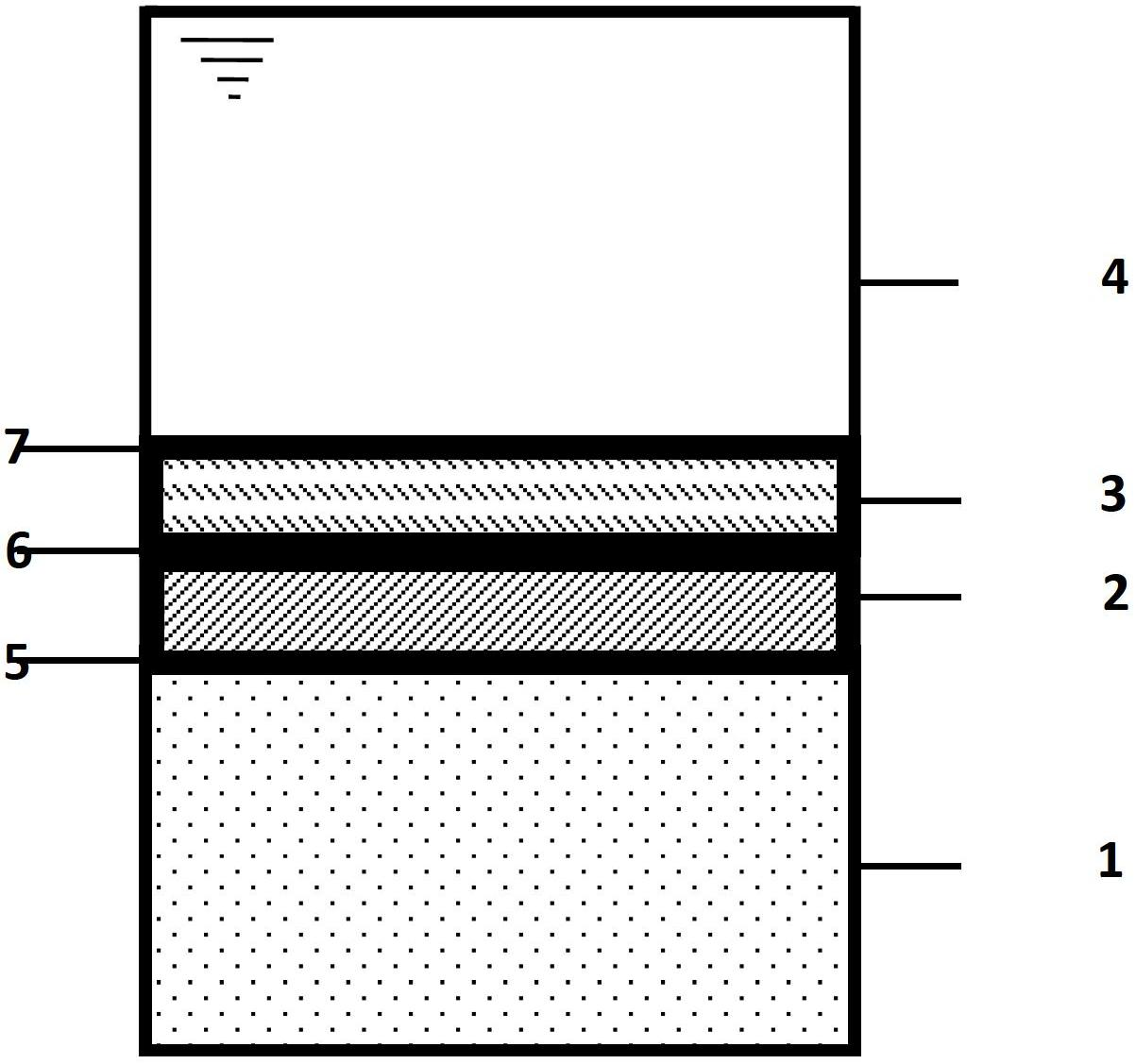
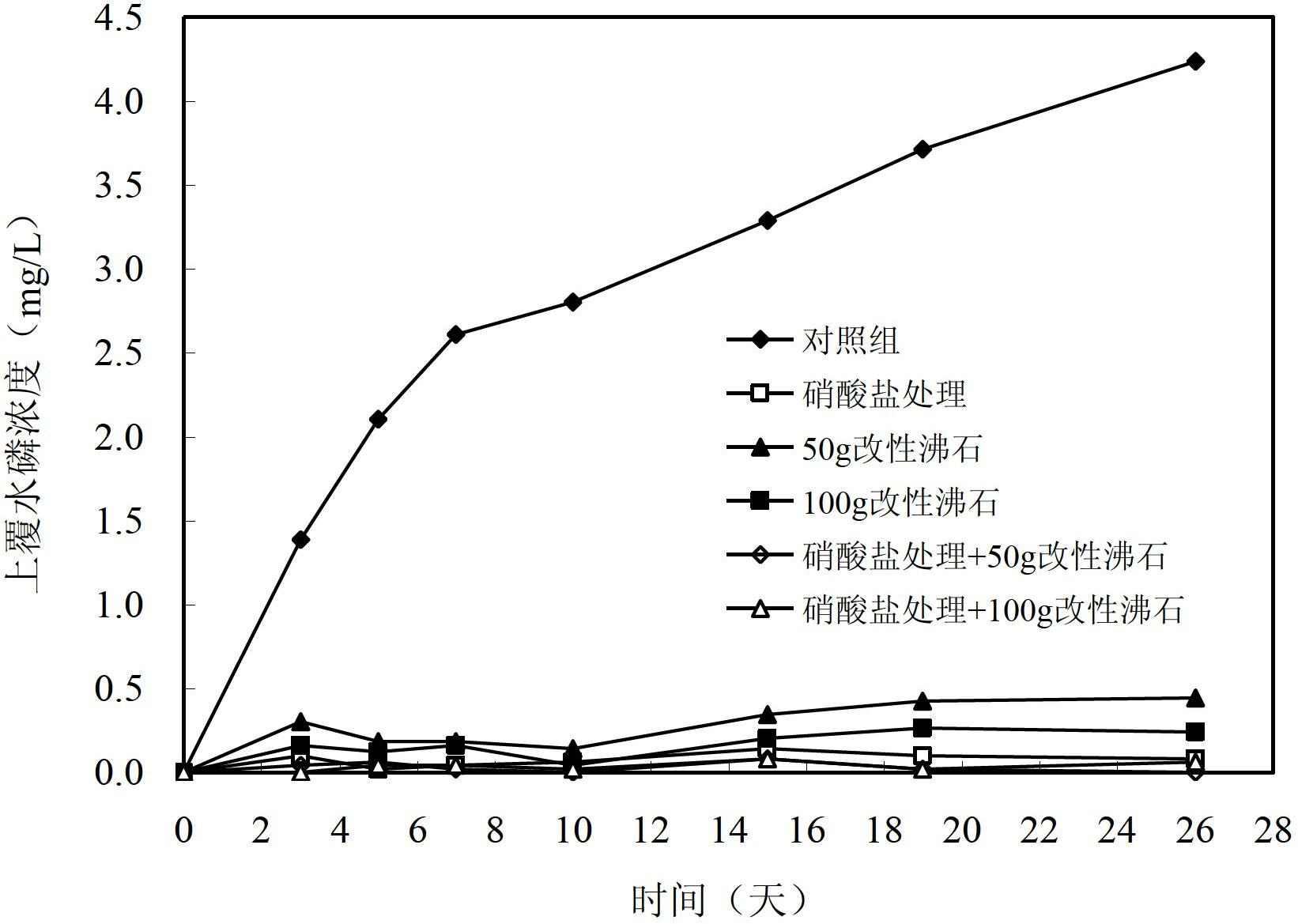
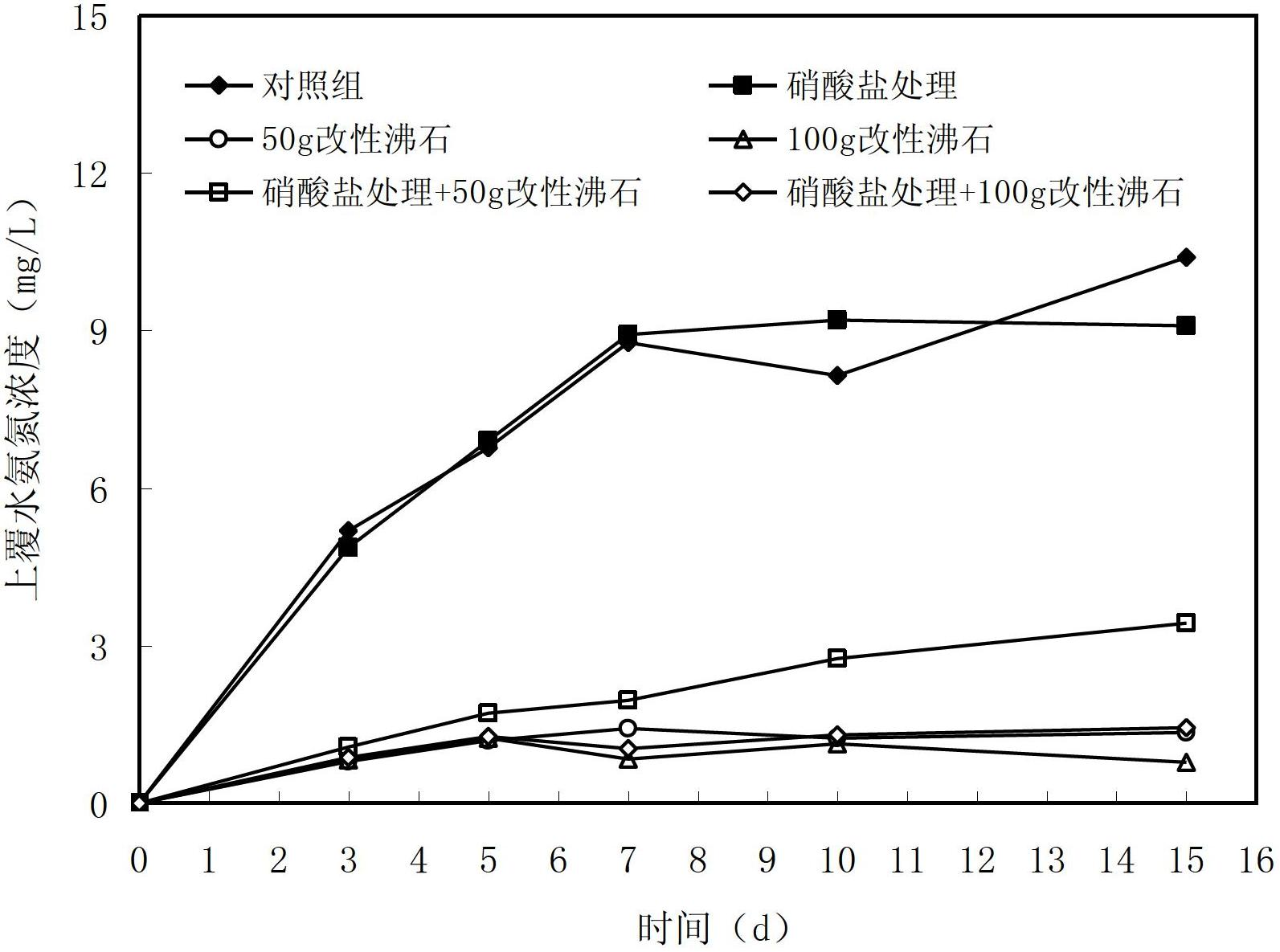
In-situ restoring method of bottom mud polluted by surface water body
A water pollution and in-situ remediation technology, applied in water/sludge/sewage treatment, sludge treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve obstacles, reduce service life, unfavorable degradation and removal of sediment organic pollutants, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of inhibiting migration, reducing the proportion, and replacing it regularly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] (1) Take 62.5g of natural zeolite that has been washed with distilled water, dried and passed through an 80-mesh sieve in a 1L conical flask, and pipette 500mL of cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) with a concentration of 50mmol / L After the stock solution was fully mixed with zeolite, it was placed in a constant temperature water area at 40°C and oscillated at 150rpm for 2 days. The concentration of CPB in the supernatant was analyzed by ultraviolet spectrophotometry (λ=259nm), and the equilibrium concentration was calculated according to the standard curve of CPB. The adsorption amount of CPB is 359 mmol / kg zeolite. Finally, the CPB modified zeolite was washed with distilled water until no bromide ions were detected in the cleaning supernatant, and then placed in an oven at 50° C. for blast drying. After cooling, the CPB modified zeolite was obtained. Repeat the above process 8 times to collect all CPB modified zeolites for later use.
[0037] (2) Collect surface sediment ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] (1) Take 62.5g of natural zeolite that has been washed with distilled water, dried and passed through an 80-mesh sieve in a 1L conical flask, and pipette 500mL of cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) with a concentration of 50mmol / L After the stock solution was fully mixed with zeolite, it was placed in a constant temperature water area at 40°C and oscillated at 150rpm for 2 days. The concentration of CPB in the supernatant was analyzed by ultraviolet spectrophotometry (λ=259nm), and the equilibrium concentration was calculated according to the standard curve of CPB. The adsorption capacity of CPB is 334 mmol / kg zeolite. Finally, the CPB modified zeolite was washed with distilled water until no bromide ions were detected in the cleaning supernatant, and then placed in an oven at 50° C. for blast drying. After cooling, the CPB modified zeolite was obtained. Repeat the above process 8 times to collect all CPB modified zeolites for later use.
[0042] (2) Collect surface sedimen...
Embodiment 3
[0046](1) Take 62.5g of natural zeolite that has been washed with distilled water, dried and passed through an 80-mesh sieve in a 1L conical flask, and pipette 500mL of cetylpyridinium bromide (CPB) with a concentration of 50mmol / L After the stock solution was fully mixed with zeolite, it was placed in a constant temperature water area at 40°C and oscillated at 150rpm for 2 days. The concentration of CPB in the supernatant was analyzed by ultraviolet spectrophotometry (λ=259nm), and the equilibrium concentration was calculated according to the standard curve of CPB. The adsorption amount of CPB is 359 mmol / kg zeolite. Finally, the CPB modified zeolite was washed with distilled water until no bromide ions were detected in the cleaning supernatant, and then placed in an oven at 50° C. for blast drying. After cooling, the CPB modified zeolite was obtained. Repeat the above process 8 times to collect all CPB modified zeolites for later use.
[0047] (2) Collect surface sediment f...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com