Method for improving write redundancy of high SRAM (static random access memory)
A write redundant, static random technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, electrical components, circuits, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
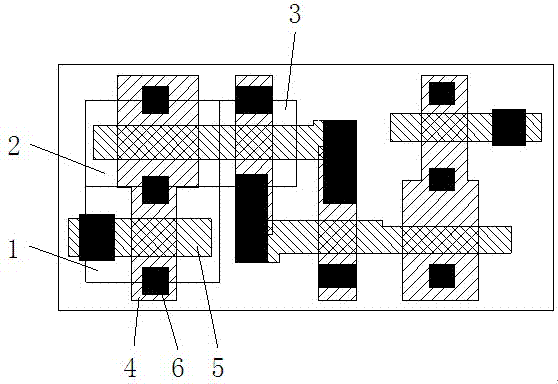
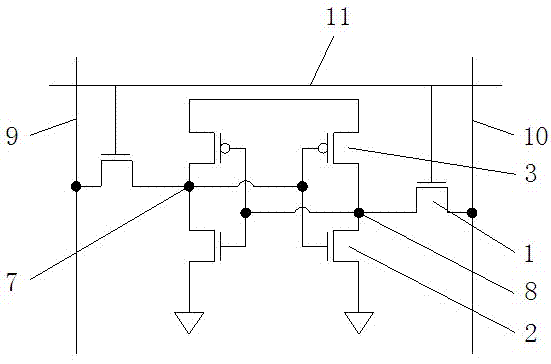
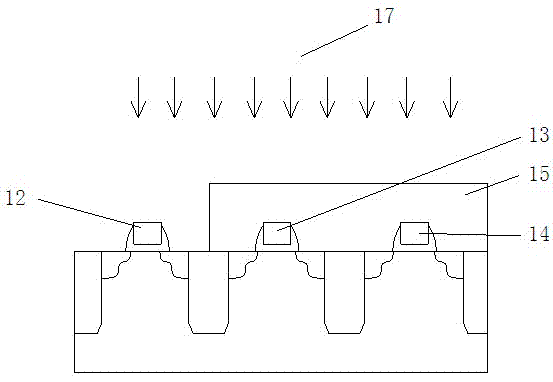
[0022] In the first embodiment of the present invention, please continue to refer to Figure 4a and Figure 4b shown. The above-mentioned lattice structure 18 is specifically a silicon carbide lattice structure. After the carbon implantation 17 process is performed, the source and drain ends of the NMOS device 12 and the source and drain ends of the pull-up tube 14 form a silicon carbide lattice structure.
[0023] In the second embodiment of the present invention, the above-mentioned covering layer 15 is photoresist.
[0024] In the third embodiment of the present invention, after carbon implantation 17 is performed on the NMOS device 12, the PMOS device 13 and the pull-up tube 14, an annealing process is required to finally make the source and drain ends of the NMOS device 12 and the pull-up tube 14 The source-drain two-terminal silicon carbide lattice structure.
[0025] To sum up, using the method of the present invention to improve the writing redundancy of the SRAM, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com