Creation method and purpose of paddy rice male sterile line
A technology for male sterility and rice, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, biochemical equipment and methods, and applications, etc., can solve the difficulty of screening excellent combinations, the limitation of the relationship between restorer lines and maintainer lines, and the seed advantage of three-line hybrid rice. complex performance issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Embodiment 1, the method for the creation of rice male sterile lines
[0026] 1.1 Create eat1 rice male sterile lines by genetic engineering or other means
[0027] The sequence of the coding region of the EAT1 gene in this example is shown in SEQ ID NO.3. The eat1 mutant material in this example was obtained from the conventional japonica rice variety Wuyujing 7 (also known as 9522) through RNA interference or sequence variation of the EAT1 gene.
[0028] 1.2 Cloning of rice fertility control protein gene
[0029] Utilize the population of rice gene positioning cloning (map-based cloning or position cloning) that comprises the fertility control protein gene EAT1 and its mutant gene eat1 that the inventor constructed, and is clear to those skilled in the art. Within the genome fragment, for example, within 100Kb. On this basis, a genomic DNA clone containing the fragment was isolated by a conventional method. After sequencing and further hybridization identificati...
Embodiment 2
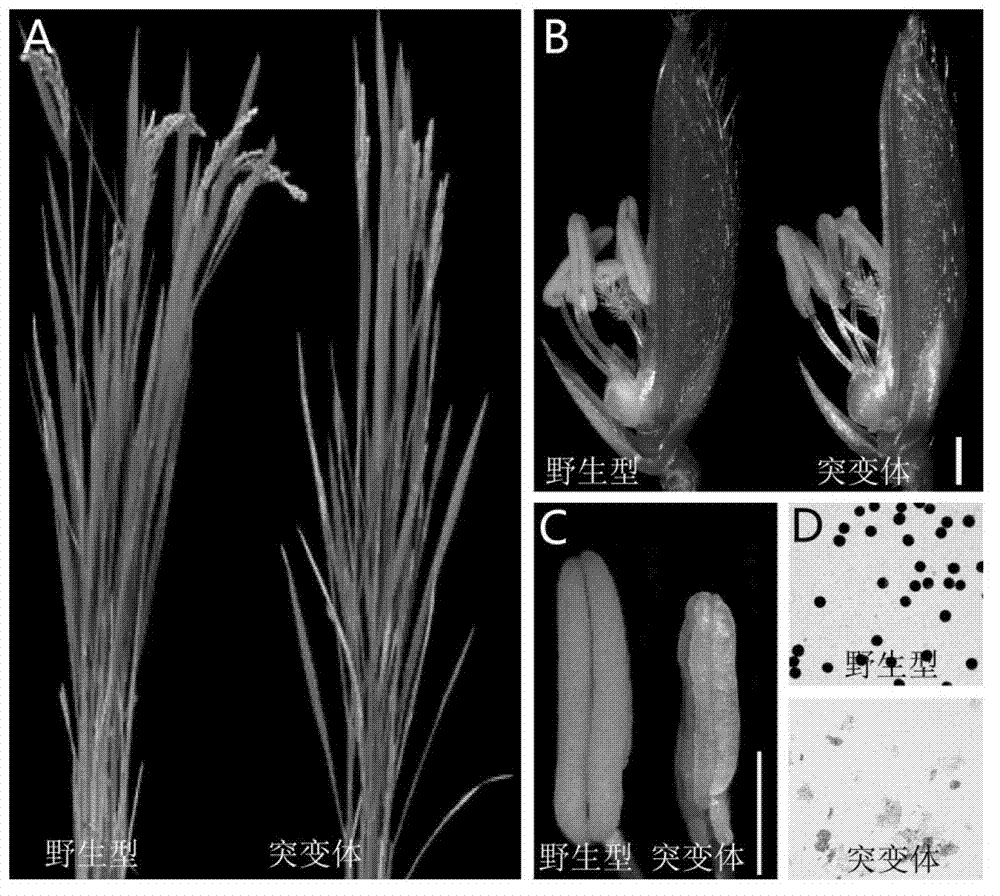
[0048] The purposes of embodiment 2eat1 mutant in rice seed production
[0049] The eat1 mutant was used as the male parent to cross the sterile parent in the three-line or two-line cross combination to obtain the F1 generation. In the F2 generation, a plant with both male sterility and sterility characteristics was screened, and the plant was crossed with the maintainer line corresponding to the original sterile parent. In the F2 generation, the plants with both male sterility and sterility characteristics are screened again and crossed with the maintainer line. After multiple generations of cross screening, a new male sterile line is obtained, which is suitable as the female parent in the hybrid combination.
Embodiment 3
[0050] Embodiment 3 restores the method for eat1 mutant male sterility trait
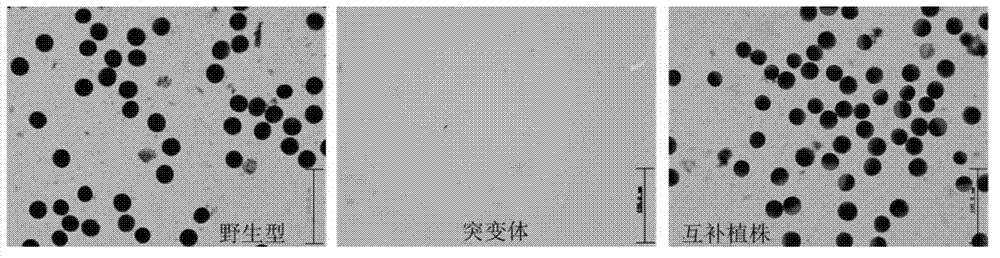
[0051] Transferring the genomic nucleotide sequence encoding the EAT1 gene into the mutant eat1 plant can restore the mutant to the wild-type phenotype.
[0052] Primers used from rice Nipponbare BAC clone (OSJNba0093F12):
[0053] EAT 1-COM-F: 5'AAAAGTCGACCCGAACTGCCGTCTTAATGT 3' and
[0054] EAT 1-COM-R: 5'AAAAGGTGACCGCAGTGACCAGATTGAGATAAC3'
[0055] A 5225bp genome sequence fragment of the EAT1 gene was amplified.
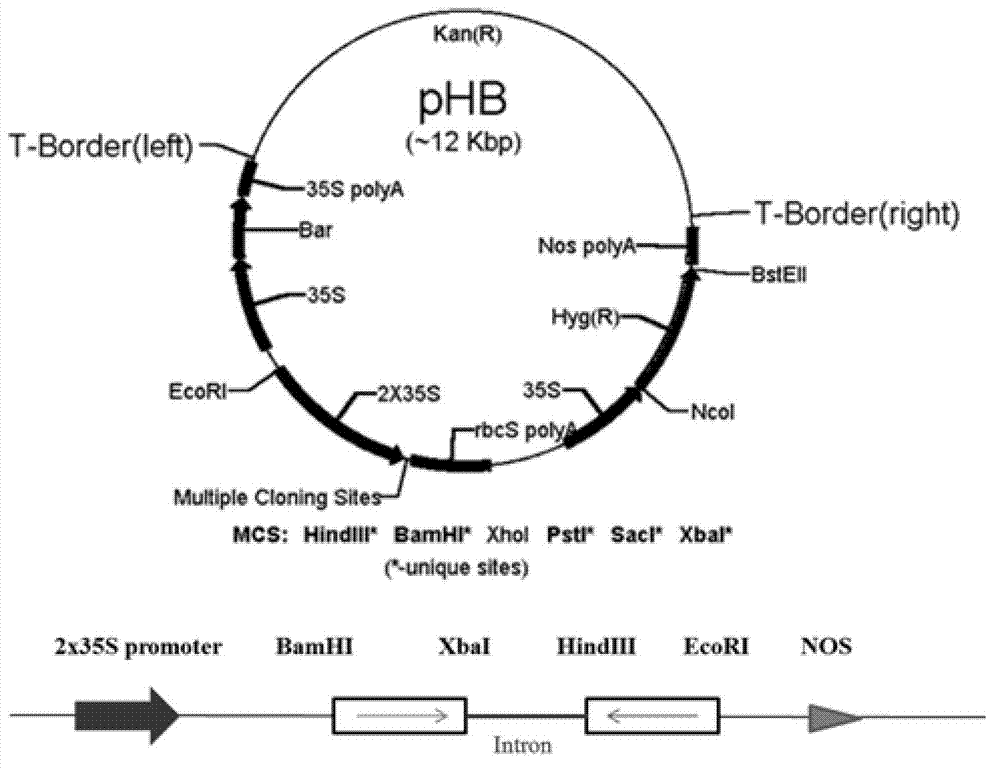
[0056] The fragment was inserted into the binary vector pCAMBIA1301 vector used for transformation of rice through Sal I and BstEII; the sequencing verification was correct, and the vector was introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105 by electroporation to obtain EAT1 complementary Agrobacterium tumefaciens EHA105, The mutant eat1 and wild-type 9522 mature embryo calluses were transformed by genetic transformation to observe whether the mutants would return to the wild-type...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com