Method for irrigating rice by appropriately utilizing rainwater
A technology of rice and water depth, applied in the fields of rice cultivation, botanical equipment and methods, watering devices, etc., can solve problems such as inexhaustible science, large amount of irrigation, delayed flooding, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0098] Rain-appropriate irrigation mode for flat land.
[0099] Field surface improvement and characteristics: The rice field is conventionally gridded, the field surface is flat, and the height of the ridge is 35-45cm.
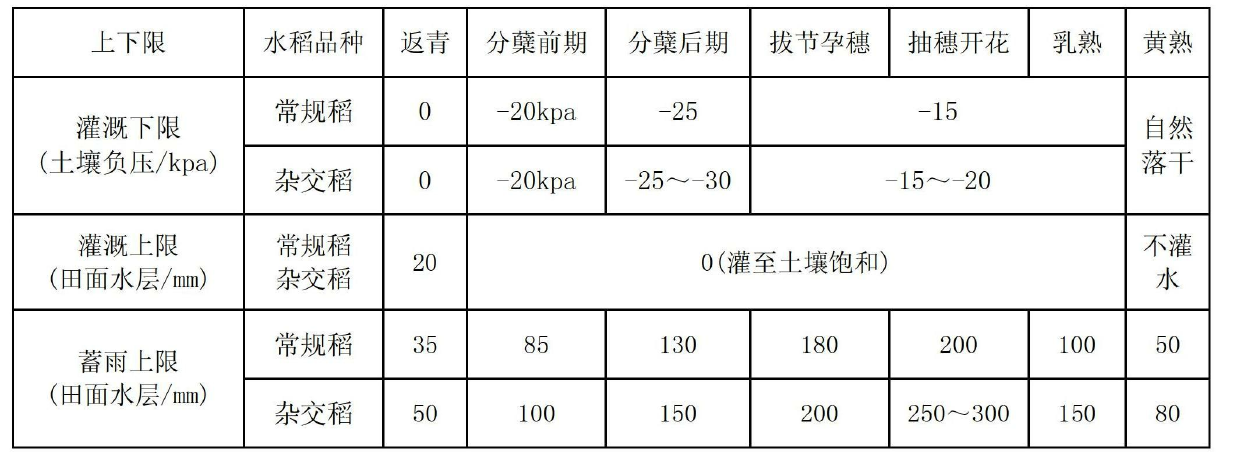
[0100] Field moisture control: Field moisture control indicators are related to rice varieties, soil permeability, groundwater level, etc. See Table 1 for detailed control indicators.
[0101] It should be noted:
[0102] 1. The soil texture is different. The soil water potential is the same at the lower limit of irrigation, but the soil water content is different. Here, the soil water potential is uniformly expressed. In actual operation, the corresponding soil water content can be determined by checking the soil moisture characteristic curve. For medium loam soil, when the soil water potential is -15 to -20kpa, the soil water content is about 80% to 90% of the field water holding capacity.
[0103] 2. At the later stage of rice tillering, attention should...
Embodiment 2
[0120] Rain-adapted irrigation mode for furrows and furrows.
[0121] Field surface improvement and characteristics: rice field with regular grid, ridge height 35-45cm, ditch width 0.2m, ditch depth 0.2-0.25m. There is no need to dig another field irrigation and drainage ditches; the furrow width between ditches is about 3.0m, and should not be less than 2.0m (too much land occupation), nor greater than 4.0m (unsuitable for water control in the furrow).
[0122] Field Moisture Control:
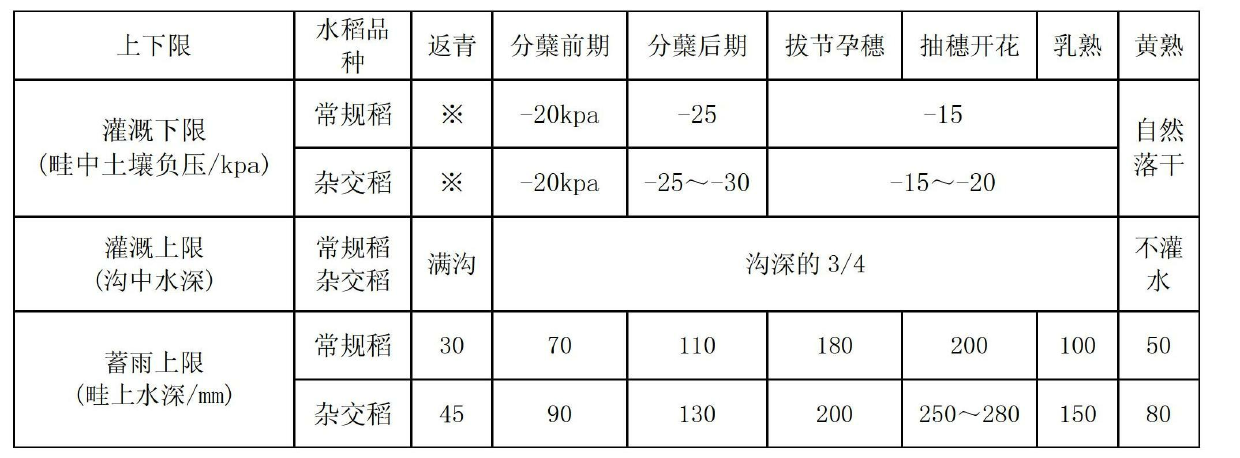
[0123] Field moisture control indicators are related to rice varieties, soil permeability, groundwater level, etc. See Table 2 for detailed control indicators.
[0124] It should be noted:
[0125] a. The lower limit of field irrigation in the rain-appropriate irrigation mode of furrows and furrows is controlled by the soil moisture between the furrows. The soil texture is different, and the soil water potential is the same at the lower limit of irrigation, but the soil water content is dif...
Embodiment 3
[0145] Straw mulching rain-appropriate irrigation mode.
[0146] Field surface improvement and characteristics: rice fields are conventionally gridded, the ground is flat, and the height of the ridge is 35-45cm. Break wheat or rice straw into 10cm lengths, and spread them evenly on the field surface for about 2 to 3cm. It can be laid before transplanting or during the greening period.
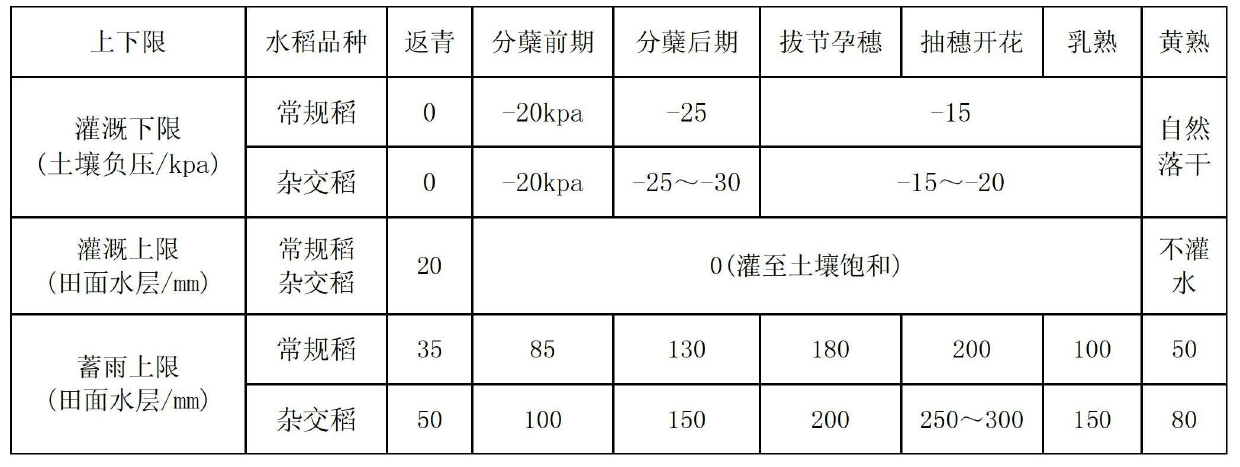
[0147] Field moisture control: Field moisture control indicators are related to rice varieties, soil permeability, groundwater level, etc. See Table 3 for detailed control indicators.
[0148] It should be noted:
[0149] a. The soil texture is different. The soil water potential is the same at the lower limit of irrigation, but the soil water content is different. Here, the soil water potential is uniformly expressed. In practice, the corresponding soil water content can be determined by checking the soil moisture characteristic curve. For medium loam soil, when the soil water potential is -...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com