Degradable, high-toughness and ultrafine-grained magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy used for bone fixation and method for preparing same
A technology of rare earth alloys and ultra-fine crystals, which is applied in the field of bioalloy processing and can solve problems such as poor biocorrosion resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
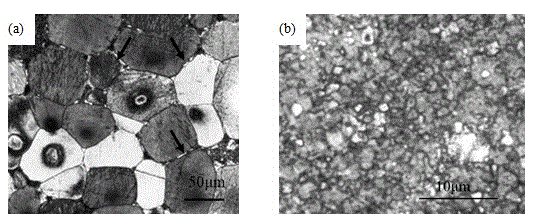
[0016] The magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy ingot is smelted according to the designed composition, and its composition and weight percentage are Zn 3.7%, rare earth elements 1.5%, Zr7 Zn 3 (RE), REMg 12 phase composition (see figure 1 (a)), the average size of microscopic grains is about 60 μm. The as-cast magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy is processed into a columnar specimen of 19.5mm×19.5mm×40mm by wire cutting, and the cut specimen is subjected to surface pretreatment, and then placed in an equal-diameter channel corner mold and heated to 330°C with the furnace Keep warm for 10 minutes, and then apply pressure to carry out 60 consecutive equal-diameter channel angular extrusions. The sample is rotated 180° between adjacent extrusion passes (that is, the traditional C path) to improve the uniformity of the extrusion structure. After processing, the alloy structure Significant refinement (see figure 1(b)), the average size of the microscopic grains is less than 1.5 μm, an...
Embodiment 2
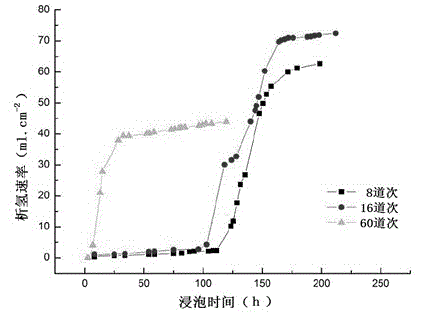
[0018] The magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy ingot is smelted according to the designed composition, and its composition and weight percentage are Zn 4.5%, rare earth element 1.0%, Zr figure 2 ), and its initial incubation period is measured to be longer (the hydrogen evolution rate is about 0.022ml / (cm 2 .h), converted into a degradation rate of about 0.011 mm / a), then enters a stable stage through a rapid corrosion stage, and the hydrogen evolution rate is only 0.050 ml / (cm 2 .h), and the corresponding degradation rate is about 0.026 mm / a, which can meet the requirements of biocorrosion resistance as a biodegradable medical magnesium alloy for bone fixation.
Embodiment 3
[0020] The magnesium-zinc rare earth alloy ingot is smelted according to the designed composition, and its composition and weight percentage are Zn 4.1%, rare earth elements 1.2%, Zr2 .h), the converted degradation rate is about 0.010mm / a), and then enters the stable stage through the rapid corrosion stage. After stabilization, the hydrogen evolution rate is only 0.075 ml / (cm 2 .h), and the corresponding degradation rate is about 0.038 mm / a, which can meet the requirements of biocorrosion resistance as a biodegradable medical magnesium alloy for bone fixation.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com