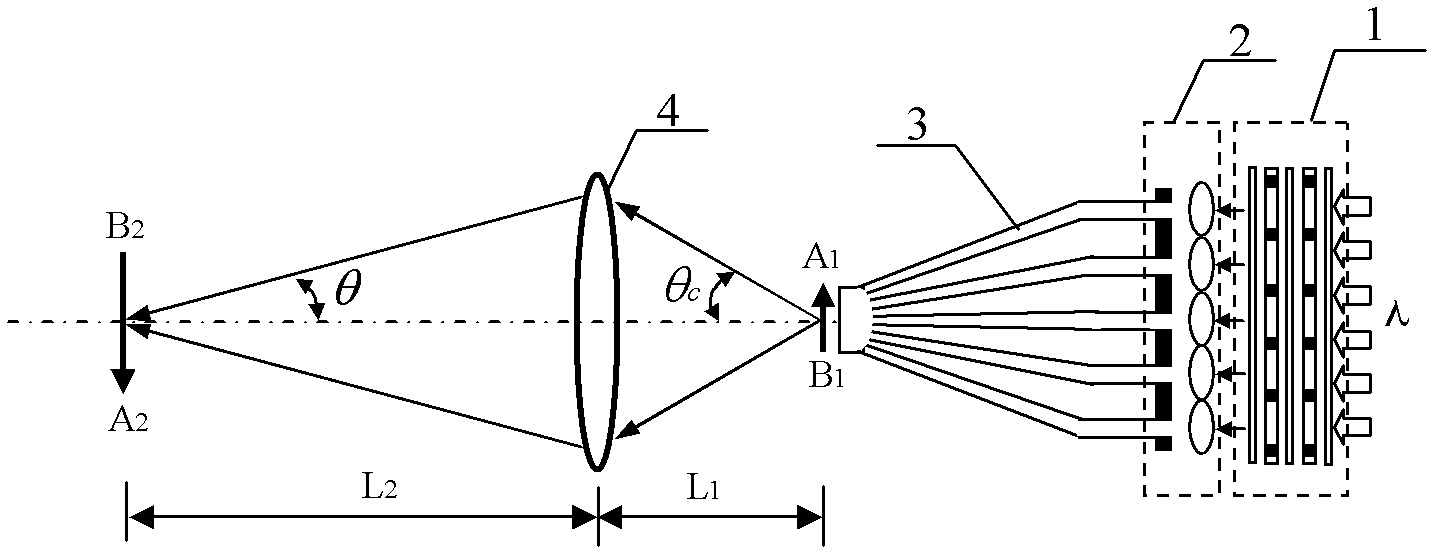
Laser optical tweezer microscope
A technology of microscope and microscopic objective lens, which is applied in the field of micro-optics and nanometers, can solve the problems of precision limitation and difficulty, and achieve the effect of increasing the moving speed, convenient operation and increasing the number of optical tweezers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
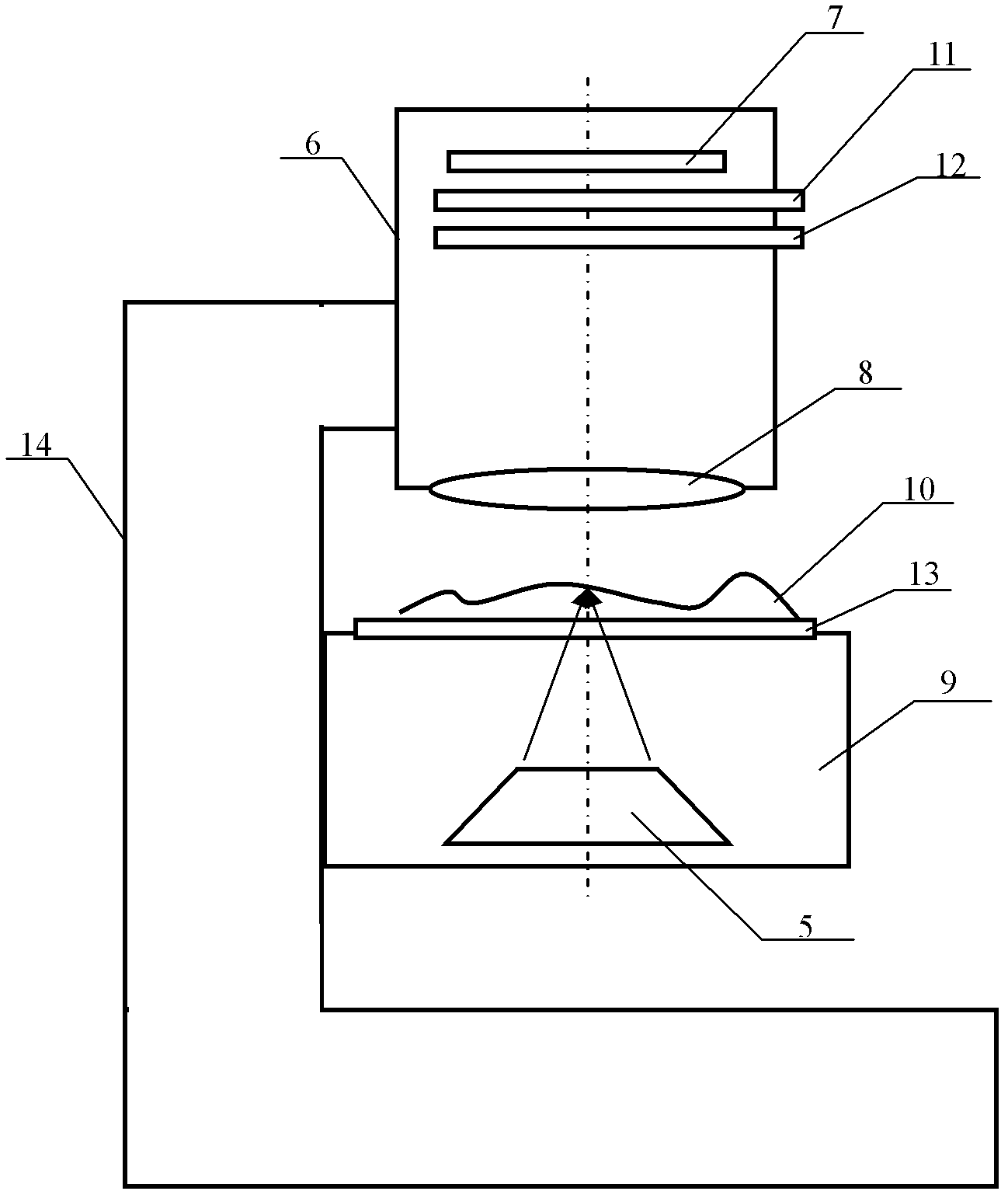
[0030] figure 2 A schematic diagram of the structure of a laser optical tweezers microscope working in reflection mode is given. It includes a lens barrel 6, an image sensor 7, a microscope objective lens 8, a movable stage 9 up and down, a substrate 13, a support 14, and digital optics for generating laser optical tweezers and focusing the optical tweezers on an object 10. The phase conjugation device 5, the lens barrel 6 is fixed on the support 14, the movable stage 9 is connected to the support 14 through the rack, and the substrate 13 is placed on the movable stage 9, which is used for The object 10 placed on the substrate 13 is placed on the bottom of the lens barrel 6 for magnifying and imaging the object 10, and the image sensor 7 for recording the magnified microscopic image is arranged in the lens barrel 6 and positioned at the microscope objective 8. above. Since the digital optical phase conjugation device 5 is fixed together with the stage 9 of the digital optical...
Embodiment 2
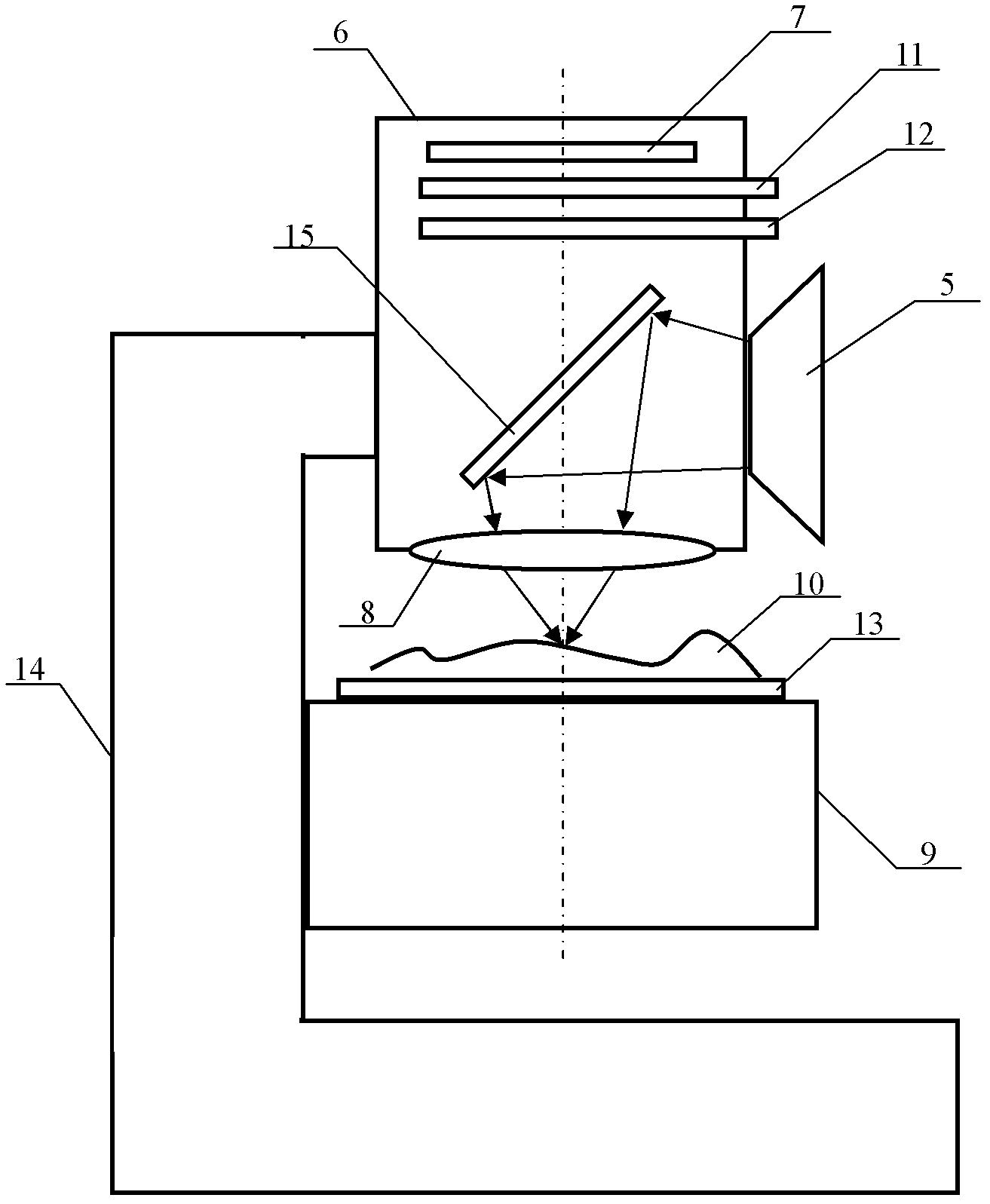
[0036] image 3 A schematic diagram of the structure of a laser optical tweezers microscope working in reflection mode is given, with figure 2 Compared with the laser optical tweezers microscope working in the transmission mode, it also includes a half-mirror 15, and the half-mirror 15 is arranged in the lens barrel 6 and is located between the microscope objective lens 8 and the image sensor 7 , the reflective surface of the half mirror 15 is placed at 45 degrees to the optical axis of the microscope objective lens 8, and the digital optical phase conjugation device 5 is arranged on the side of the lens barrel, so that the laser light produced by the digital optical phase conjugation device 5 The tweezers focus on the object 10 placed on the object-carrying substrate 13 from above after being reflected by the half-mirror 15 and refracted by the microscope objective lens 8 .
[0037] and figure 2 Compared with the arrangement shown, the major difference lies in the focusin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com