Random laser based on wave-guiding structure
A random laser and waveguide structure technology, applied in the laser field, can solve the problems that it cannot be used as a light source for micro-nano integrated optical systems, and achieve the effects of easy implementation, lower emission threshold, and lower scattering loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
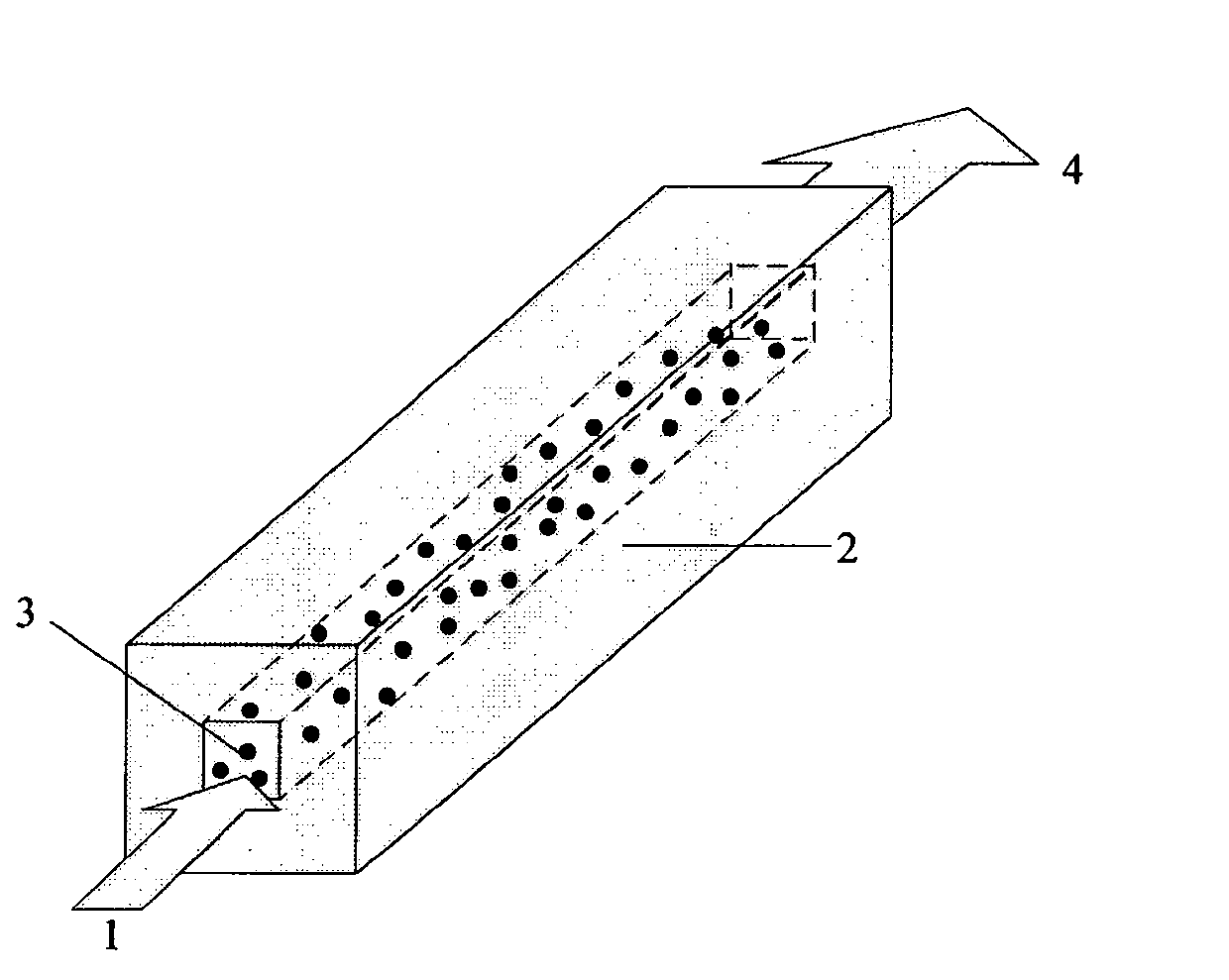
[0012] Such as figure 1 As shown, it is a random laser based on a waveguide structure, and its structure includes a pumping light source 1. The pumping light source can be a typical Nd:YAG laser, which is incident from the side of the waveguide to provide energy for the internal ZnO random particles 3; The waveguide structure formed by ZnO particles is surrounded by MgO cladding layer 2 with a thickness of 200nm; ZnO random particles play the role of scattering and providing gain in this structure; and MgO cladding layer 2 has a smaller refractive index than ZnO random particles 3. Therefore, when the scattered light propagates to the MgO cladding layer 2 or the MgO cladding layer 2 and air, it will be fed back into the waveguide in the form of total reflection, thereby reducing the threshold of scattering loss and laser radiation 4 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com