Method for producing hydrogen through intensified anaerobic fermentation
An anaerobic fermentation and fermentation vessel technology, applied in the field of enhanced anaerobic fermentation for hydrogen production, can solve the problems of low hydrogen production rate and low raw material conversion rate, and achieve the effects of simple operation, increased permeability and easy realization.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
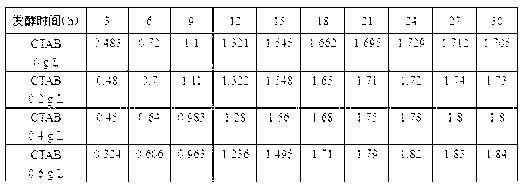
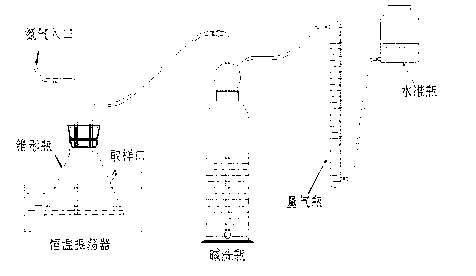
[0030] In a 500mL conical flask as a batch reactor, add 100mL of medium, 0.1mg of resazurin, and then add 5mL of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide solution with a mass concentration of 0.2g / L, mix After uniformity, sterilize at 121°C for 15 minutes, then inoculate 5mL of the fermented liquid from cow dung, and then pass sterile nitrogen into the Erlenmeyer flask and the connected alkaline washing bottle until the color of the fermentation system changes from The pink color becomes colorless (the aeration time is about 10 minutes), and then the sterile nitrogen gas inlet is sealed, and the flask is shaken and cultured under the conditions of 37°C constant temperature and 155r / min. The gas generated by fermentation enters the container with a concentration of 2mol / L sodium hydroxide solution in the alkali washing bottle, and then collect the gas overflowing from the alkali washing bottle, which is the hydrogen produced by fermentation;
[0031] The composition of described culture...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Experimental apparatus used, experimental condition and experimental operation are all identical with embodiment 1, and the concentration of the CTAB that adds is 0.4g / L, and the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution in the alkaline water bottle is 3mol / L.
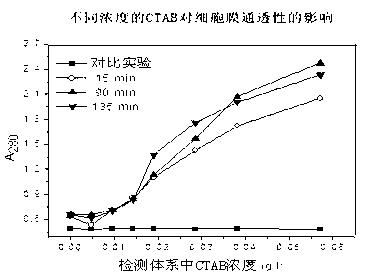
[0044] Adopt gas chromatography to detect hydrogen content, and compare with the situation that does not add CTAB, the result is as attached Figure 5 shown.
[0045] attached by Figure 5 It is concluded that adding 0.4g / L of CTAB is more than that without adding CTAB, the hydrogen production rate has increased by 15.26%, the maximum hydrogen production rate has increased by 31.10%, and the cumulative hydrogen production has increased by 22.73%; at the same time, although the addition of CTAB makes The stagnation time of hydrogen production is prolonged, but the OD of terminal fermentation 600 and pH had no significant effect, and CTAB had no significant effect on microbial growth and hydrogen production met...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Experimental apparatus used, experimental condition and experimental operation are all identical with embodiment 1, and the concentration of the CTAB that adds is 0.6g / L, and the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution in the alkaline water bottle is 4mol / L.
[0048] Adopt gas chromatography to detect hydrogen content, and compare with the situation that does not add CTAB, the result is as attached Figure 6 shown.
[0049] attached by Figure 6 It is concluded that adding 0.6g / L of CTAB is more than that without adding CTAB, the hydrogen production rate has increased by 18.70%, the maximum hydrogen production rate has increased by 43.91%, and the cumulative hydrogen production has increased by 38.18%; at the same time, although the addition of CTAB makes The stagnation time of hydrogen production is prolonged, but the OD of terminal fermentation 600 and pH had no significant effect, and CTAB had no significant effect on microbial growth and hydrogen production met...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com