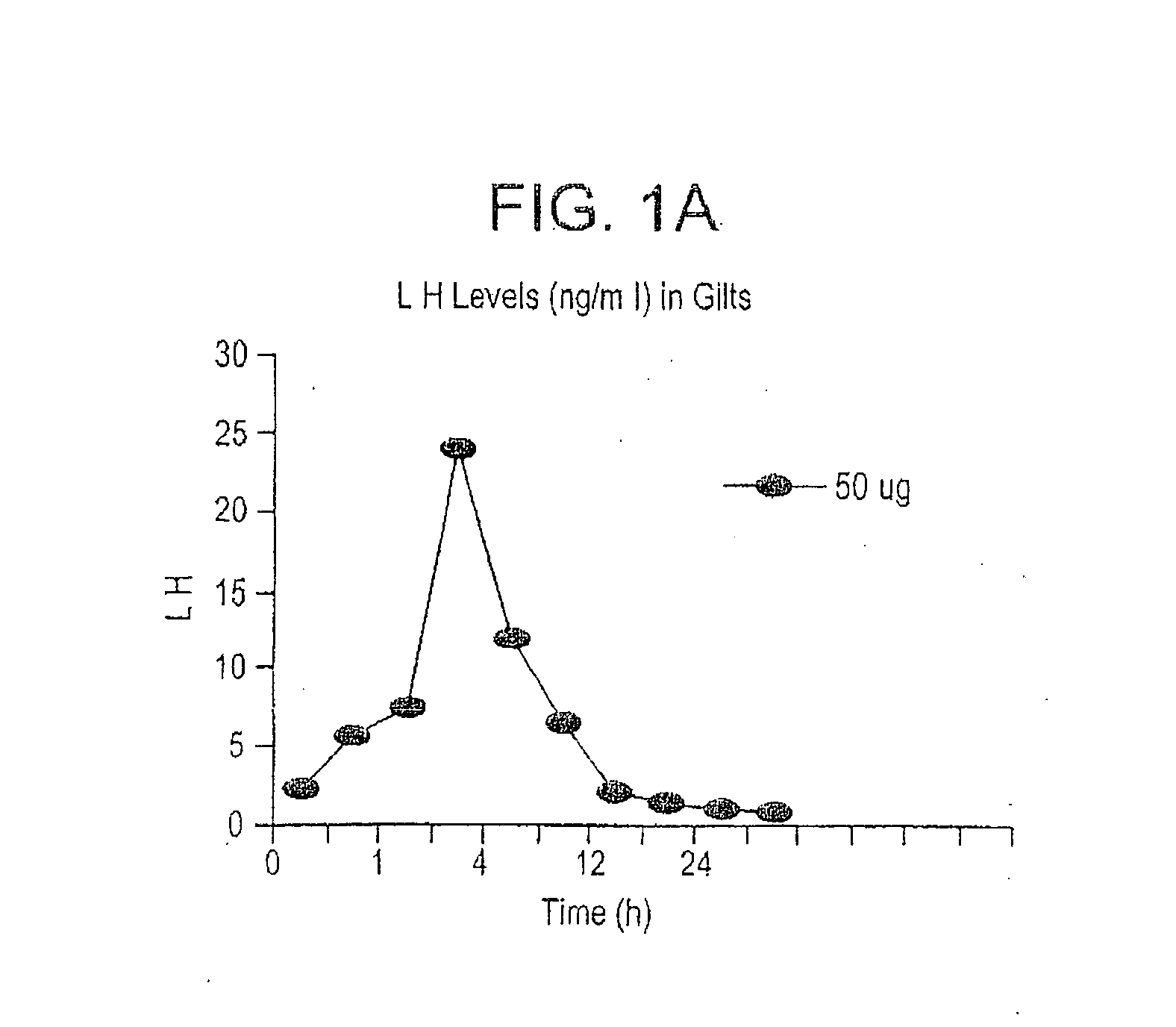
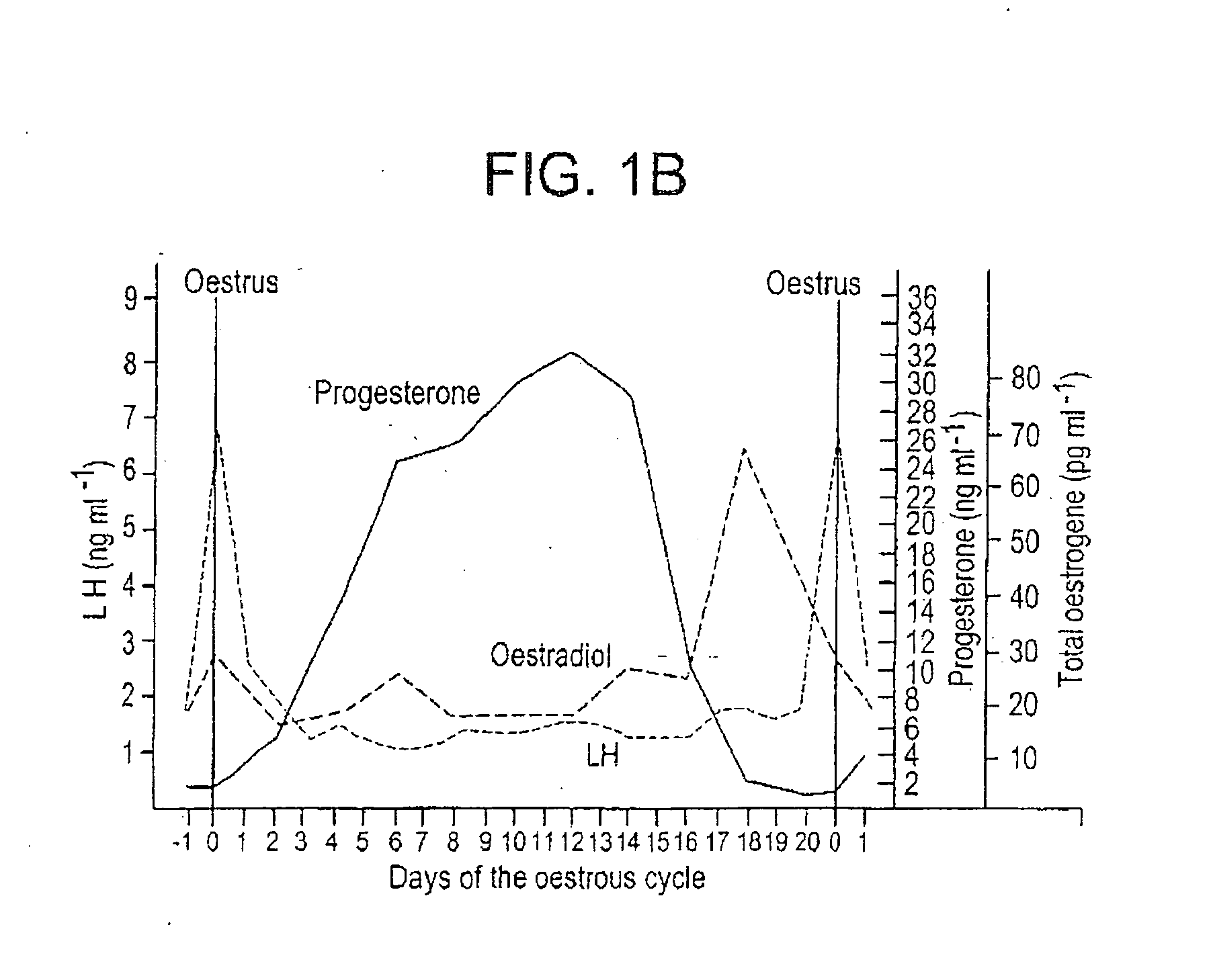
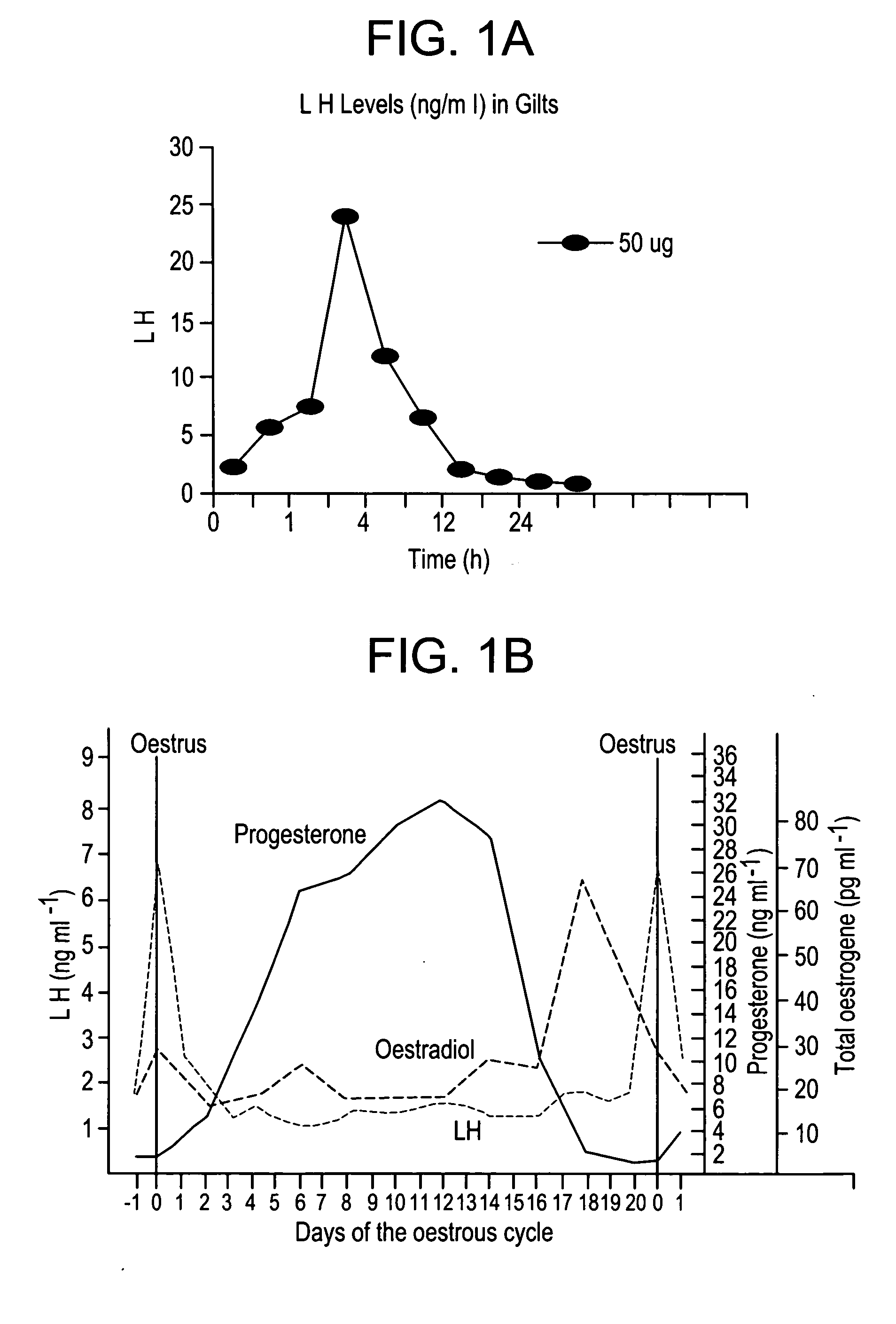
A method for synchronizing ovulation in sows and gilts by a single injection of hormones is disclosed. A hormone, gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), analogues, derivatives, agonists or combinations thereof is administered to an open sow post weaning at a specific time to stimulate ovulation of mature responsive follicles. The sow is then bred, without heat detection, at a specific subsequent timed interval after injection with hormone, with one or two artificial or natural breedings. In gilts, the hormone is injected at a timed interval from onset of estrus or at a specific timed interval following Prostaglandin F2a for those gilts which have been held in a state of pseudopregnancy.
Owner:JBS UNITED
Quinoline derivatives, their production and use
The present compounds are intermediates for the preparation of quinoline derivatives and compositions having gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonistic activity useful as propylactics or therapeutic agent for the prevention or treatment of several hormone dependent diseases, for example, a sex hormone dependent cancer (e.g. prostatic cancer, uterine or cervical cancer, breast cancer, pituitary adenoma), benign prostatic hypertrophy, myoma of the uterus, endometriosis, precocious puberty, amenorrhea, premenstrual syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome and acne vulgaris; are effective as a fertility controlling agent in both sexes (e.g. a pregnancy controlling agent and a menstrual cycle controlling agent); can be used as a male or female contraceptive, as an ovulation-inducing agent; can be used as an infertility treating agent by using a rebound effect owing to a stoppage of administration thereof; and are useful for modulating estrous cycles in animals in the field of animal husbandry, as agents for improving the quality of edible meat or promoting the growth of animals, and as agents for promoting spawning in fish.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Liposomal vaccine
InactiveUS20070082043A1High weight ratioHigh encapsulation efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedWater solubleLiposome
The invention provides liposomal vehicles for encapsulating relatively high levels of water-soluble substances including immunogens directed against gastrin and gonadotropin releasing hormone. The liposome encapsulating large amounts of immunogens can be injected parentally to induce effective immune responses without exhibiting significant adverse tissue reactogenicity.
Owner:RECEPTOR BIOLOGIX
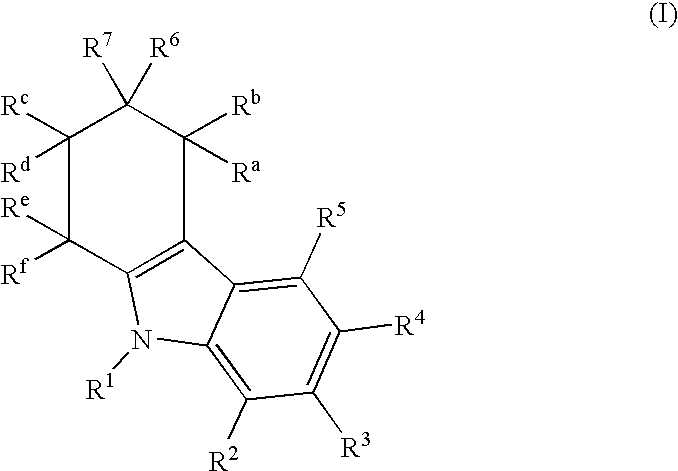
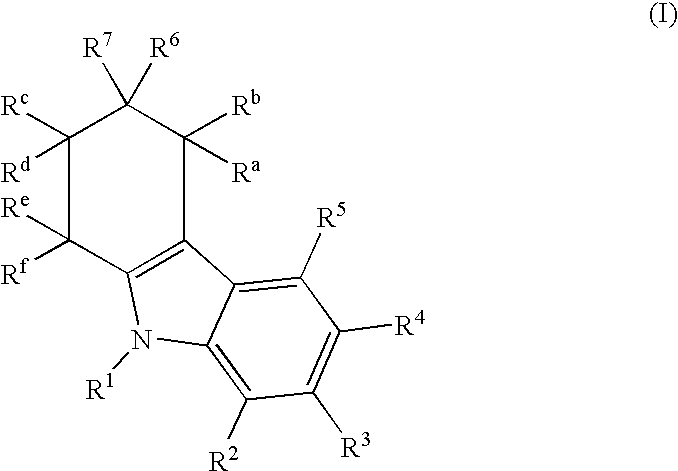
Tetrahydrocarbazol derivatives as ligands for G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR)
InactiveUS7122570B2Low estrogen dosagesReduction in the hormone dosagesBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCarbazoleG protein-coupled receptor
This invention provides new tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives that act as ligands for G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCR), especially as antagonists of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH). A pharmaceutical composition that contains these new tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives as well as a process for the production of the new tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives are also provided. Moreover, this invention relates to the administration of tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives for treating pathologic conditions that are mediated by GPCR, especially for inhibiting GnRH, in mammals, especially humans, who require such an administration, as well as the use of tetrahydrocarbazole derivatives for the production of a pharmaceutical agent for treating GPCR-mediated pathologic conditions, especially for inhibiting GnRH.
Owner:AETERNA ZENTARIS GMBH
Compositions and methods for contraception in or sterilization of mammals
InactiveUS6680058B1Prevents sexual maturationInhibition of maturationHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsLytic peptideMammal
Amphipathic lytic peptides are ideally suited to use in a ligand / cytotoxin combination to induce sterility or long-term contraception in mammals. The peptides act directly on cell membranes, and need not be internalized. Administering a combination of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) (or a GnRH agonist) and a membrane-active lytic peptide produces long-term contraception or sterilization in mammals in vivo. The compounds are relatively small, and are not antigenic. Lysis of gonadotropes has been observed to be very rapid (on the order of ten minutes.) The two components-the ligand and the lytic peptide-may optionally be administered as a fusion peptide, or they may be administered separately, with the ligand administered slightly before the lytic peptide, to activate cells with receptors for the ligand, and thereby make those cells susceptible to lysis by the lytic peptide.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Process for the synchronization of ovulation for timed breeding without heat detection
ActiveUS20050130894A1Efficient methodAnimal reproductionPeptide/protein ingredientsOvulation timesSingle injection
A method for synchronizing ovulation in sows and gilts by a single injection of hormones is disclosed. A hormone, gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), analogues, derivatives, agonists or combinations thereof is administered to an open sow post weaning at a specific time to stimulate ovulation of mature responsive follicles. The sow is then bred, without heat detection, at a specific subsequent timed interval after injection with hormone, with one or two artificial or natural breedings. In gilts, the hormone is injected at a timed interval from onset of estrus or at a specific timed interval following Prostaglandin F2a for those gilts which have been held in a state of pseudopregnancy.
Owner:THORN BIOSCI
Compositions and methods for treating precocious puberty
ActiveUS20060019903A1Avoid lostPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismHistrelinPhysiology
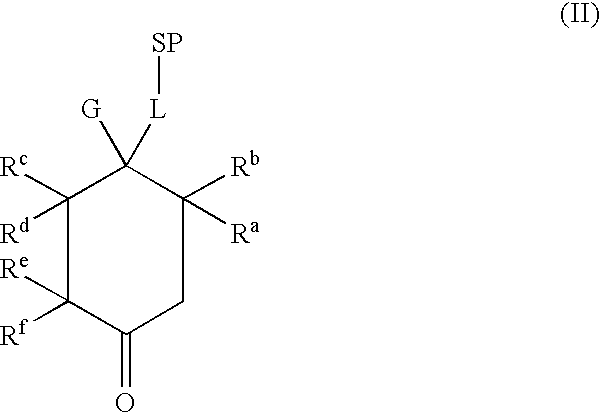
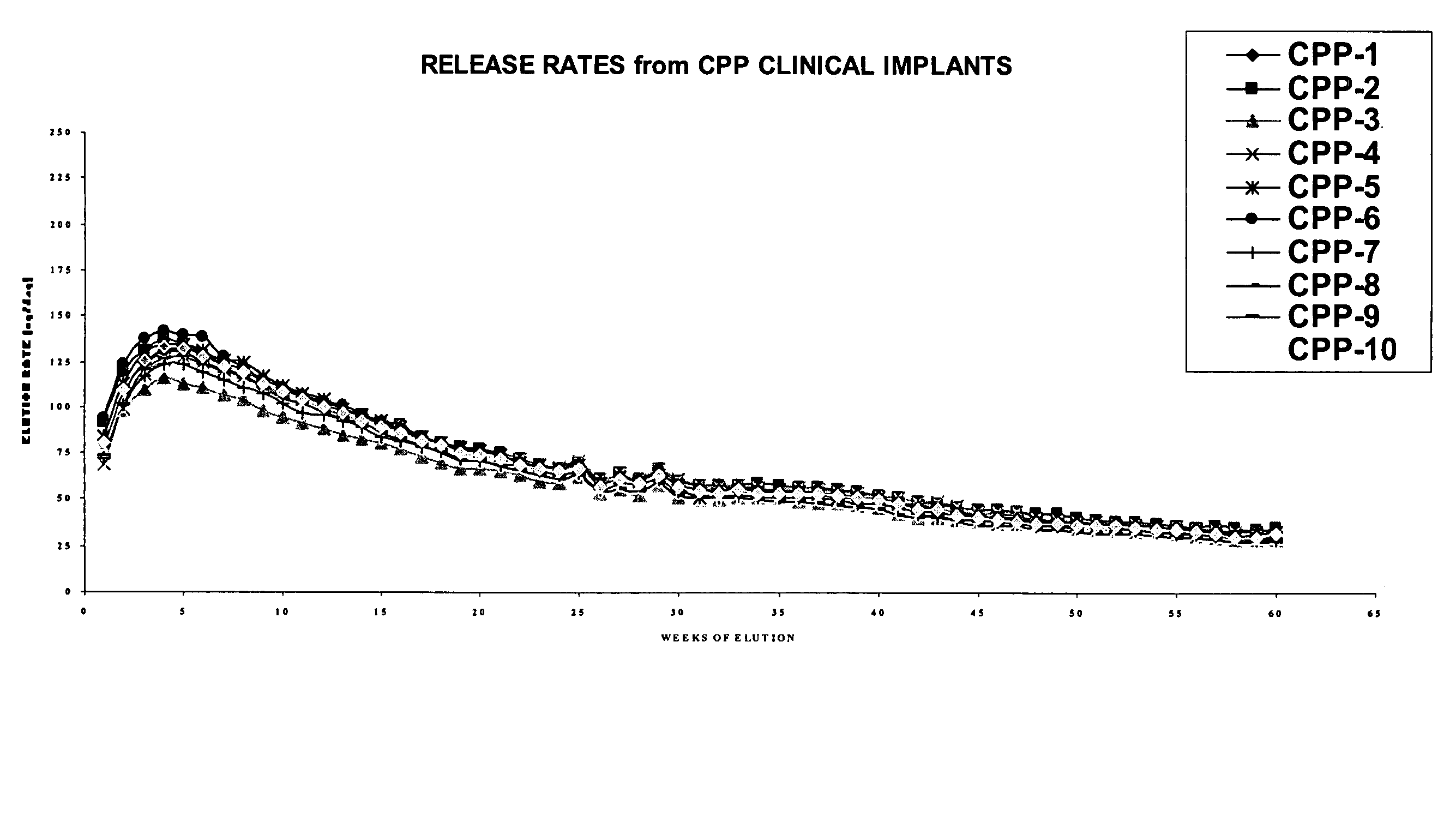
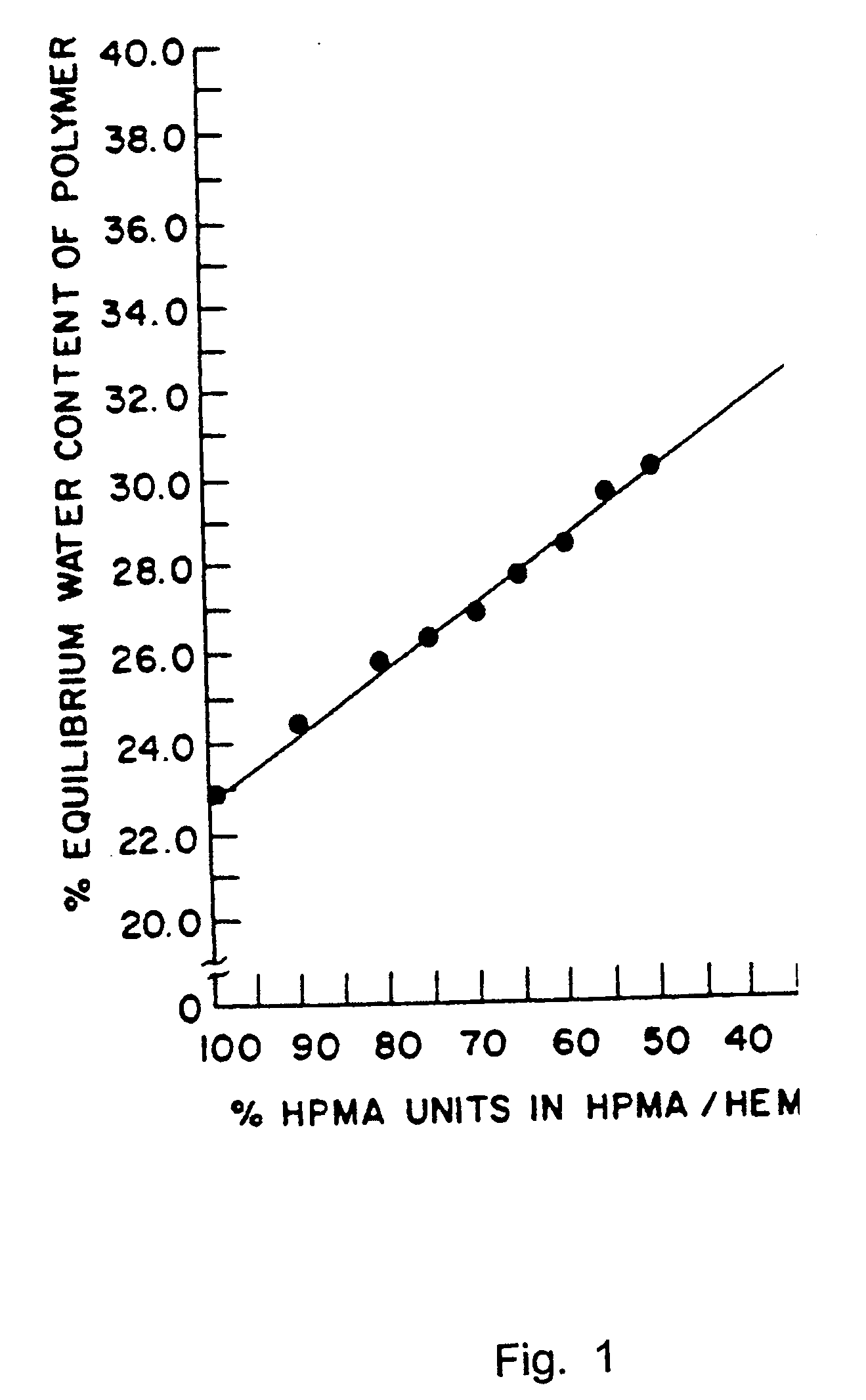
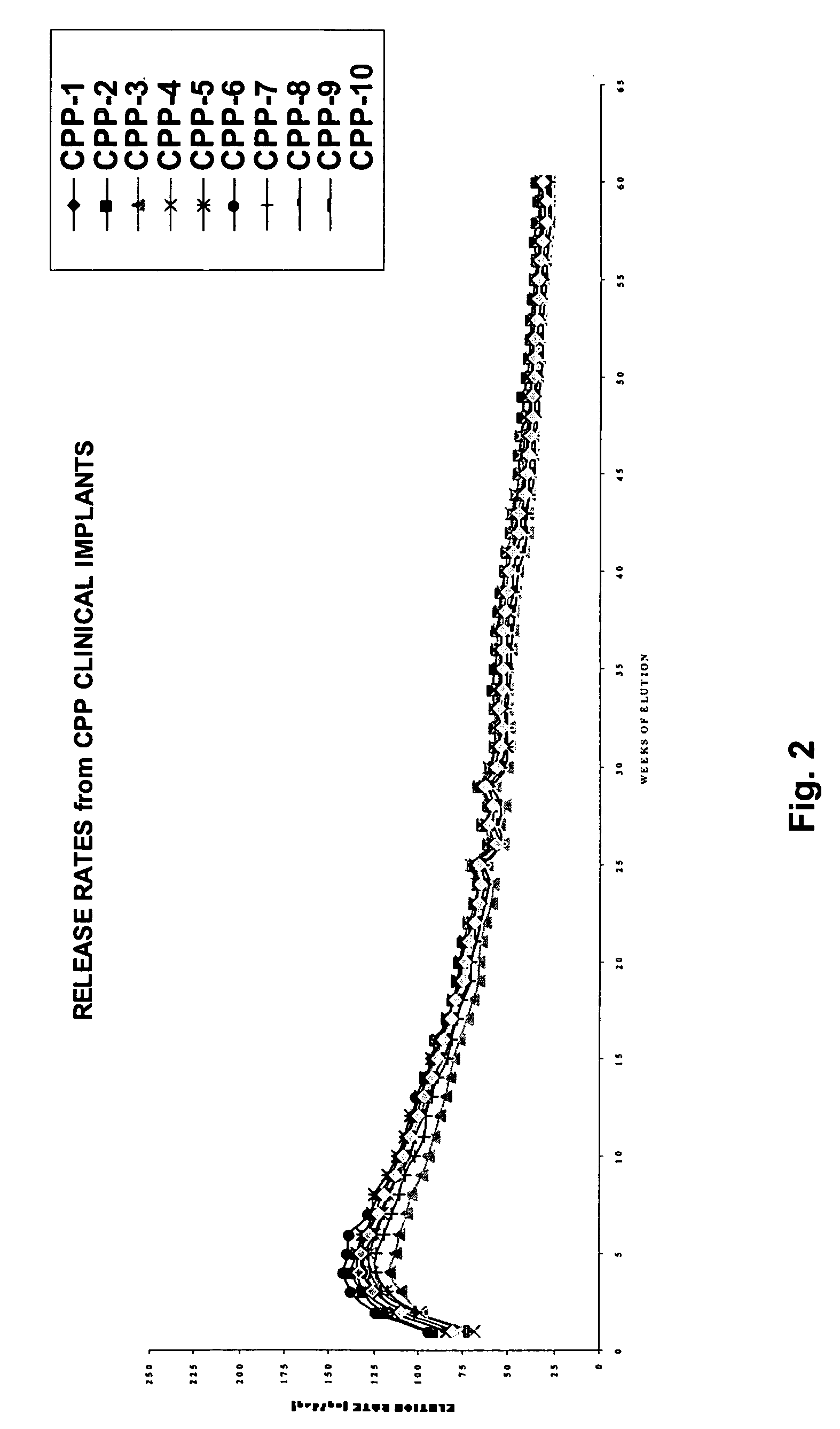
The present invention is directed to the controlled delivery of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, preferably from a polymeric material that is implanted in the body. More specifically, the present invention relates to compositions comprised of a GnRH agonist, preferably histrelin, in a polymeric material that results in a desired and controlled delivery of a therapeutically effective amount of GnRH agonist over an extended period of time in order to treat central precocious puberty (CPP).
Owner:ENDO PHARMA SOLUTIONS
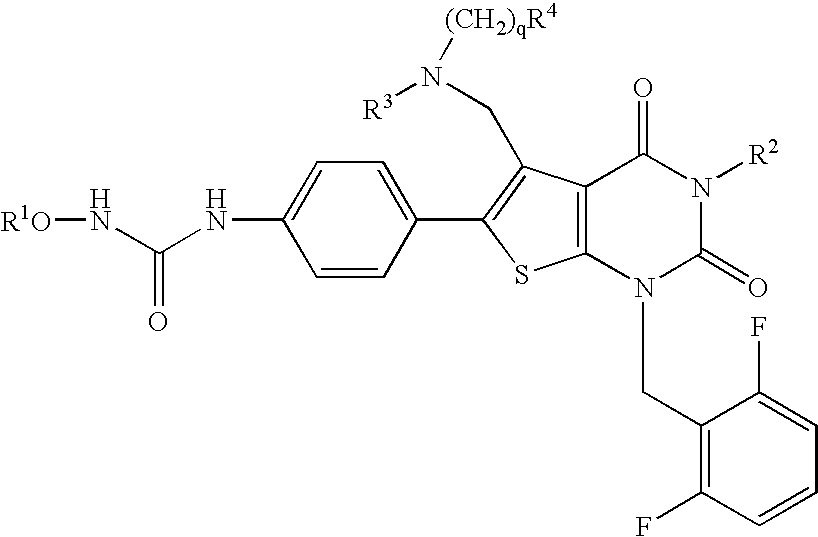
Condensed-ring thiophene derivatives, their production and use
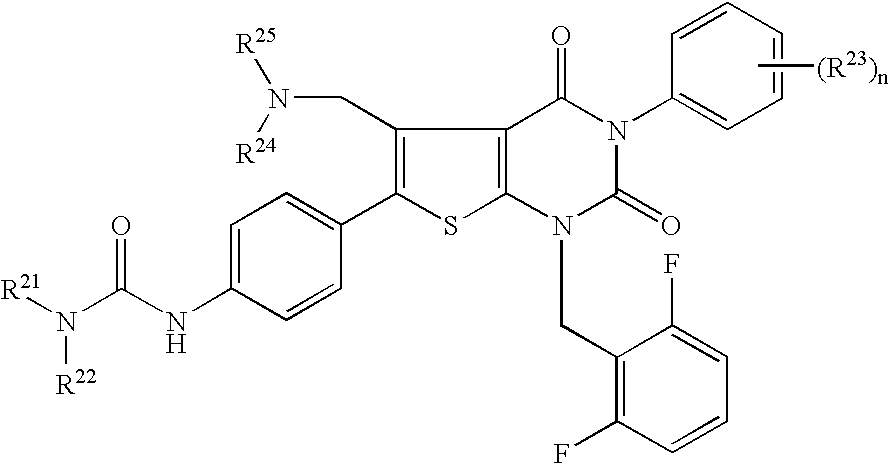
A gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonistic composition, which comprises an optionally substituted condensed-bicyclic compound consisting of a homo or hetero 5 to 7 membered ring and a homo or hetero 5 to 7 membered ring is effective as a propylactic or therapeutic agent for the prevention or treatment of several hormone dependent diseases, for example, a sex hormone dependent cancer (e.g. prostatic cancer, cancer of uterine cervix, breast cancer, pituitary adenoma), benign prostatic hypertrophy, myoma of the uterus, endometriosis, precocious puberty, amenorrhea, premenstrual syndrome, polycystic ovary syndrome and acne vulgaris; is effective as a fertility controlling agent in both sexes (e.g. a pregnancy controlling agent and a menstrual cycle controlling agent); can be used as a contraceptive of male or female, as an ovulation-inducing agent of female; can be used as an infertility treating agent by using a rebound effect owing to a stoppage of administration thereof; is useful as modulating estrous cycles in animals in the field of animal husbandry, as an agent fro improving the quality of edible meat or promoting the growth of animals; is useful as an agent of spawning promotion in fish.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Inducing sterility in fish by disrupting the development of the GnRH system
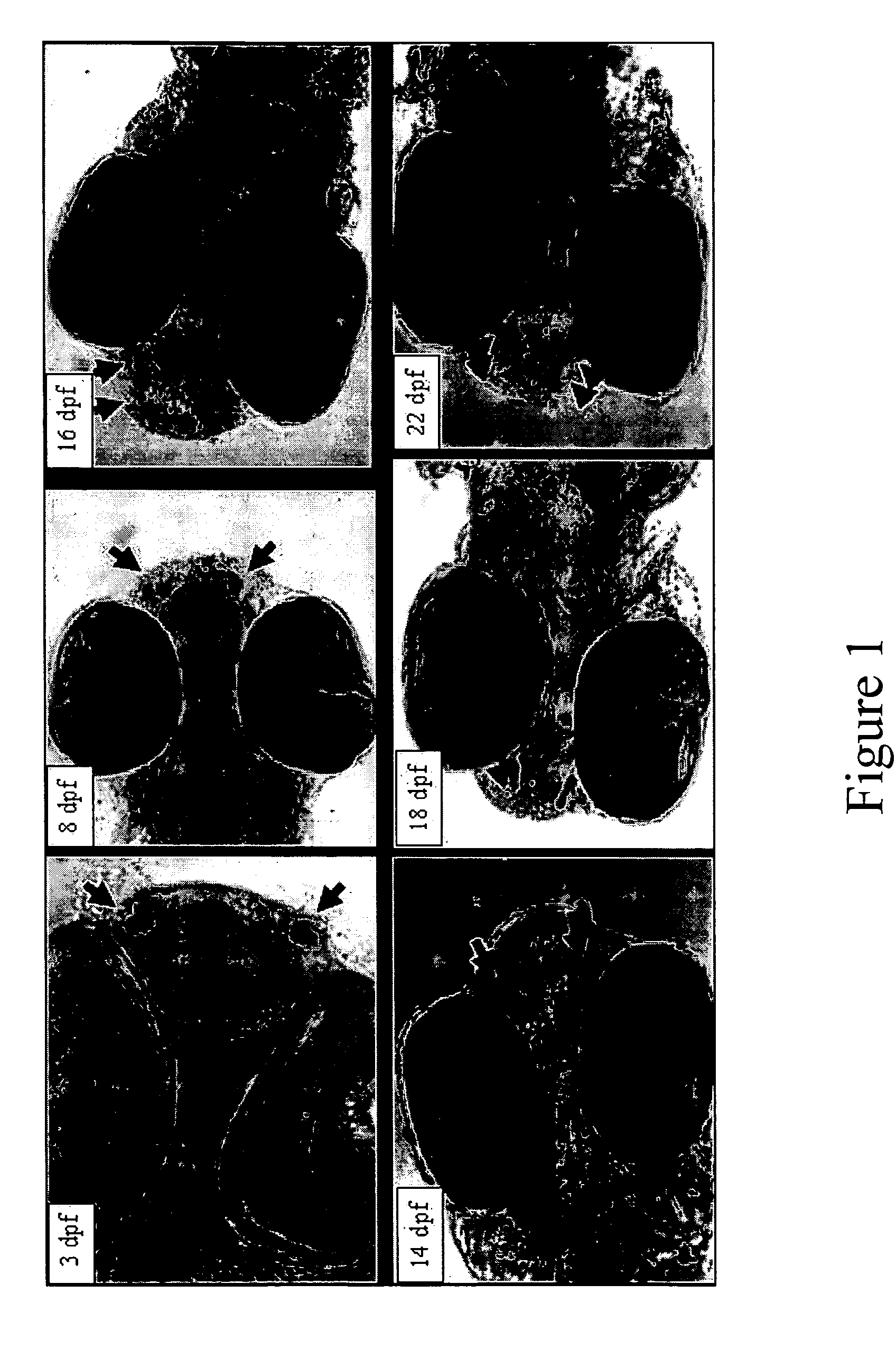
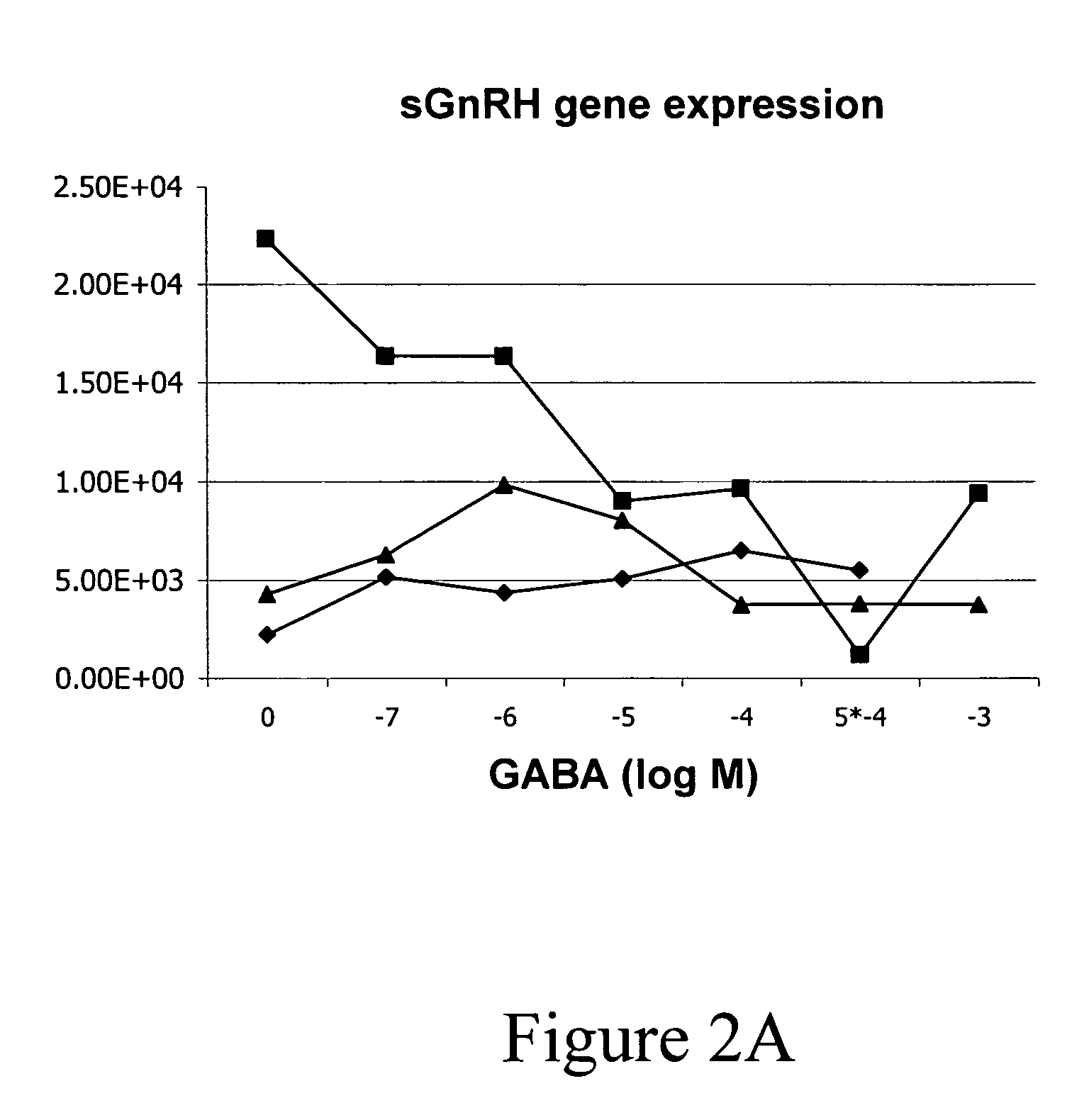
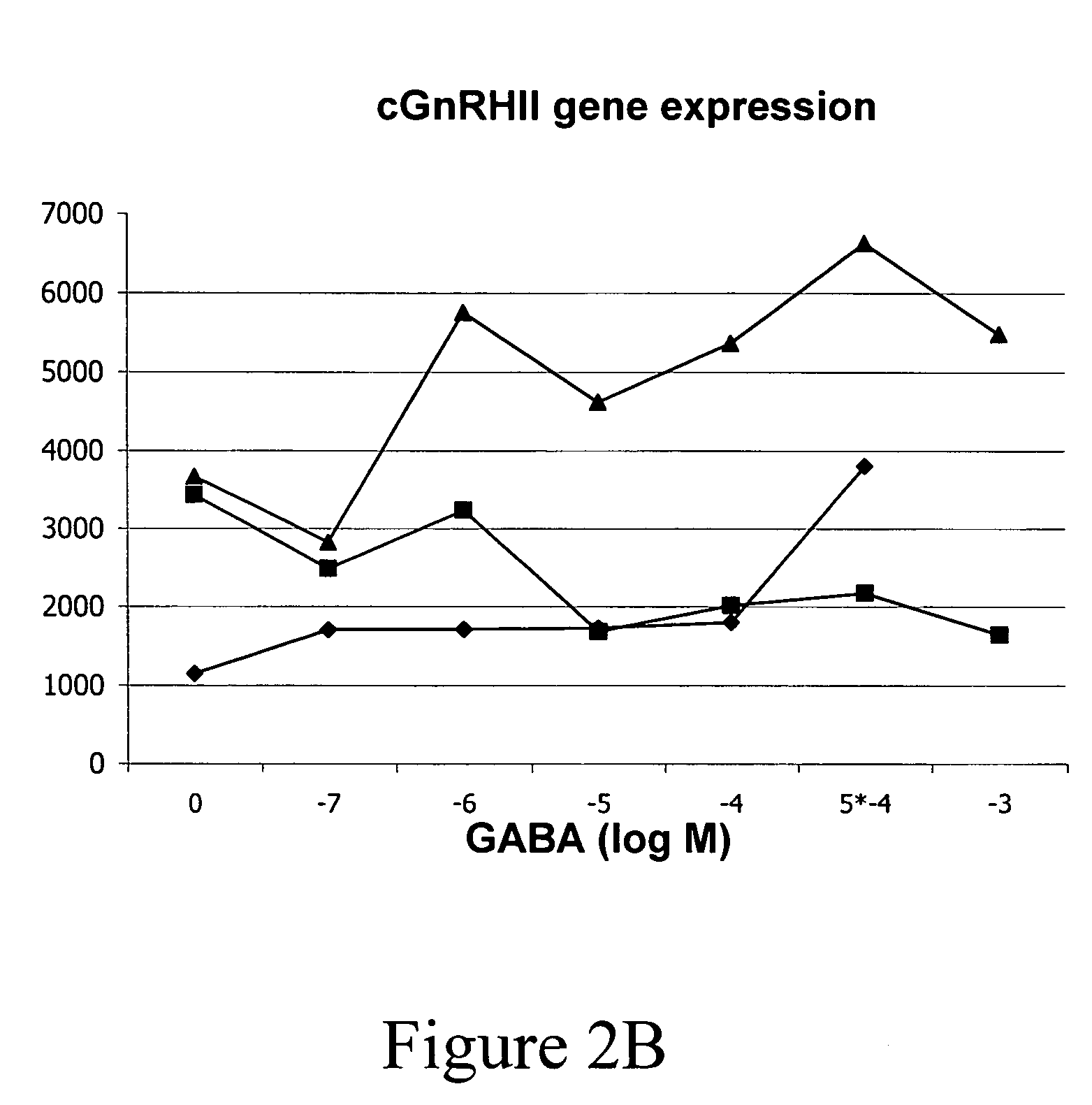
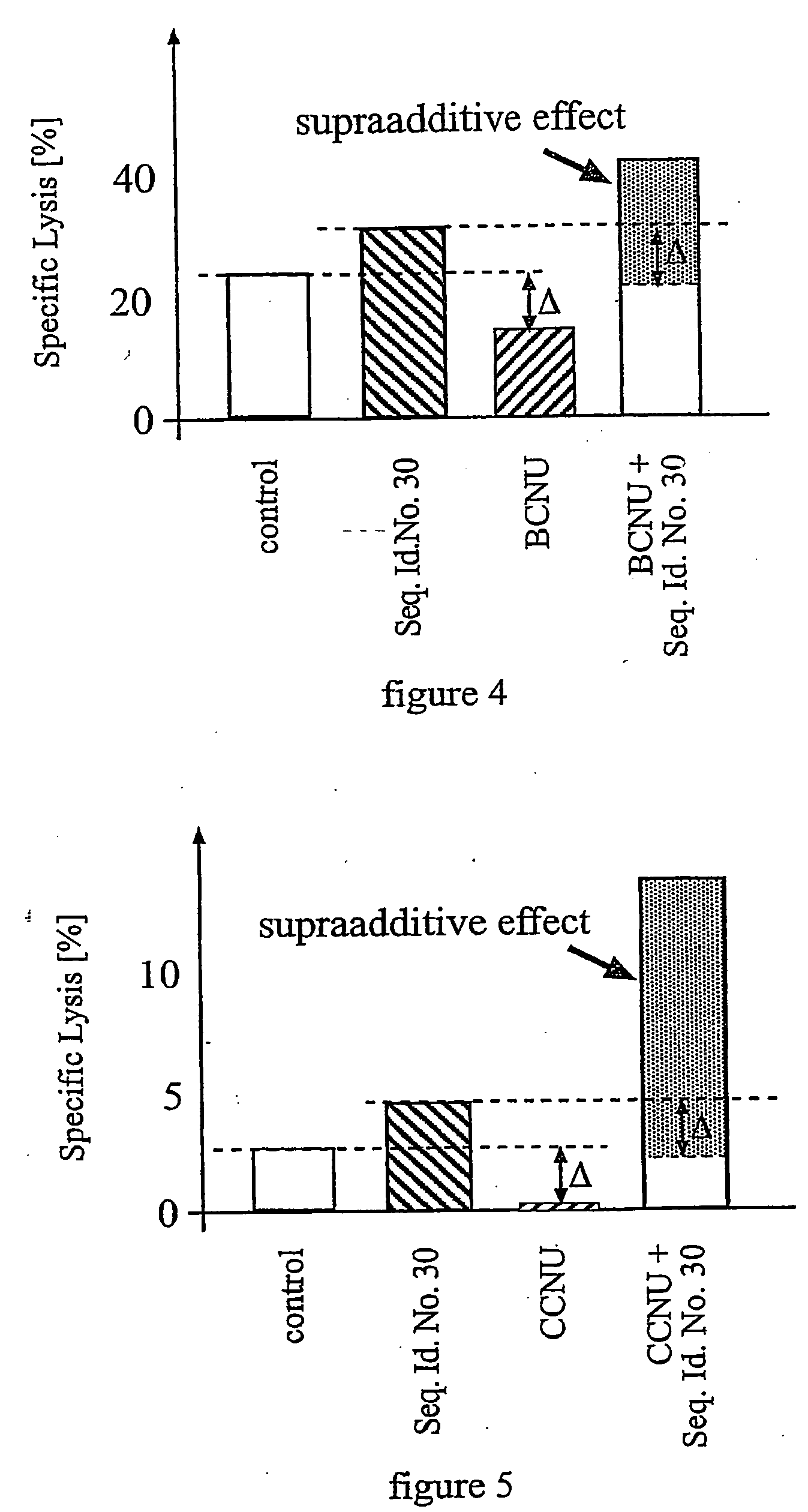
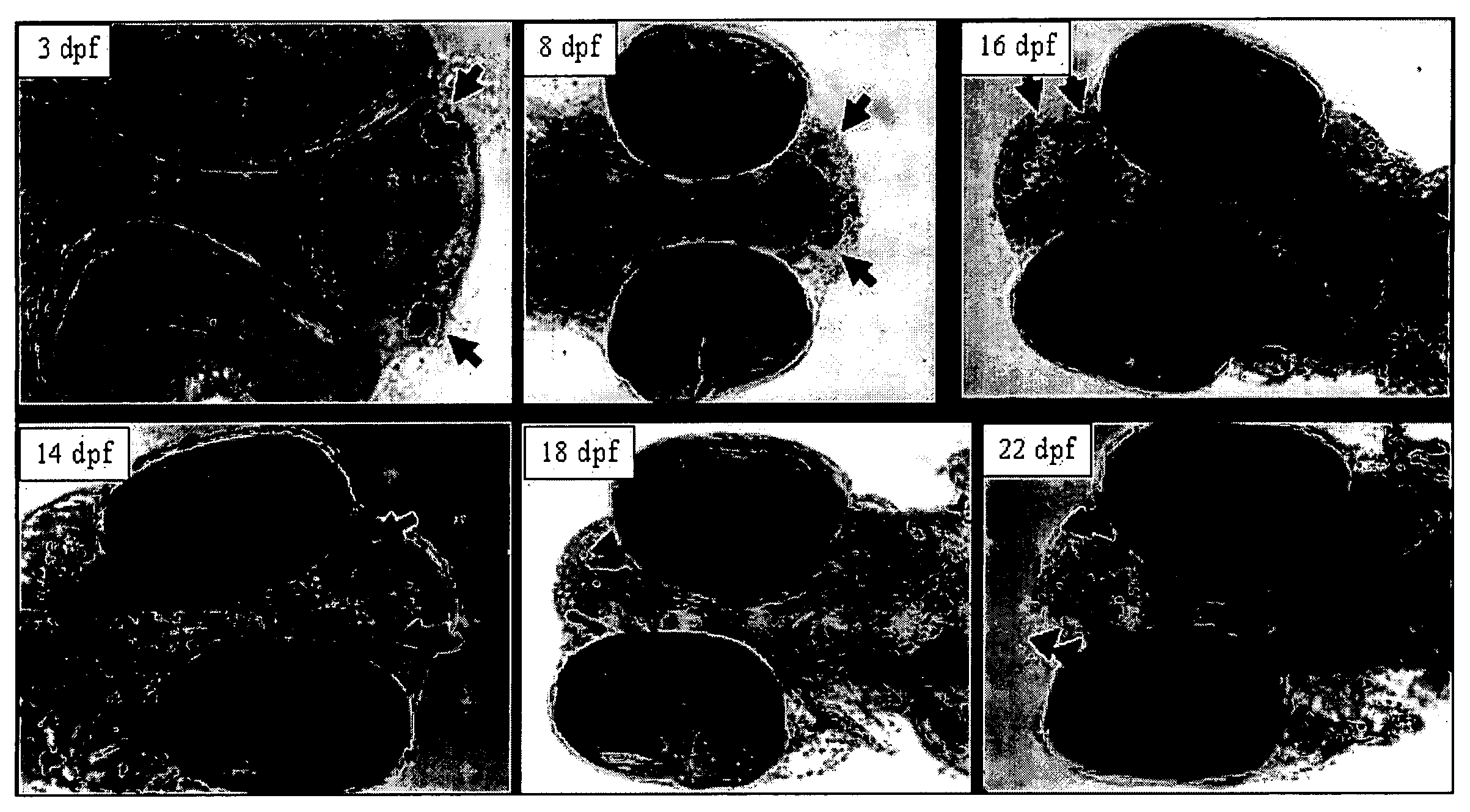
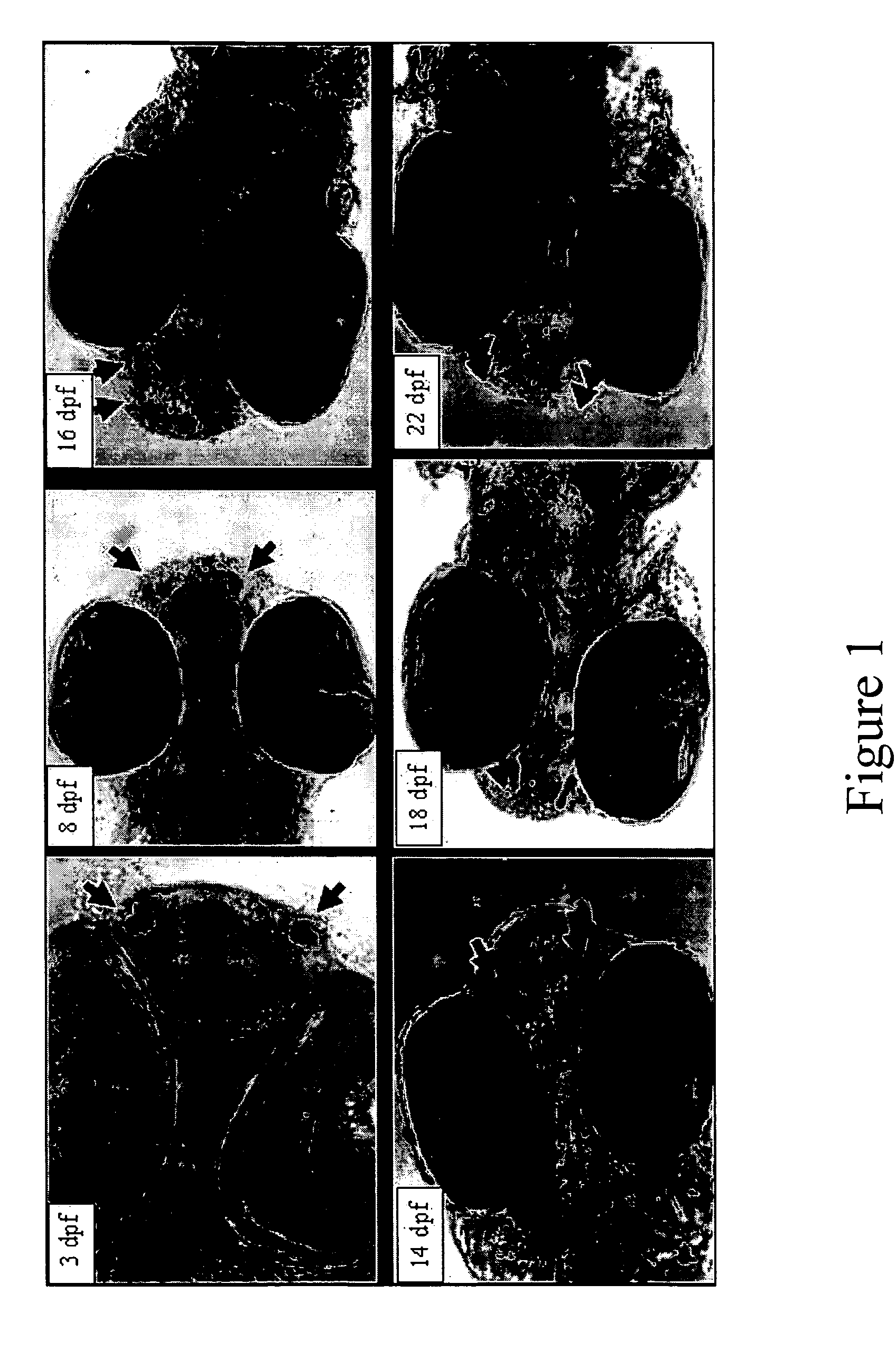
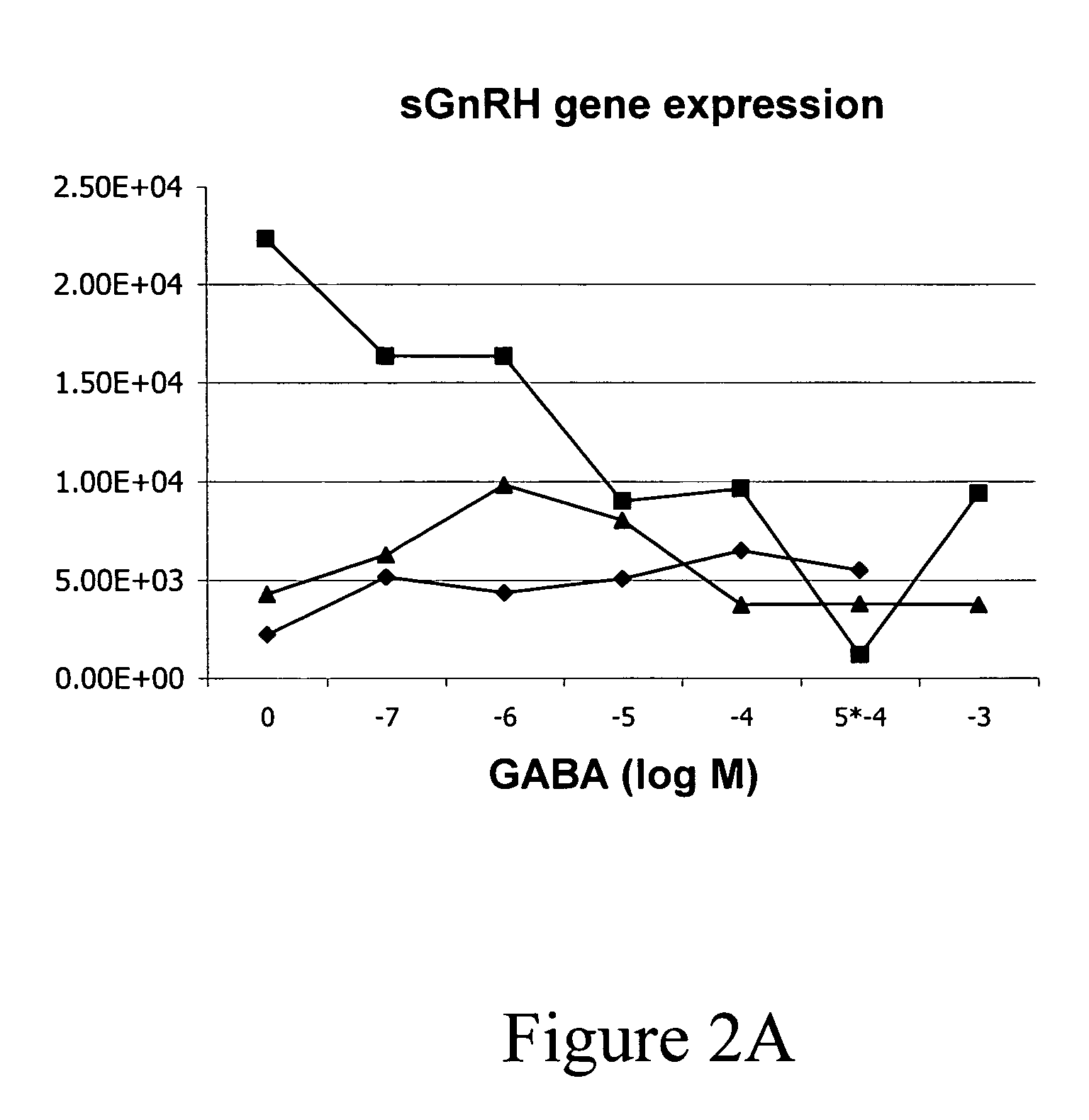
InactiveUS20050132969A1Less gonadMore muscleHormone peptidesPisciculture and aquariaGABA receptor agonistGABA receptor antagonist
The present invention provides for a method for inducing sterility in fish by administering at least one compound that disrupts the establishment of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone system during early development thereby inhibiting sexual maturity in the treated fish. Effective compounds include GABA, GABA receptor agonists, or GABA receptor antagonists.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD +2
Process for the synchronization of ovulation for timed breeding without heat detection
A method for synchronizing ovulation in sows and gilts by a single injection of hormones is disclosed. A hormone, gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), analogues, derivatives, agonists or combinations thereof is administered to an open sow post weaning at a specific time to stimulate ovulation of mature responsive follicles. The sow is then bred, without heat detection, at a specific subsequent timed interval after injection with hormone, with one or two artificial or natural breedings. In gilts, the hormone is injected at a timed interval from onset of estrus or at a specific timed interval following Prostaglandin F2a for those gilts which have been held in a state of pseudopregnancy.
Owner:JBS UNITED +1
Process for the synchronization of ovulation for timed breeding without heat detection
A method for synchronizing ovulation in sows and gilts by a single injection of hormones is disclosed. A hormone, gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH), luteinizing hormone (LH), follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), analogues, derivatives, agonists or combinations thereof is administered to an open sow post weaning at a specific time to stimulate ovulation of mature responsive follicles. The sow is then bred, without heat detection, at a specific subsequent timed interval after injection with hormone, with one or two artificial or natural breedings. In gilts, the hormone is injected at a timed interval from onset of estrus or at a specific timed interval following Prostaglandin F2a for those gilts which have been held in a state of pseudopregnancy.
Owner:THORN BIOSCI
Processes for the preparation of uracil derivatives
The present invention relates to processes and intermediates for preparing Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) receptor antagonists of structure (VI); and stereoisomers and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof.
Owner:NEUROCRINE BIOSCI INC
Method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation and pharmaceutical kit for use in such method
InactiveUS20050235374A1Easy to solveImprove developmentPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsGanirelixCo administration
One aspect of the present invention is concerned with a method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in a mammalian female, said method comprising the co-administration to said female of a substance having follicle stimulating hormone activity (FSH substance) in an amount effective to stimulate multiple follicular development;—gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist in an amount equivalent to a daily subcutaneous dose of at least 0.5 mg ganirelix to prevent a premature LH-surge; and—a LH substance in an amount effective to prevent or suppress symptoms of luteinising hormone (LH) deficiency resulting from the administration of the GnRH antagonist; followed by administering a meiosis and luteinisation inducing substance (ML substance) in an amount effective to stimulate resumption of meiosis and luteinisation, and wherein the LH substance is not obtained from the urine of human females. Another aspect of the to invention relates to a pharmaceutical kit for use in a method of controlled hyperstimulation, which kit comprises:—at least one parenteral or oral dosage unit containing one or more FSH substances in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 50-1500 I.U. FSH;—at least one parenteral dosage unit containing one or more GnRH antagonists in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 0.5-25 mg ganirelix;—at least one parenteral dosage unit containing one or more LH substances in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 50-3000 I.U. recombinant LH; wherein the LH substance is not obtained from the urine of human females.
Owner:ZONE IND DE IOURIETTAZ
Method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation and pharmaceutical kit for use in such method
InactiveUS7815912B2Easy to solveIncrease dosePeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesGanirelixCo administration
One aspect of the present invention is concerned with a method of controlled ovarian hyperstimulation in a mammalian female, said method comprising the co-administration to said female of —a substance having follicle stimulating hormone activity (FSH substance) in an amount effective to stimulate multiple follicular development; —gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) antagonist in an amount equivalent to a daily subcutaneous dose of at least 0.5 mg ganirelix to prevent a premature LH-surge; and —a LH substance in an amount effective to prevent or suppress symptoms of luteinising hormone (LH) deficiency resulting from the administration of the GnRH antagonist; followed by administering a meiosis and luteinisation inducing substance (ML substance) in an amount effective to stimulate resumption of meiosis and luteinisation, and wherein the LH substance is not obtained from the urine of human females. Another aspect of the to invention relates to a pharmaceutical kit for use in a method of controlled hyperstimulation, which kit comprises: —at least one parenteral or oral dosage unit containing one or more FSH substances in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 50-1500 I.U. FSH; —at least one parenteral dosage unit containing one or more GnRH antagonists in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 0.5-25 mg ganirelix; —at least one parenteral dosage unit containing one or more LH substances in an amount equivalent to a subcutaneous dose of 50-3000 I.U. recombinant LH; wherein the LH substance is not obtained from the urine of human females.
Owner:ZONE IND DE IOURIETTAZ
Premature ovulation preventive agent
InactiveUS20090048273A1Low toxicIncrease resistanceBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBuccal administrationBiology
The present invention provides a premature ovulation inhibitor for use in in vitro fertilization or embryo transfer process, which contains a nonpeptidic compound having a gonadotropin releasing hormone antagonistic action. The premature ovulation inhibitor for use in in vitro fertilization or embryo transfer process of the present invention is low toxic, permits oral administration, and has a superior inhibitory effect on premature ovulation in in vitro fertilization or embryo transfer process.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Artificial propagation method of esox reichertii
InactiveCN103222436AShorten spawn timeMature syncClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaBroodstockEsox
The invention discloses an artificial propagation method of esox reichertii, belongs to the cultivation filed of the esox reichertii, and is mainly used for solving the technical problems that the existing natural egg-laying process of the wild esox reichertii is unfocused in egg-laying time, long in egg-laying period, non-synchronous in maturity of male and female parent fishes and low in hatching rate. The artificial propagation method of the esox reichertii comprises the following steps of: sorting parents; and carrying out artificial impregnation after injecting the medicine twice by S-GnRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone)-A, HCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) or DOM (Dimethoxy Mephentermine) in April, so that the artificial propagation of esox reichertii is completed. The artificial propagation method of the esox reichertii disclosed by the invention can be used for enabling the maturity of male and female parent fishes to be synchronous, enabling the egg-laying time to be focused and shortening the egg-laying period by 15-20 days, and also has a fertility rate of 85%-90% and a hatching rate of 60%-70%. The parent fishes are propagated artificially, the propagation success rate of male fishes is 97% and the propagation success rate of the female fishes is 70%-85%.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG RIVER FISHERY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF FISHERIES SCI
Compositions comprising a SARM ad GnRH agonist or a GnRH antagonist, and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060287282A1Reduce morbidityDecreased sexual libidoBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsSelective androgen receptor modulatorAndrogen Receptor Gene
The present invention relates to compositions comprising a selective androgen receptor modulators (SARM) and a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) agonist or a GnRH antagonist, and their use, inter-alia for treating hormone-associated conditions in males and females, which arise as a result of androgen decline, suppression or abrogation, or in treating, suppressing, inhibiting or preventing prostate cancer.
Owner:GTX INCORPORATED
Methods and compositions using gonadotropin hormone releasing hormone
InactiveCN1780634AOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsProstate cancerHormones regulation
The present invention relates to compositions comprising two sustained-release formulations, the first capable of releasing the gonadotropin-releasing hormone component and the second capable of releasing the estrogenic component. Compositions of the present invention can be used for improved androgen ablation therapy of prostate cancer to minimize loss of bone mineral density and frequency and severity of hot flashes by maintaining low adequate estrogen levels during treatment .
Owner:DEBIOPHARM SA
Treatment of polycystic ovarian disease
Agents which increase the levels of human insulin-like growth factor-1 binding protein (h-IGFBP-1), such as an estrogen, are used in conjunction with a gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) analogue in the treatment of PCOD and associated infertility.
Owner:LAB SERONO SA
Pharmaceutical composition
InactiveUS20100160208A1Solution to short lifeReduce dosageAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderMessenger RNAPurine
Owner:ANTISENSE PHARMA GMBH
Inducing sterility in fish by disrupting the development of the GnRH system
InactiveUS7194978B2More muscleLess gonadHormone peptidesPisciculture and aquariaGABA receptor agonistGABA receptor antagonist
The present invention provides for a method for inducing sterility in fish by administering at least one compound that disrupts the establishment of the gonadotropin-releasing hormone system during early development thereby inhibiting sexual maturity in the treated fish. Effective compounds include GABA, GABA receptor agonists, or GABA receptor antagonists.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD +2
Veterinary composition and methods for non-surgical neutering and castration
ActiveUS20150230430A1Great tasteReduction in hormone levelPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsWilms' tumorInverted Terminal Repeat
A method for non-surgical neutering or castration of a non-human mammal for AAV-mediated delivery of an anti-GnRH polypeptide to a non-human animal is described. More particularly, the animal is administered an adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector having an AAV capsid having packaged therein nucleic acid sequences comprising an AAV 5′ inverted terminal repeat (ITR), a sequence encoding a polypeptide which specifically binds gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) under control of regulatory sequences which direct expression of the polypeptide, and an AAV 3′ ITR. A composition comprising the AAV-anti-GnRH may also be used for inhibiting tumor growth in a mammal with a cancer responsive to gonadal steroid hormones.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Livestock synchronous ovulation and fixed-time artificial insemination method
InactiveCN105613423APromote maturationOmit heat detectionAnimal husbandryIntramuscular injectionArtificial insemination
The invention relates to a livestock synchronous ovulation and fixed-time artificial insemination method. The method includes: intramuscularly injecting GnRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone) or analogues thereof to cows in any day of an estrus period, injecting PG (prostaglandin) or analogues thereof after 7-8 days, and injecting the GnRH or the analogues thereof for the second time after 2-3 days. Twice fixed-time artificial insemination in advance or twice fixed-time artificial insemination in delay is carried out respectively according to follicular development conditions of the cows. By regulation of follicular development time of the cows, fixed-time artificial insemination is carried out in relatively fixed estrus time to increase sperm-egg binding probability and the estrus conception rate of the cows, and accordingly reproduction efficiency of the cows is improved. In addition, compared with a conventional OFAI (ovsynch and fixed-time artificial insemination) technology, the livestock synchronous ovulation and fixed-time artificial insemination method has the advantage that the estrus conception rate is increased by 10%-15% due to avoiding of estrus diagnosis before insemination, thereby having promising market application prospect.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com