Method for detecting in-vitro enzymolysis of cross-linked hyaluronic acid by utilizing water-phase gel permeation chromatography
A technology of gel permeation chromatography and cross-linked hyaluronic acid, which can be used in measurement devices, instruments, scientific instruments, etc., and can solve problems such as affecting test results and errors.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0030] Preparation of hyaluronic acid gel
[0031] Dissolve 0.5g of sodium hydroxide in 20ml of water, add 5g of sodium hyaluronate (produced by Shandong Freda Biotechnology Co., Ltd.), stir for 12-14 hours, stir until the sodium hyaluronate is completely dissolved, then add to the reaction system 5g of 1,2,7,8-diepoxyoctane (DEO), stirred quickly and evenly, and reacted at 25°C for 24 hours. The reaction was terminated with 2mol / L hydrochloric acid, and the pH was adjusted to about 5. At the same time, the water in the reaction system was distilled off at 40°C and a vacuum of 13.3Kpa. When the distilled water reached 50mL, the vacuum distillation was stopped. Soak with 200mL sodium hydroxide solution containing 30% ethanol with pH=8-9 for 3 times to neutralize the hydrochloric acid of the gel. Transfer the neutralized gel into a vacuum drying oven, and dry it at 60° C. and 40 Kpa for 10 hours to solidify and shape the gel. The water absorption rate of the gel is 45 times. T...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Enzymatic hydrolysis experiment of cross-linked hyaluronic acid microparticles and molecular weight detection by simultaneous aqueous gel permeation chromatography
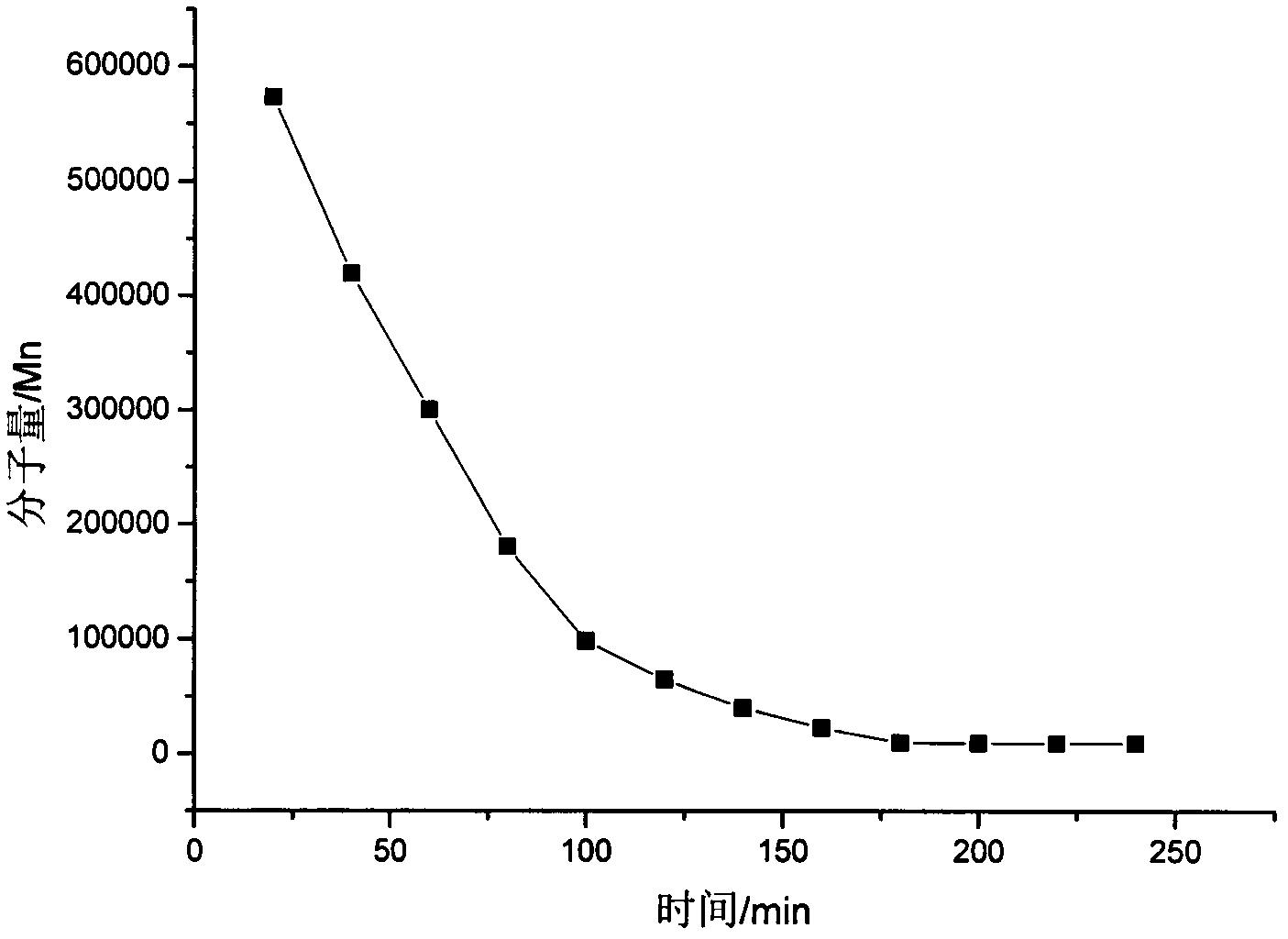
[0034] Take 1 mL of the micro-particle cross-linked hyaluronic acid prepared in Example 1 in a colorimetric tube, add 300 units of hyaluronidase (HAase), dilute to 2 mL with water, and place in a constant temperature water bath shaker at 37 ° C. In the middle, start timing after dilution, and start from the 20th minute, take 50 μL of supernatant with a micro syringe every 20 minutes, place the taken out supernatant in an ice-water bath and cool it down to below 5°C rapidly to inhibit hyaluronic acid Enzyme activity. Take the enzymatic hydrolysis supernatant within 4 hours, and detect the molecular weight of the supernatant at different time periods by aqueous gel permeation chromatography (GPC). When the molecular weight tends to a constant, it can be determined that the enzymatic hydrolysis of the product ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com