Electrothermal drive outer rotor stepping micro-motor
An electrothermal drive, external rotor technology, applied in the direction of electrical components, electromechanical devices, etc., can solve the problems of difficult direct application of MEMS devices, difficult miniaturization of structure, and inability to directly apply, etc., to achieve large output force, novel and unique structure, easy to use The effect of control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
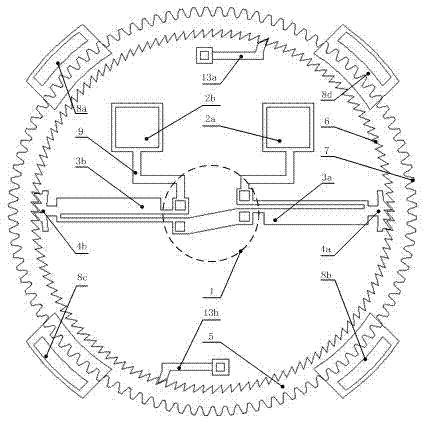
[0023] join figure 1 and figure 2 , the electrothermally driven outer rotor stepping micromotor, including a stator and a rotor (5), is characterized in that: the stator is an electrothermal actuator (3a, 3b) with cold and hot arms, and the rotor (5) is a ring wheel; One end of the actuator (3a, 3b) is fixed on the silicon substrate plane (12) through an anchor point, and the other end is a movable driving pawl (4a, 4b), and the ratchet teeth of the driving pawl (4a, 4b) It meshes with the inner ratchet (6) of the rotor (5), there is a gap between the driving pawls (4a, 4b) and the inner ratchet (6), the rotor (5) is a floating wheel, and there are standard involute gear teeth on the outer periphery (7), constrained by four uniformly distributed confinement hoods (8a, 8b, 8c, 8d), the fixed electrodes (2a, 2b) are electrically connected to the anchor point (1) through wires (9), and are connected to the hot and cold arms The electrothermal actuators (3a, 3b) are powered.
Embodiment 2
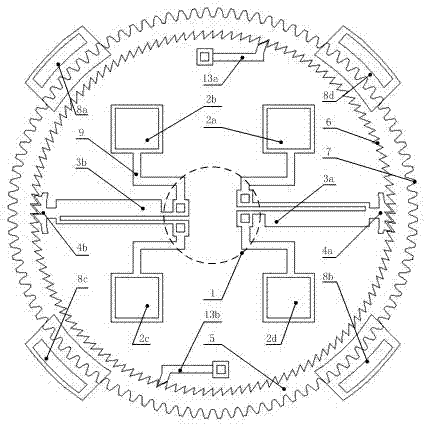
[0025] join figure 1 , figure 2 and image 3 , the present embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
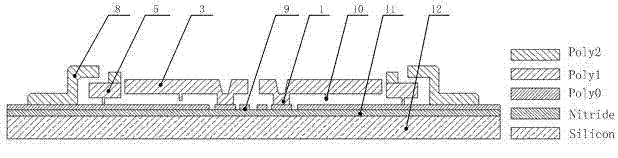
[0026] The hot and cold arm electrothermal actuators (3a, 3b) are U-shaped single-arm electrothermal actuators, or U-shaped double-arm electrothermal actuators. The number of the hot and cold arm electrothermal actuators can be 2, 4 or 6. The inner side of the rotor (5) is further provided with 1~2 stop ratchets (13a, 13b) meshing with the inner ratchet (6) of the rotor (5). The stator and rotor (5) are prepared by MEMS surface technology, on the silicon substrate plane (12), there is a silicon nitride layer (11), and on the silicon nitride layer (11) there is a fixed polysilicon layer used as a wire Poly0 (9), on the polysilicon layer Poly0 (9), there is a fixed structural layer Poly2 constituting the constraint cover (8a, 8b, 8c, 8d) and the anchor point (1) of the structural layer Poly1, on Poly0 (9) there is a The str...
Embodiment 3
[0028] In this micro-motor, in the initial state, the driving pawl 4, the stop pawl 13 and the triangular ratchet 6 on the inner wall of the rotor 5 are in the meshing state (due to technological reasons, there is a gap at the meshing part of the ratchet), and the electrode 2 is used to feed the actuator 3 power supply. The working principle of the micro-motor is: after the electrodes are energized, there is a current passing through the actuator. Since the actuators of the cold and hot arms are not equal in width, the resistance heat generated by the hot arm 15 is greater than that of the cold arm 16, so the actuator is under the resistance thermal stress. Under the action of Figure 5 As shown in the flexible arc movement, the driving pawl can drive the rotor to rotate clockwise through a certain angle. When the driving pawl returns, the ratchet of the pawl passes through the ratchet of the rotor, while the stationary driving pawl or stop pawl starts and stops For action, t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com