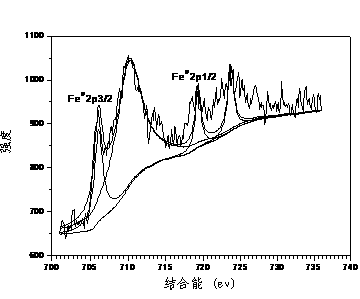
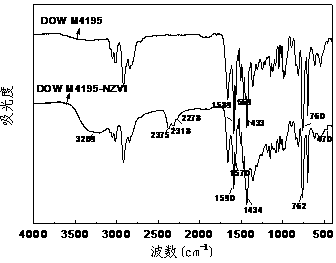
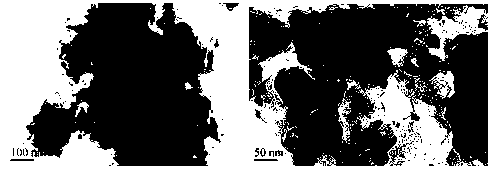
Nitrogen ligand chelate resin nanoscale zero-valent iron-loaded composite material and method thereof for reduction of bromate in water
A nano-zero valent iron, chelating resin technology, applied in the reduction water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of high treatment cost, secondary pollutants, low removal rate, etc. , to achieve the effect of stable performance and rapid degradation ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] A nitrogen ligand chelating resin loaded nanometer zero-valent iron composite material, the synthesis method of which is as follows:
[0029] (1) Put 4ml Reillex 402 into a glass adsorption column of Ф1.0cm×20cm, add 0.2% (W / W), pH=2.4 Fe 3+ The solution was loaded with metal ions through the adsorption column, which was recorded as Reillex 402-Fe after loading for 24 hours, and then the Reillex 402-Fe was poured out of the glass column and washed with deionized water until neutral.
[0030] (2) NaBH with a concentration of 0.2mol / L 4 Mix 200ml of aqueous solution with Reillex 402-Fe in a three-necked flask while stirring with a stirring paddle, NaBH 4 The aqueous solution is deoxygenated beforehand. When NaBH 4 When the solution was added dropwise to the three-necked flask, the resin immediately turned black. After the dropwise addition was completed and the reaction was continued for 2 hours, the material was filtered, rinsed with an ethanol solution except peroxy...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Step is the same as embodiment 1, but the 0.2% (W / W) in the step, the Fe of pH=2.4 3+ The aqueous solution is replaced by Fe with p H=3.5 2+ Aqueous solution, other conditions remain unchanged, the iron loading amount of the material is 90mg / g. For BrO 3 - The working capacity was 0.656g / l, and no iron ions were detected throughout the process.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The steps are the same as in Example 1, but the Reillex 402 resin in the step is replaced by Reillex 425 resin, other conditions are unchanged, and the iron loading amount of the material is 124 mg / g. For BrO 3 - The working capacity was 1.077 g / l, and no iron ions were detected throughout the process.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com