Method for detecting damage of first wall of tokamak fusion reactor with polarized light
A tokamak and polarized light technology, applied in the direction of optical testing flaws/defects, polarization effects, etc., can solve problems such as surface damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] Specific embodiments of the present invention are given below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings to describe the technical solution of the present invention in detail.
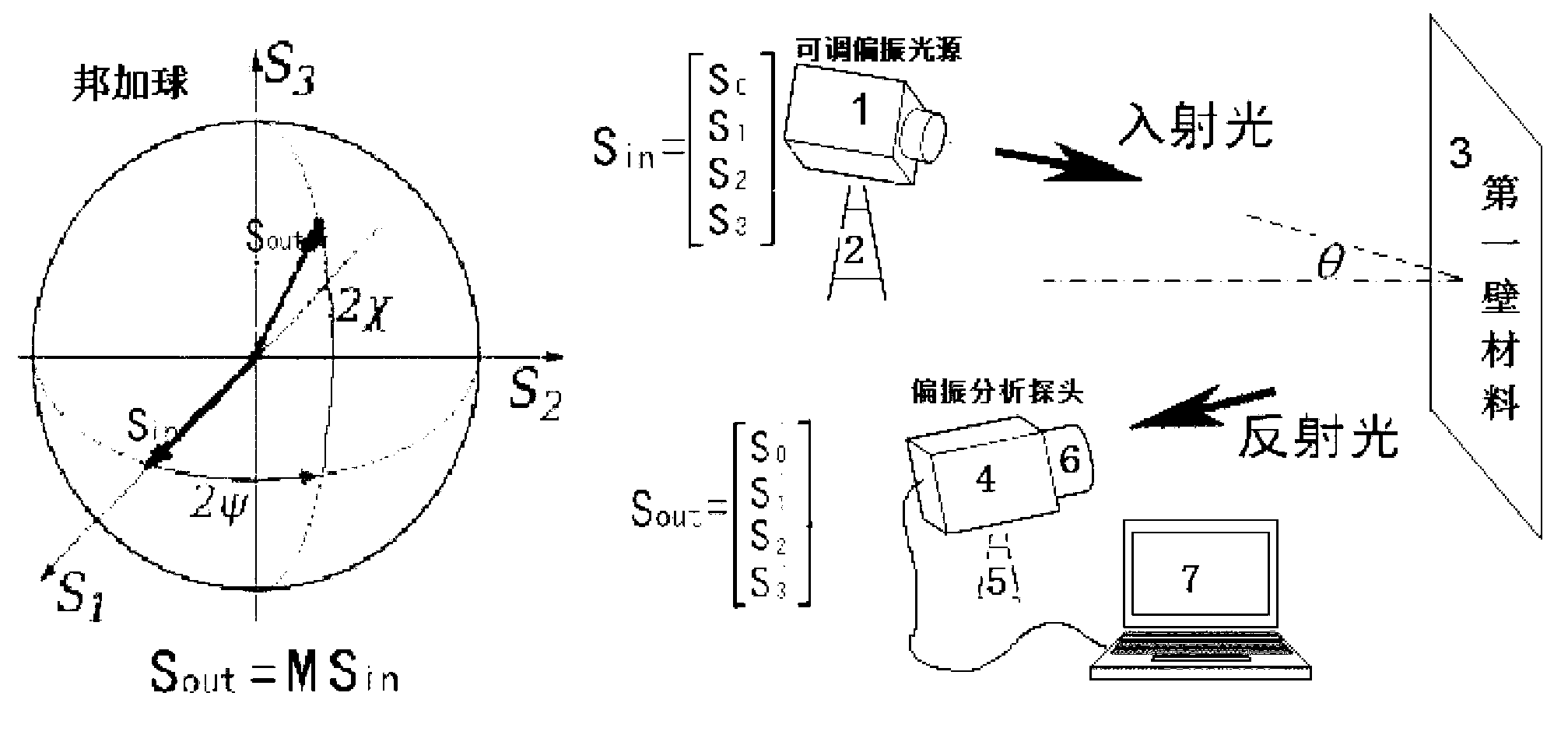
[0020] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of the optical path implemented in the present invention.
[0021] Step 1 Set linearly polarized light source 1. (The linearly polarized light source 1 is a visible / near-infrared laser. This example uses a laser source with a wavelength of 650nm and an adjustable polarized light vibration plane.) The linearly polarized light source 1 is fixed on a bracket 2 that can adjust the angle, such as figure 1 As shown, the linearly polarized light source 1 is aimed at the first wall surface 3 .
[0022] Step 2 Adjust the position of the first wall. The polarized incident light is irradiated on the first wall surface 3 at an incident angle of about θ=58°.
[0023] Step 3 Determine the position of the probe 4 of the polarization analyzer. The pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com