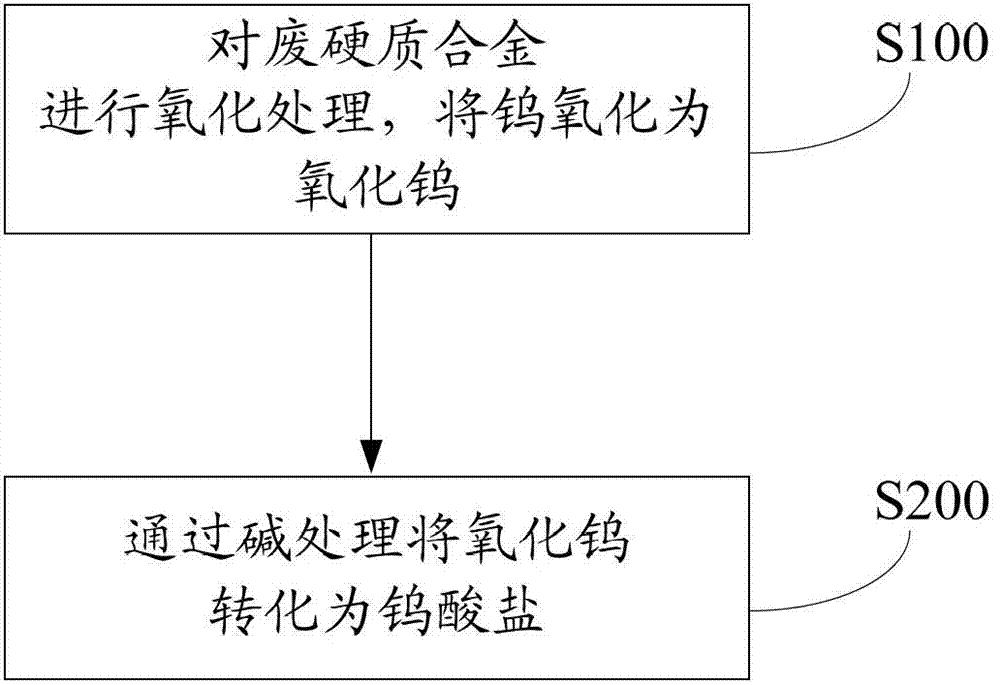
Method for treating waste hard alloy
A cemented carbide and oxidation treatment technology, applied in the field of metallurgy, to achieve the effects of reducing recycling costs, increasing daily processing capacity, improving recycling efficiency and recovery rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Scrap cemented carbide was processed following the procedure described in General Methods. Among them, the speed of pushing the boat is 2 boats / 25 minutes, and the process temperature is: the first temperature zone is 800 °C, the second temperature zone is 820 °C, the third temperature zone is 880 °C, and the fourth temperature zone is 900 °C ℃, the fifth temperature zone is 920℃, according to 25m 3 / h flow rate into the compressed air from the tail of the furnace.
[0067] Take 30kg of waste cemented carbide balls and place them flat in the boat at a rate of 0.7kg per boat. Open the front furnace door and push it into the boat according to the process requirements. The front furnace door is kept open to facilitate the discharge of gas and excess air generated by the reaction. Continuous push boat operation, after more than 6 hours of treatment, the oxidized waste alloy balls split from the surface to the inside, and flakes fell off. Put alloy balls and oxidized waste...
Embodiment 2
[0069] Scrap cemented carbide was processed following the procedure described in General Methods. Among them, the speed of pushing the boat is 2 boats / 35 minutes, and the process temperature is: the first temperature zone is 840 °C, the second temperature zone is 860 °C, the third temperature zone is 880 °C, the fourth and fifth temperature zones 920℃, according to 25m 3 / h flow rate into the compressed air from the tail of the furnace.
[0070] Take 30kg of waste cemented carbide balls and place them flat in the boat at a rate of 0.7kg per boat. Open the front furnace door and push it into the boat according to the process requirements. The front furnace door is kept open to facilitate the discharge of gas and excess air generated by the reaction. Pushing the boat continuously, after more than 8 hours of treatment, the oxidized waste alloy balls split from the surface to the inside, and flakes fell off. Put alloy balls and oxidized waste cemented carbide into a ball mill fo...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Scrap cemented carbide was processed following the procedure described in General Methods. Among them, the speed of pushing the boat is 2 boats / 40 minutes, and the process temperature is: the first temperature zone is 860°C, the second temperature zone is 880°C, the third temperature zone is 900°C, and the fourth temperature zone is 940°C , the fifth temperature zone is 950℃, according to 25m 3 / h speed into the compressed air from the tail of the furnace.
[0073] Take 30kg of waste cemented carbide balls and place them flat in the boat at a rate of 0.7kg per boat. Open the front furnace door and push it into the boat according to the process requirements. The front furnace door is kept open to facilitate the discharge of gas and excess air generated by the reaction. Continuous push boat operation, after more than 10 hours of treatment, the oxidized waste alloy balls cracked from the surface to the inside, and flakes fell off. Put alloy balls and oxidized waste cemen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com