ECO (Engineering Change Order) optimization method of multiplier based on standard cell library extension
A standard cell library, standard cell technology, applied in instruments, special data processing applications, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of inconvenient design automation, limited drive capability, long design time, etc., to achieve design automation, improve performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] A kind of ECO optimization method based on the multiplier of standard cell library expansion, specifically:
[0039] Step (1). Generate the layout of the expansion unit, the specific method is:
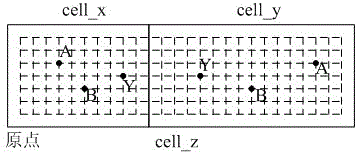
[0040] First, splicing two cells cell_x and cell_y of the same type in the standard cell library to obtain the extension cell cell_z, such as figure 1 shown. Standard cells are equal in height and unequal in width. Place cell_x at the origin, and the direction is R0; place cell_y close to the right of cell_x, and the placement direction is mirrored along the y axis. This placement method facilitates wiring. After placement, the power / ground rails of cell_x and cell_y are automatically spliced together, such as figure 1 shown.
[0041] Then, use metal to connect the same ports of the standard unit as the ports of the expansion unit. cell_x and cell_y are the same type of unit, with the same port A, B, Y, such as figure 1 shown. Connect the ports A, B, and Y correspo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com