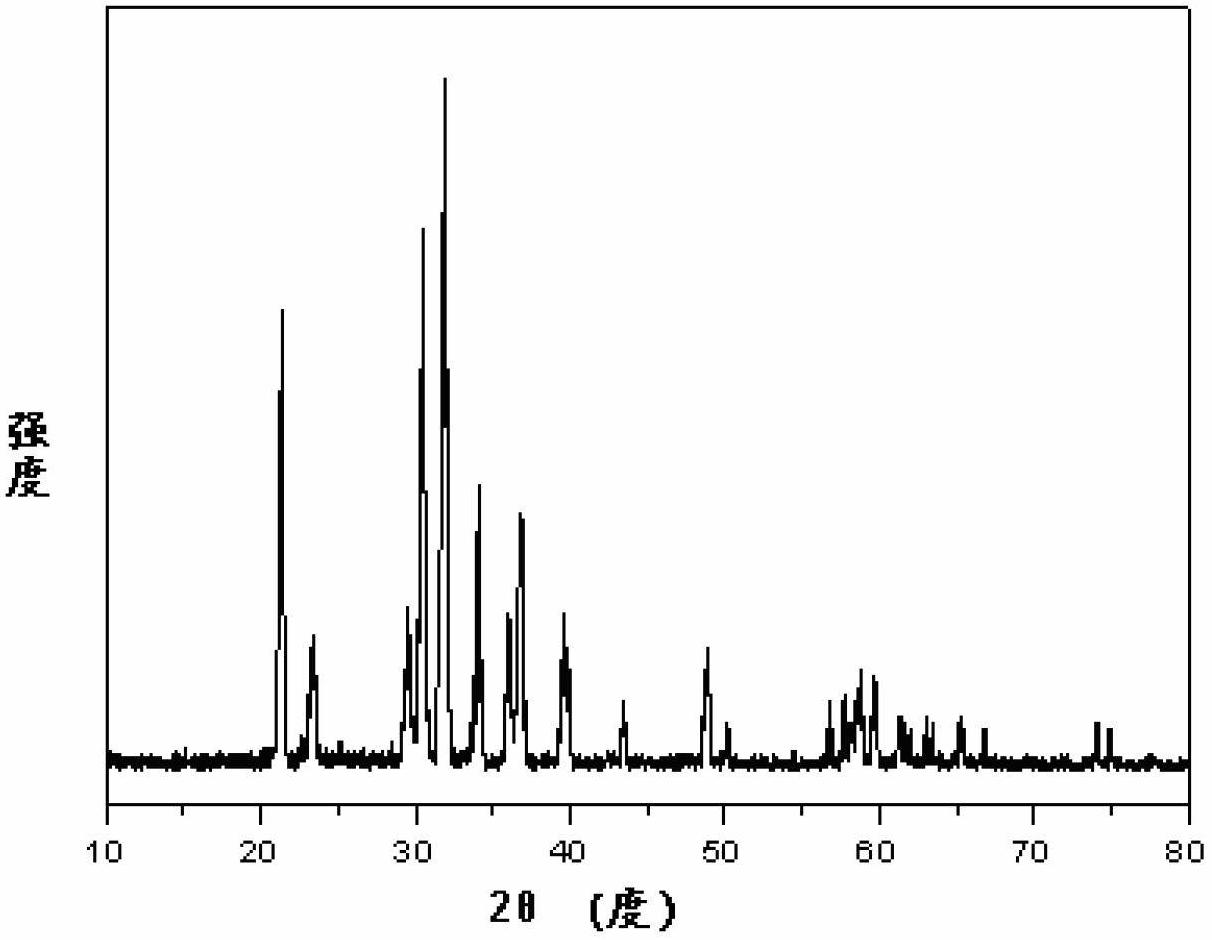
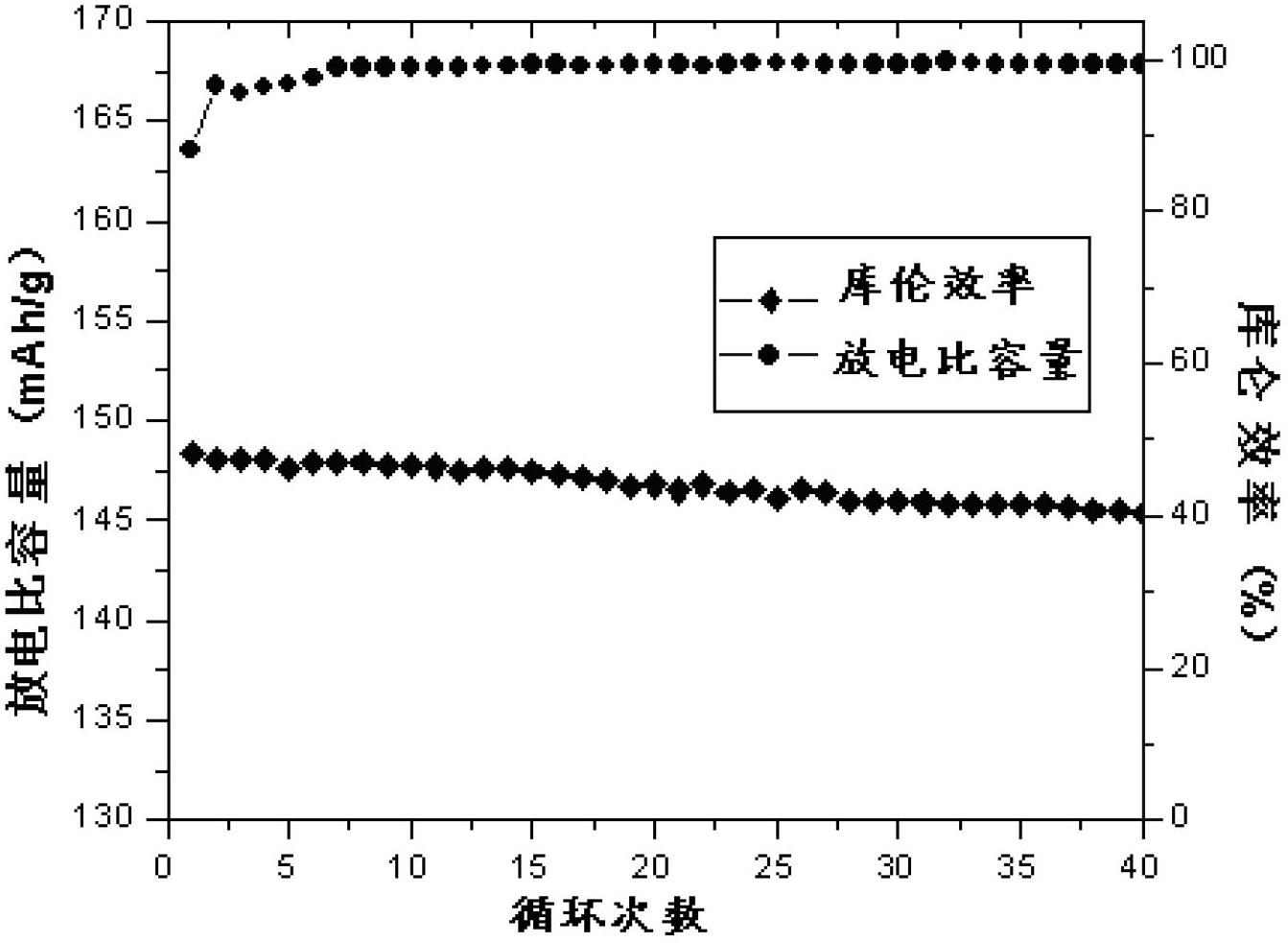
Method for recovering valuable metal from nickel cobalt lithium manganate batteries and positive pole materials
A technology of nickel cobalt lithium manganate and valuable metals, applied in the field of waste power battery recycling, can solve problems such as inconsistent proportions, and achieve the effects of low cost, simple process and environmental friendliness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
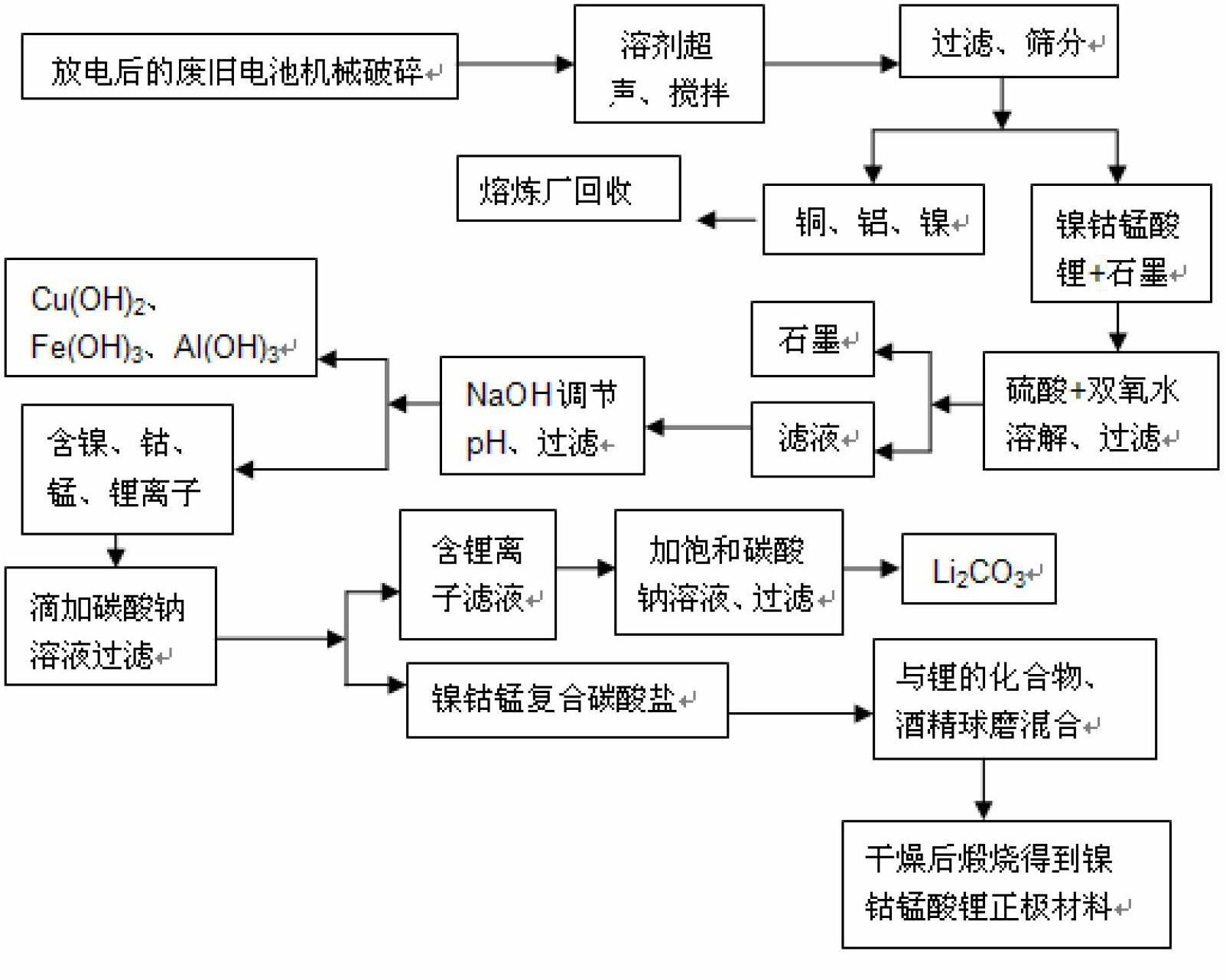
[0043] This embodiment provides a method for recovering valuable metals from waste nickel-cobalt lithium manganese oxide batteries, which includes the following steps:
[0044] S1: Sorting waste nickel-cobalt lithium manganese oxide batteries, and using waste nickel-cobalt lithium manganese oxide batteries containing nickel, cobalt, and manganese in a mass ratio of 1:1:1 as recycling materials.
[0045] S2: Discharge the above-mentioned recycled raw materials and remove the outer packaging and shell of the battery with the help of a shearing machine, take out the battery cell, and crush the battery cell until the area of the cell fragment is less than or equal to 5cm 2 .
[0046] S3: Soak the cell fragments in N,N-dimethylformamide, wherein the solid-liquid ratio of the cell fragments to N,N-dimethylformamide is 20g / L, and at the same time, treat with mechanical stirring and ultrasonic oscillation for 2 hours , to obtain a solid-liquid mixture.
[0047] S4: Filtrate the so...
Embodiment 2
[0062] This embodiment provides a method for recovering valuable metals from waste nickel-cobalt lithium manganese oxide batteries, which includes the following steps:
[0063] S1: Sorting waste nickel-cobalt lithium manganese oxide batteries, and using waste nickel-cobalt lithium manganese oxide batteries containing nickel, cobalt, and manganese in a mass ratio of 2:1:2 as recycling materials.
[0064] S2: Discharge the above-mentioned recycled raw materials and remove the outer packaging and casing of the battery with the help of a shear, take out the battery cell, and crush the battery cell until the area of the cell fragment is less than or equal to 4cm 2 .
[0065] S3: Soak the cell fragments in N-methylpyrrolidone, wherein the solid-to-liquid ratio of the cell fragments to N-methylpyrrolidone is 60 g / L, while mechanically stirring and ultrasonically oscillating for 0.5 h to obtain a solid-liquid mixture.
[0066] S4: Filtrate the solid-liquid mixture obtained in step ...
Embodiment 3
[0076] This embodiment provides a method for recovering valuable metals from waste nickel-cobalt lithium manganese oxide batteries, which includes the following steps:
[0077] S1: Sorting waste nickel-cobalt lithium-manganese oxide batteries, and using waste nickel-cobalt lithium-manganese oxide batteries containing nickel, cobalt, and manganese in a mass ratio of 5:2:3 as recycling materials.
[0078] S2: Discharge the above-mentioned recycled raw materials and remove the outer packaging and casing of the battery with the help of a shearing machine, take out the battery cell, and crush the battery cell until the area of the cell fragment is less than or equal to 3cm 2 .
[0079] S3: Soak the cell fragments in a mixture of N,N-dimethylformamide and N-methylpyrrolidone with a mass ratio of 1:1, wherein the solid-liquid ratio of the cell fragments to the mixture is 100g / L , and simultaneously stirred and ultrasonically oscillated for 3 h to obtain a solid-liquid mixture.
...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com