Method for treating cobalt-nickel-copper hydrometallurgy wastewater residue
A technology of hydrometallurgy and waste water slag, which is applied in the field of metallurgy, can solve the problems of difficult separation of valuable metals, the influence of leaching and extraction, and low metal recovery rate, and achieve good economic benefits, good social benefits, and high metal recovery rates. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
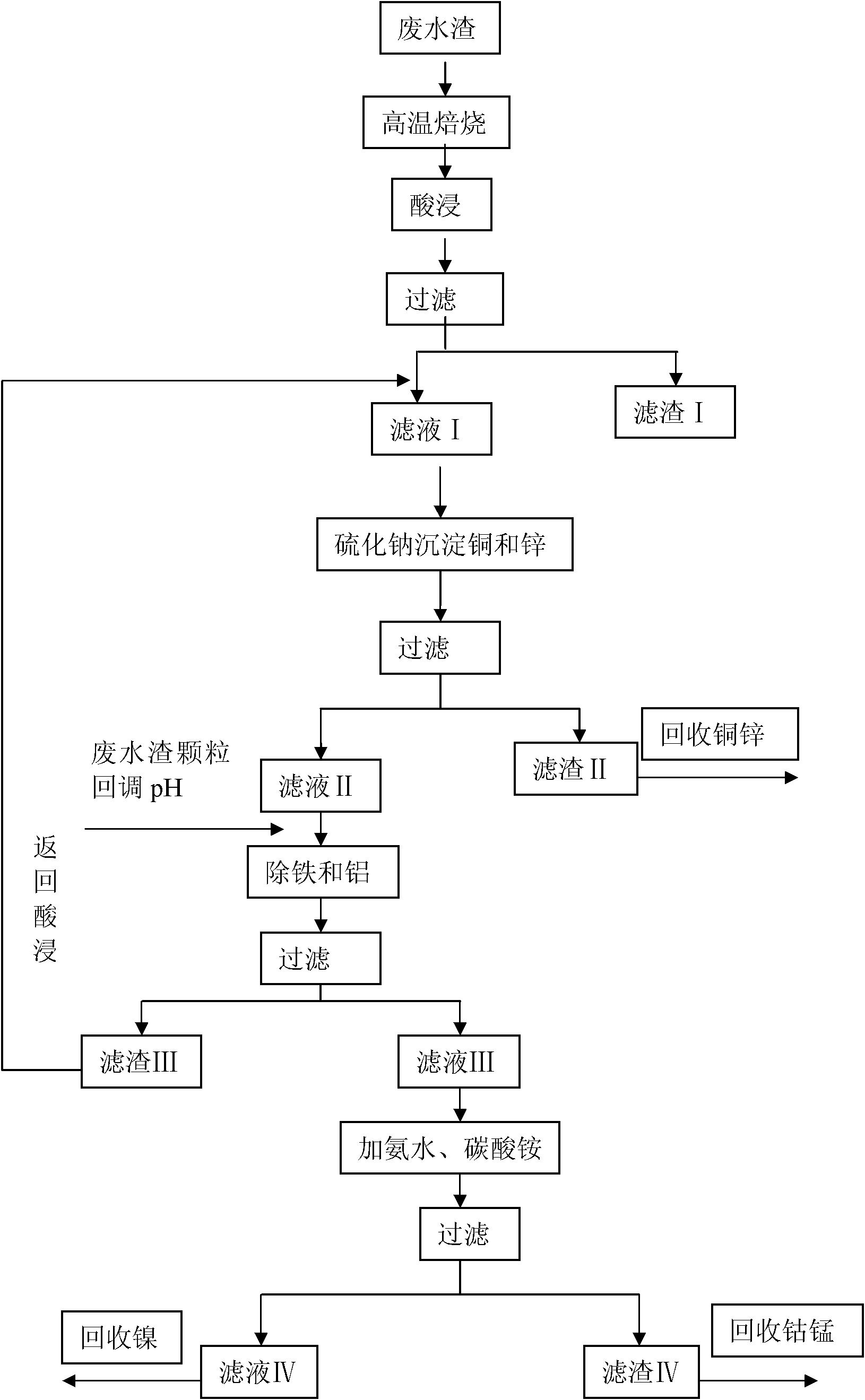
[0026] A method for processing cobalt-nickel-copper hydrometallurgical wastewater slag, comprising the following steps:
[0027] (1) High-temperature roasting: get 1000g of low-grade cobalt-nickel-copper hydrometallurgical wastewater slag, wherein by weight percentage, the cobalt content is 0.21%, the nickel content is 0.62%, the copper content is 0.72%, and the moisture content is 70.5%. In addition, cobalt-nickel-copper hydrometallurgical wastewater slag contains impurities such as iron and aluminum;
[0028] Airing and weathering, placing in a rotary kiln or muffle furnace and roasting at a high temperature of 500 ° C for 2 hours to obtain 275 g of waste water slag particles, the average particle size of waste water slag particles is 15 μm;
[0029] (2) Acid leaching: according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:4, the wastewater slag particles in step (1) are dropped into 1100ml of 25g / L sulfuric acid solution for leaching, and 30g of sodium sulfite is added at the same tim...
Embodiment 2
[0036] A method for cobalt-nickel-copper hydrometallurgical wastewater slag and sludge treatment, comprising the following steps:
[0037] (1) High-temperature roasting: get 1000g of low-grade cobalt-nickel-copper hydrometallurgical wastewater slag, wherein by weight percentage, the cobalt content is 0.21%, the nickel content is 0.62%, the copper content is 0.72%, and the moisture content is 70.5%. In addition, cobalt-nickel-copper hydrometallurgical wastewater slag contains impurities such as iron and aluminum;
[0038] Airing and weathering, placing in a rotary kiln or muffle furnace and roasting at a high temperature of 700 ° C for 1 hour to obtain 261 g of waste water slag particles, the average particle size of waste water slag particles is 10 μm;
[0039] (2) Acid leaching: according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:4, the wastewater slag particles in step (1) are dropped into 1044ml of 35g / L sulfuric acid solution for leaching, and 25g of sodium sulfite is added at the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com