Vulcanization and startup method of dehydrogenation catalyst
A technology of dehydrogenation catalyst and sulfurizing agent, which is applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, chemical instruments and methods, metal/metal oxide/metal hydroxide catalyst, etc., which can solve the problems of insufficient catalyst selectivity and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0014] The dehydrogenation catalyst can be prepared by a conventional method, such as using an impregnation method to support the dehydrogenation active metal, and the auxiliary agent can be introduced during the preparation of the alumina carrier and / or by an impregnation method.
[0015] The catalyst of the present invention uses Sn-containing alumina as a carrier, and the dehydrogenation active metal component is generally selected from one or more of platinum, palladium, iridium, rhodium or osmium in the platinum group, and the amount is calculated as the weight of the carrier in terms of simple substance. 0.01% to 2%. The content of Sn is 0.1%-10% of the weight of the carrier in terms of simple substance.
[0016] In the dehydrogenation catalyst with Sn-containing alumina as the carrier, Sn is introduced into the Sn-containing material when the alumina is gelled, and then made into a carrier.
[0017] The specific process and conditions for the preparation and sulfidatio...
Embodiment 1
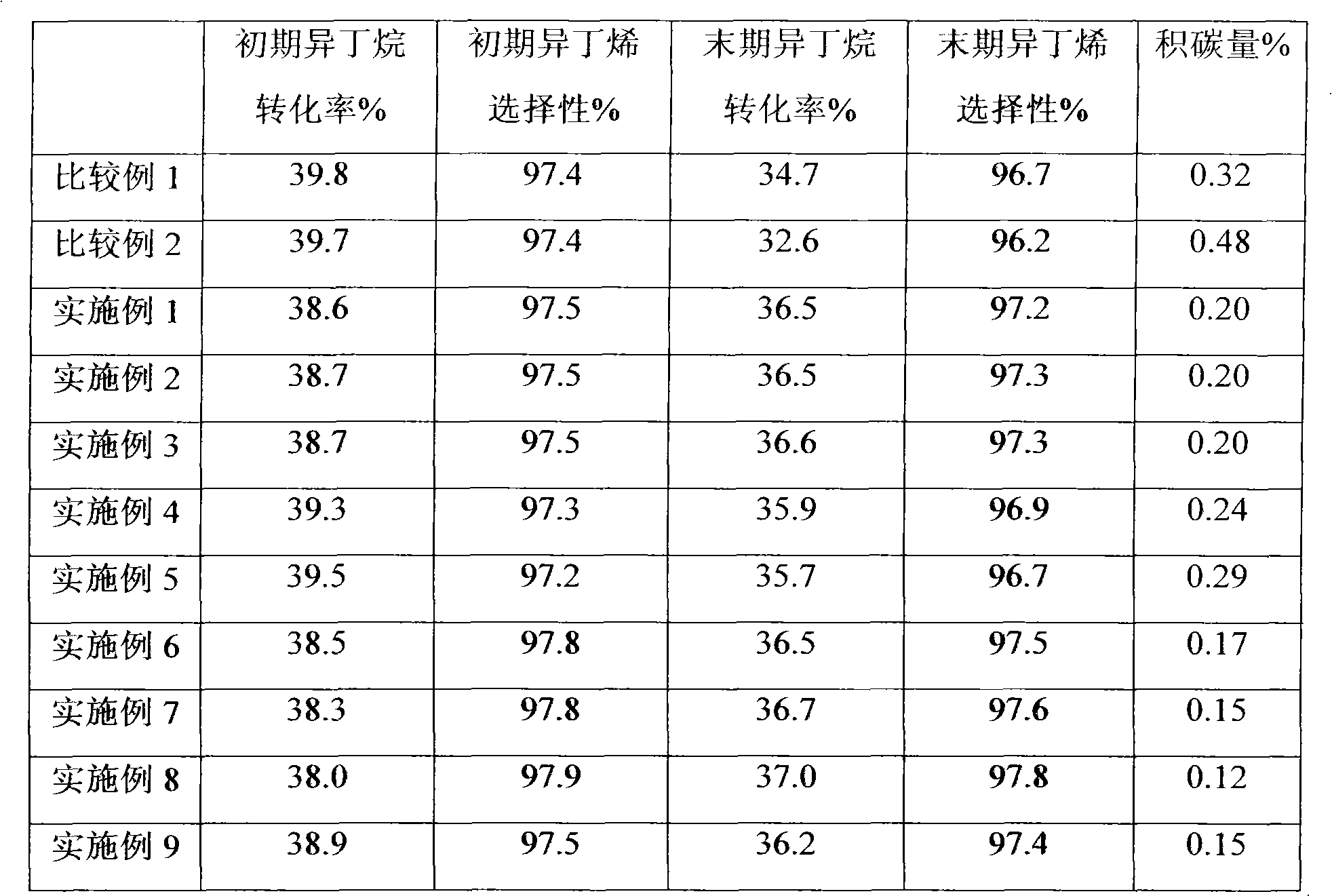
[0036] Catalyst PDH-FY was prepared in the same manner as Comparative Example 1. The molten elemental sulfur is introduced into the PDH-FY catalyst, the amount of elemental sulfur introduced is 120% of the theoretical sulfur demand of the catalyst, and then impregnated with n-butyl acetate solvent, and the amount of elemental sulfur is 25% of the weight of the catalyst. Then treat at 180° C. for 6 hours at normal pressure and in the presence of water vapor, and pass 2 kg of steam per 50 kg of catalyst to obtain the final dehydrogenation catalyst FSHYPDH-1 containing a sulfurizing agent.
[0037] The reduction and dehydrogenation reactions of the catalyst were carried out under the same conditions as in Comparative Example 1. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1.
Embodiment 2
[0039] Catalyst PDH-FY was prepared in the same manner as Comparative Example 1. The n-butyl acetate solvent is uniformly impregnated on the PDH-FY catalyst, and its consumption is 25% of the weight of the catalyst. Then melted elemental sulfur is introduced into the catalyst, and the introduced amount of the elemental sulfur is 120% of the theoretical required sulfur amount of the catalyst. Then treat at 180° C. for 6 hours at normal pressure and in the presence of water vapor, and pass 2 kg of steam per 50 kg of catalyst to obtain the final dehydrogenation catalyst FSHYPDH-2 containing a sulfurizing agent.
[0040] During reduction, the concentration of ammonia in hydrogen was 2.0%, the reduction temperature was 480° C., and the reduction time was 1 hour. Other processes and conditions were the same as in Comparative Example 1. The evaluation results are shown in Table 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com