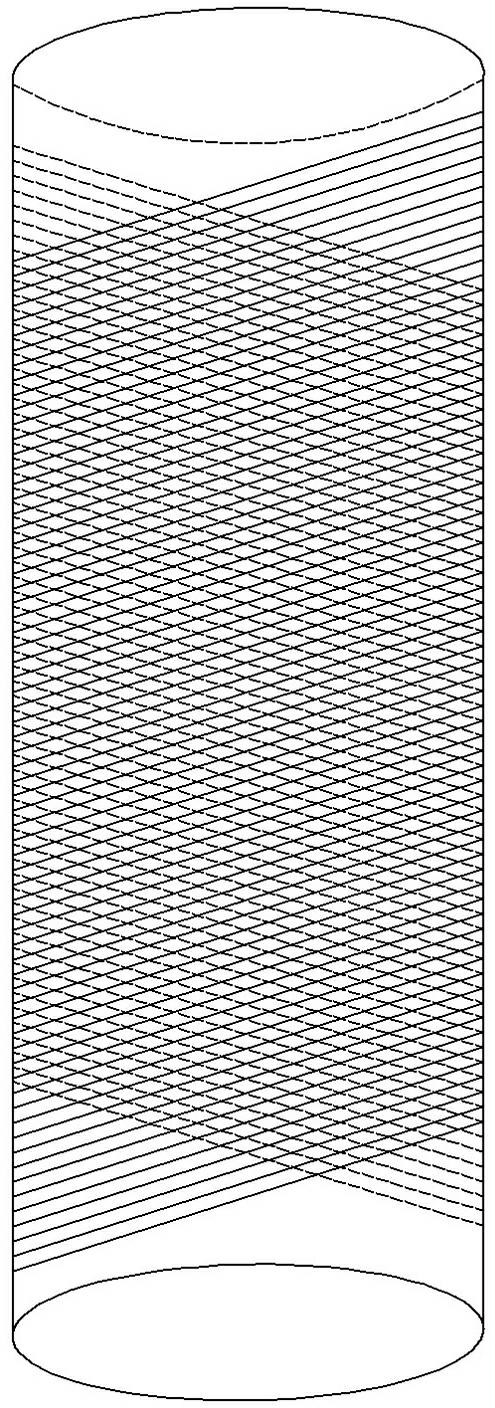
Manufacturing method for printing rotary screen
A technology for printing a rotary screen and a production method, which is applied in the directions of printing and printing plate preparation, and can solve the problems of low tensile strength of the rotary screen, short service life of the rotary screen, and low opening rate of the rotary screen.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Prepare 60 purpose circular screens, the method is as follows:
[0032] Stainless steel microwires with a diameter of 30 microns are wound on the PVC cylinder in the warp and weft direction at an interval of 390 microns to form a square grid. After chemical degreasing, hot and cold water washing, they are placed in the plating tank for nickel plating. The thickness of the coating Take it out when it reaches 60 microns, wash it with water, and take it off the net. The opening rate of the circular net made in this way is 40.7%, which is far greater than the 12-14% of the 60 mesh prepared by the existing technology.
[0033] 1. Chemical degreasing: The bath composition and working conditions are as follows:
[0034]
[0035] 2. Hot and cold water washing: first rinse with hot water (40-50°C) to prevent residual degreasing fluid on the grid surface, and then rinse with cold water (room temperature).
[0036] 3. Plating solution formula and process conditions:
[0037] ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] Prepare a 165-purpose circular screen, the method is as follows:
[0043] Copper alloy microwires (brass alloy microwires) with a diameter of 30 microns are wound on the PVC cylinder in a warp and weft manner at an interval of 123 microns to form a square grid. After chemical degreasing, they are washed with hot and cold water, and then Pickling removes the oxide film produced on the surface of the copper alloy, puts it into the plating tank for electroplating nickel, takes it out when the coating reaches 22 microns, washes it with water, and takes off the mesh. The opening rate of the rotary mesh is 27%, which is greater than that of the existing technology 19% of 165ED.
[0044] 1. Chemical degreasing: The bath composition and working conditions are as follows:
[0045]
[0046] 2. Pickling formula and working conditions:
[0047]
[0048] 3. Washing in hot and cold water: Same as Example 1.
[0049] 4. Plating solution formula and process conditions:
[005...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Prepare 60 mesh circular screens, the specific method is as follows:
[0056] After the nylon wire with a diameter of 30 microns is metallized by magnetron sputtering, it is wound on the PVC cylinder in the way of warp and weft at an interval of 390 microns to form a square grid. After chemical degreasing, hot and cold water washing Put it in the plating tank for electroplating nickel, take it out when the thickness of the coating reaches 60 microns, wash it with water, and take it off the screen. The opening rate of the circular screen made in this way is 40.7%, which is far greater than the 12-14% of the 60-mesh prepared by the existing technology. .
[0057] 1. Chemical degreasing: same as Example 1.
[0058] 2. Washing in hot and cold water: Same as Example 1.
[0059] 3. Electroplating formula and process: same as example 1.
[0060] 4. Washing
[0061] 5. Take off the net, dry and cut.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com