High temperature resistant alloy and its preparation method
A high-temperature heat-resistant alloy technology, which is applied in the fields of alloys and their preparation, high-temperature heat-resistant alloys and their preparation, can solve problems such as high-temperature heat-resistant steels that have not yet been retrieved, and achieve the goals of reducing weight, improving mechanical strength, and increasing profits Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] To produce quenching trays, the tray weighs three tons, and the charge is distributed according to the following composition ratio (Wt%):
[0036] C: 0.22, Cr: 25, Mn: 0.89, S: 0.029, P: 0.024, Si: 1.4,
[0037] D (substitute nickel alloy): 5.0, Ni: 2.3, and the balance is iron.
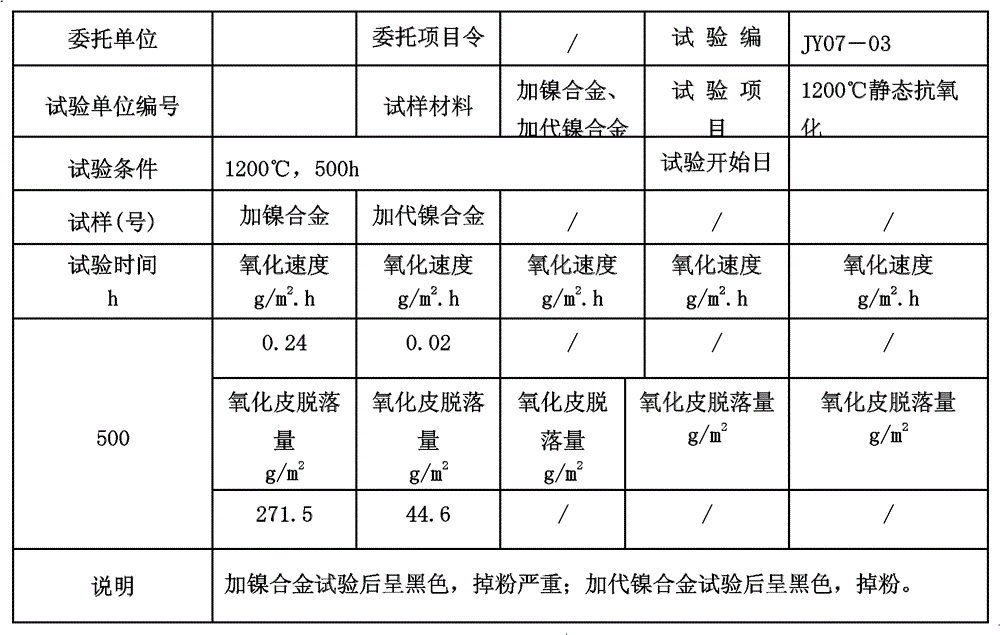
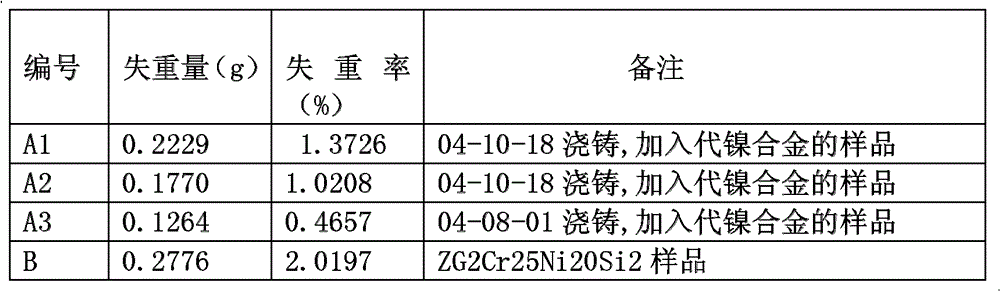
[0038] Casting is carried out, and other alloy components except the D-generation nickel alloy are smelted in an electric furnace. When the temperature reaches the pouring temperature of 1620°C, pour out one-third of the molten steel and add the D-generation nickel alloy at the same time. Continue to heat and increase the 1650 ~ 1670 ℃ outlet water pouring. After annealing treatment, the mechanical properties are tensile strength 710Mpa, yield strength 560Mpa, elongation 7%, hardness HB241. After two years and seven months of use, the tray is still in good condition, without defects such as oxidation, cracking, and serious deformation.
Embodiment 2
[0040] Production of 180KW high temperature furnace bottom plate. Furnace charge according to following composition ratio (Wt%):
[0041] C: 0.24, Cr: 23, Mn: 1.0, S: 0.03, P: 0.022, Si: 1.5,
[0042] D (substitute nickel alloy): 5.40, Ni: 1.56, and the balance is iron.
[0043] The D-generation nickel alloy and other alloys are smelted in an electric furnace at the same time. When the temperature reaches 1620°C, continue heating and increase the temperature by 30-50°C to tap molten steel and pour. After finishing, heat preservation at 650-750°C for 3-5 hours for furnace cold annealing treatment, and it is still intact after more than three years of use.
Embodiment 3
[0045] Production of heat-treated material frames. Furnace charge according to following composition ratio (Wt%):
[0046] C: 0.20, Cr: 22, Mn: 1.1, S: 0.03, P: 0.022, Si: 1.6,
[0047] D (substitute nickel alloy): 4.80, Ni: 0, and the balance is iron.
[0048]The D-generation nickel alloy and other alloys are smelted in an electric furnace, and when the temperature reaches the pouring temperature of 1650°C, the molten steel is poured. After the material frame is cooled, heat it at 650-750°C for 3-5 hours for furnace cooling annealing treatment, and it is still intact after 30 months of use.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com