Fertilizing method of enhancing wheat nitrogen use efficiency and lodging resistance
A technology of wheat nitrogen and fertilization methods, which is applied in the field of plant growth and nutritional status monitoring, can solve the problems of increasing the incidence of diseases and insect pests, only 33%, and loss, so as to improve the ability to resist low temperature stress in winter, promote deep root growth, and reduce inhibition. The effect of action
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
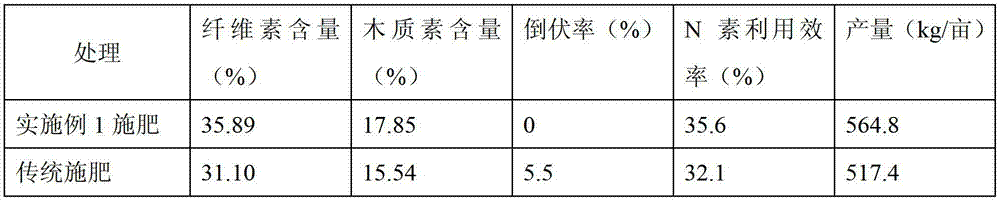
[0028] Example 1 This experiment was carried out at the experimental site of the Crop Research Institute of the Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences, where the soil fertility was moderate; the farming method was conservation tillage (after harvesting the corn crop of the previous season, the stalks were directly crushed and returned to the field, and the wheat was sown with a no-till machine). The variety is Jimai 22.
[0029] a. Base fertilizer: apply compound fertilizer before wheat sowing, N, P 2 o 5 、K 2 The amount of O was 5, 7, 7kg / mu respectively. Plow immediately after fertilization, mix the fertilizer with the soil, and avoid the volatilization of nutrients due to exposure.
[0030] b. The sowing rate of wheat is 9kg / mu, and the row spacing is 20cm.
[0031] c. The NDVI value of wheat is 0.27, and the population is 453,000 tillers / mu.
[0032] d. In the early stage of jointing of wheat (1 node), the NDVI value measured by GreenSeeker is 0.59.
[0033] e. Us...
Embodiment 2
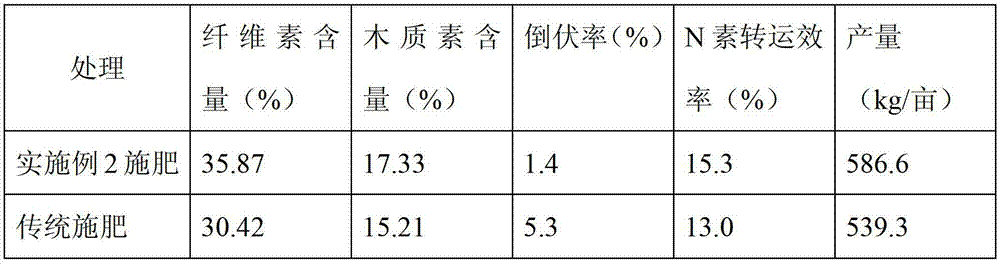
[0039] Example 2 This experiment was carried out at the Changqing Fine Seed Factory in Shandong Province. After harvesting the last crop corn, the stalks were directly crushed and returned to the field, and the soil was plowed deeply; the wheat variety was Jimai 22.
[0040] a. Base fertilizer: apply compound fertilizer before wheat sowing, N, P 2 o 5 、K 2 The amount of O was 5, 6.5, 7kg respectively. Plow immediately after fertilization, mix the fertilizer with the soil, and avoid the volatilization of nutrients due to exposure.
[0041] b. The sowing rate of wheat is 10kg / mu, and the row spacing is 22cm.
[0042] c. Wheat grows to the early stage of rising, the population is 427,000 tillers / mu, and the NDVI value is 0.28.
[0043] d. In the early stage of wheat jointing (1 node), the NDVI value was determined by GreenSeeker to be 0.49, and N, P, and K compound fertilizers were used as the base material, and potassium chloride and urea were used to adjust the nutrient con...
Embodiment 3
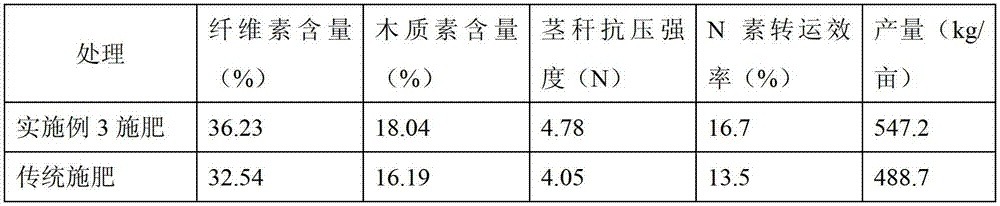
[0049] Example 3 This experiment was carried out on farmland in Zhangqiu City, Shandong Province (low soil fertility), the soil was rotary tilled, and no straw was returned to the field; the wheat variety was Yannong 19.
[0050] a. Base fertilizer: apply compound fertilizer before wheat sowing, N, P 2 o 5 、K 2 O consumption is 6,7,6kg respectively. Plow immediately after fertilization, mix the fertilizer with the soil, and avoid the volatilization of nutrients due to exposure.
[0051] b. The sowing rate of wheat is 12kg / mu, and the row spacing is 20cm.
[0052] c. Wheat grows to the early stage of rising, the population is 316,000 tillers / mu, and the NDVI value is 0.19.
[0053] d. Therefore, N, P, and K compound fertilizers are used as base materials during the rising period, and potassium sulfate and urea are used to adjust the nutritional content, and N, P are applied per mu. 2 o 5 、K 2 O was 11, 4, and 9 kg respectively (5 cm into the soil in the ditch), and then ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com