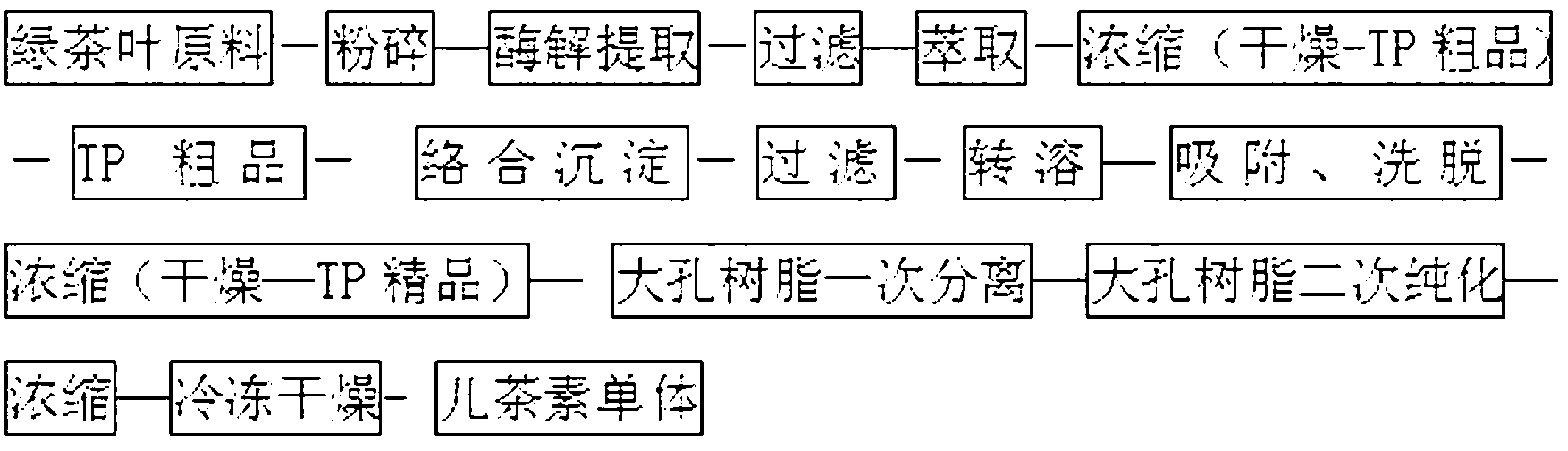
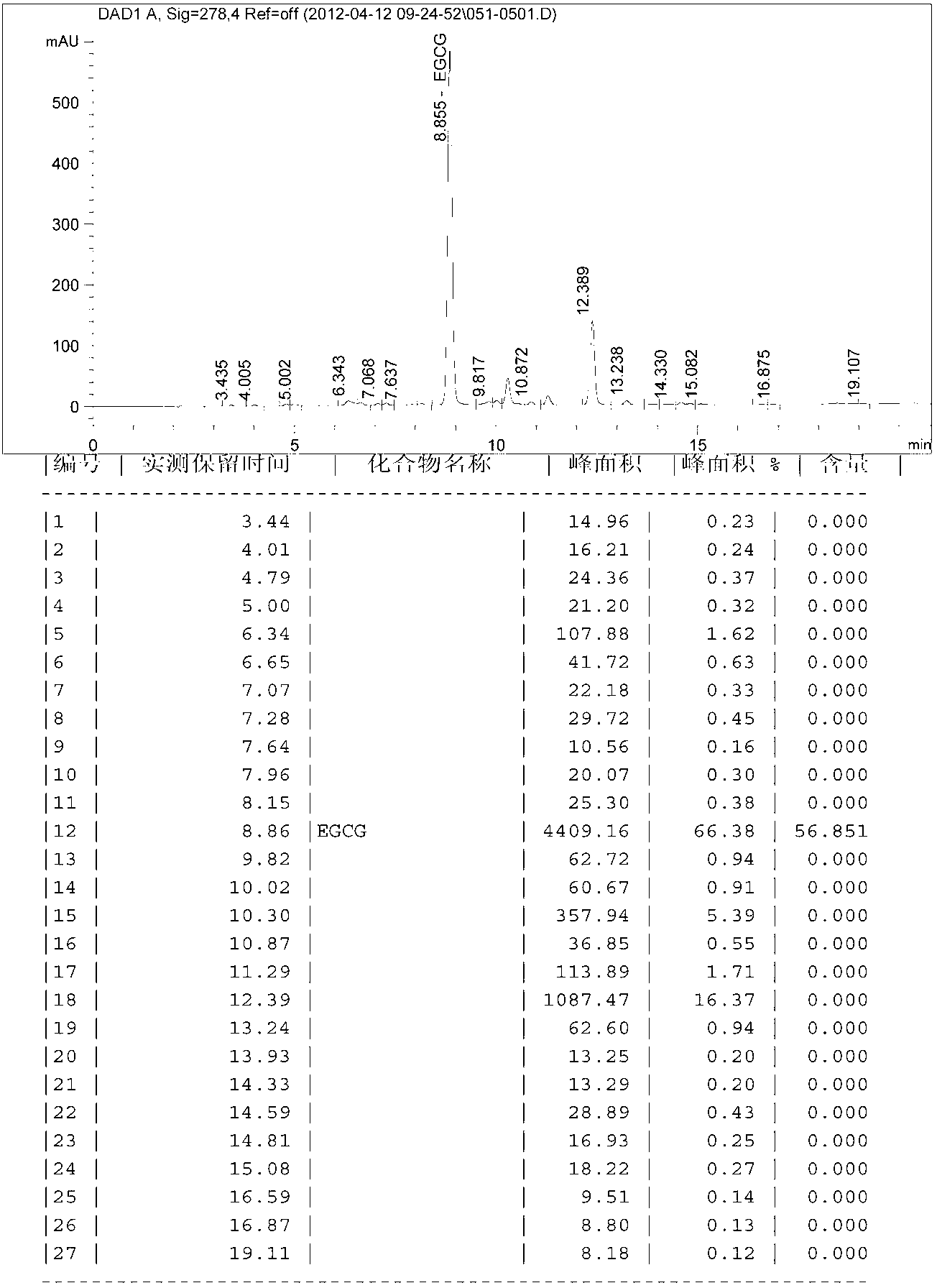
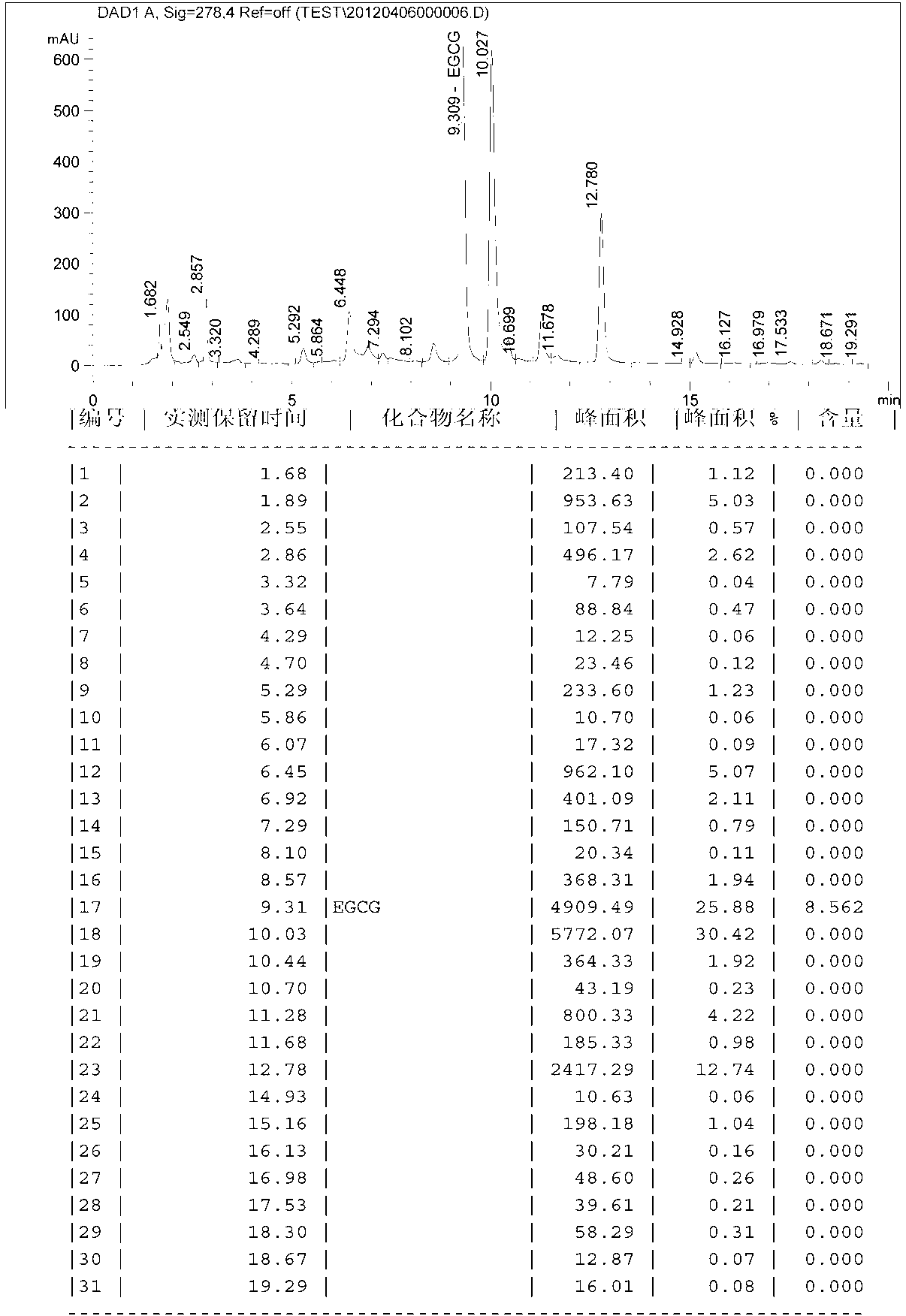Method for preparing high-purity monomer epigallocatechin gallate from processed leftovers of tea leaves
A technology for leftovers and catechins, applied in the direction of organic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of poor separation effect, inability to form a process, ideal yield, etc., and achieve the effects of high product purity, less equipment, and elimination of chloroform residues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0079] Dry tea leftovers (green tea, not black tea), 100g, crushed into 50 mesh, add 2000ml of water, warm to 60℃ soak, adjust PH=6, add a mixed enzyme composed of cellulase, protease and pectinase (Ratio 1:1:1), the compound enzyme dosage is 0.5% of the dry weight of the tea, stirred for 60 min, filtered, and repeated extraction 3 times. The combined filtrate was extracted with ethyl acetate and then concentrated and dried in vacuo. 21.8 g of tea polyphenols with a content of 18.1% were obtained. According to the dry tea containing 30% of tea polyphenols and 22% of catechins, the extraction rate of tea polyphenols is 13.2%. The content of catechins is 8.1%, and the extraction rate is 8%.
Embodiment 2
[0081] Dry fresh tea leaves at 60°C, take 100g of dry weight, smash into 20 meshes, add 1000ml of water, warm to 40°C and soak, adjust PH=3, add mixed enzyme composed of cellulase, protease and pectinase (proportion 5:0.1:5), the dosage of the complex enzyme is 0.1% of the dry weight of the tea, stir for 90min, filter, and repeat the extraction 3 times. The combined filtrate is extracted with ethyl acetate and then concentrated and dried in vacuo. 34.6 g of tea polyphenols with a content of 17.5% were obtained. According to the dry tea containing 36% of tea polyphenols and 28% of catechins, the extraction rate of tea polyphenols is 16.8%. The content of catechin is 7.6%, and the extraction rate is 9.4%.
Embodiment 3
[0083] 100g of dry tea leaves the same as in Example 1, crushed into 80 meshes, added 1500ml of water, heated to 50°C and soaked, adjusted PH=6.5, and added a mixed enzyme composed of cellulase, protease and pectinase (ratio 0.1: 5:5) The dosage of the compound enzyme is 1% of the dry weight of the tea, stirring for 30min, filtering, and repeating the extraction 3 times. The combined filtrate is extracted with ethyl acetate and then concentrated and dried in vacuo. 26.5 g of tea polyphenols with a content of 16.9% were obtained, and the extraction rate of tea polyphenols was 14.9%. The content of catechin is 6.97%, and the extraction rate is 8.4%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com