N-doped graphene preparation method and application of N-doped graphene
A technology of nitrogen-doped graphene and graphene solution, applied in the direction of graphene, nano-carbon, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to be applied on a large scale and being expensive, and achieve the effects of low cost, good stability and simple preparation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032] A preparation method of nitrogen-doped graphene, comprising the following steps:
[0033] 1) Dissolution of graphene oxide solid
[0034] Add graphene oxide solids into water and ultrasonically disperse for 30-240 minutes to form a uniformly dispersed graphene oxide solution with a concentration of 0.1-2.0 g / L;
[0035] 2) Reduction of hydrazine hydrate to obtain reduced graphene oxide solution
[0036] Put an ammonia solution with a mass fraction of 25% to 28% into the graphene oxide solution in step 1), and adjust the pH value of the graphene oxide solution to 9 to 11, and then add the graphene oxide solution with the graphene oxide solution A hydrazine hydrate solution with a volume ratio of 1:20 to 1:150 and a concentration of 1 mol / L is stirred for 30 to 60 minutes to obtain a mixed solution, and then the mixed solution is heated to 95°C and reacted for 1 hour to obtain a reduced state graphene oxide solution, and then directly cool the reduced state graphene oxi...
Embodiment 1
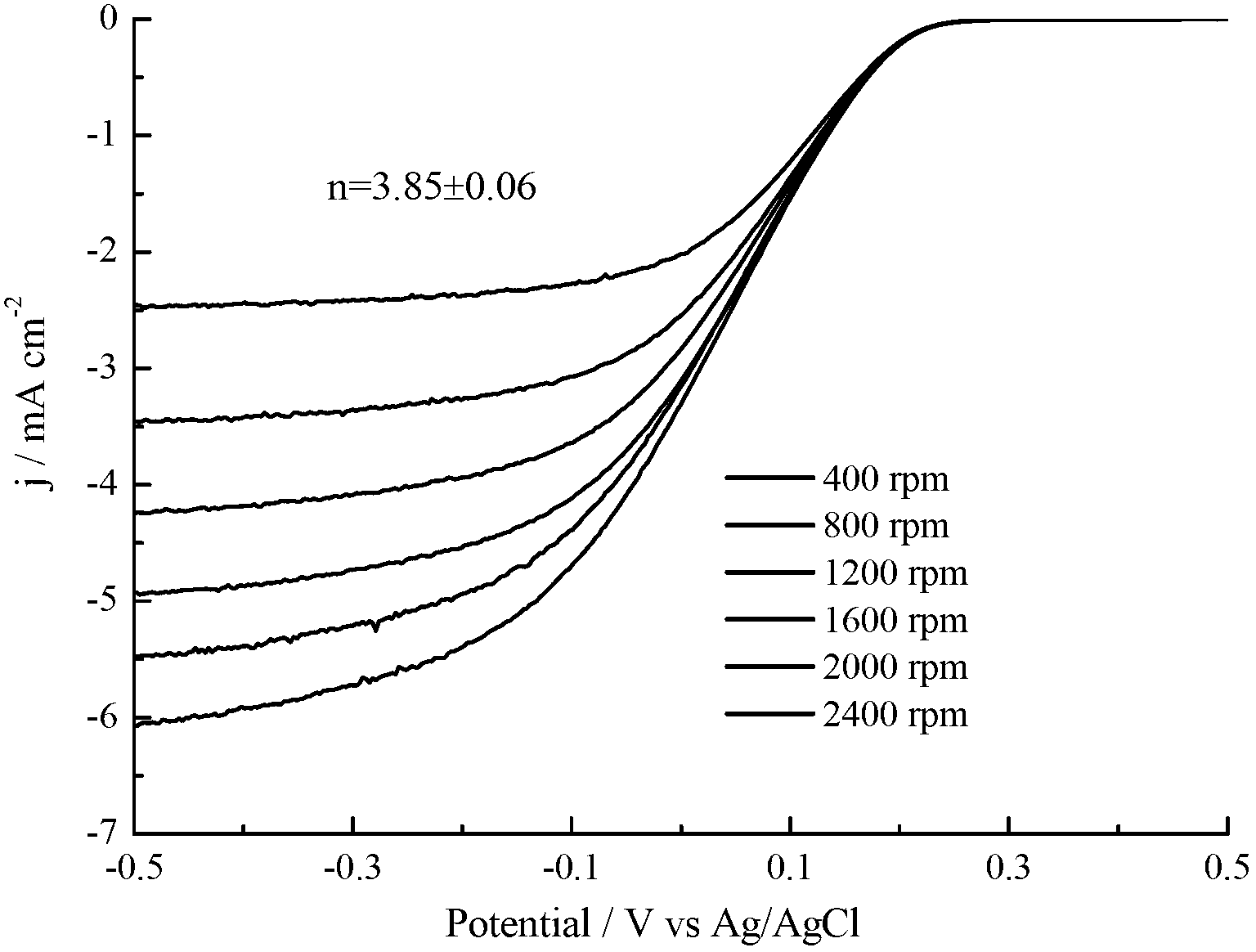
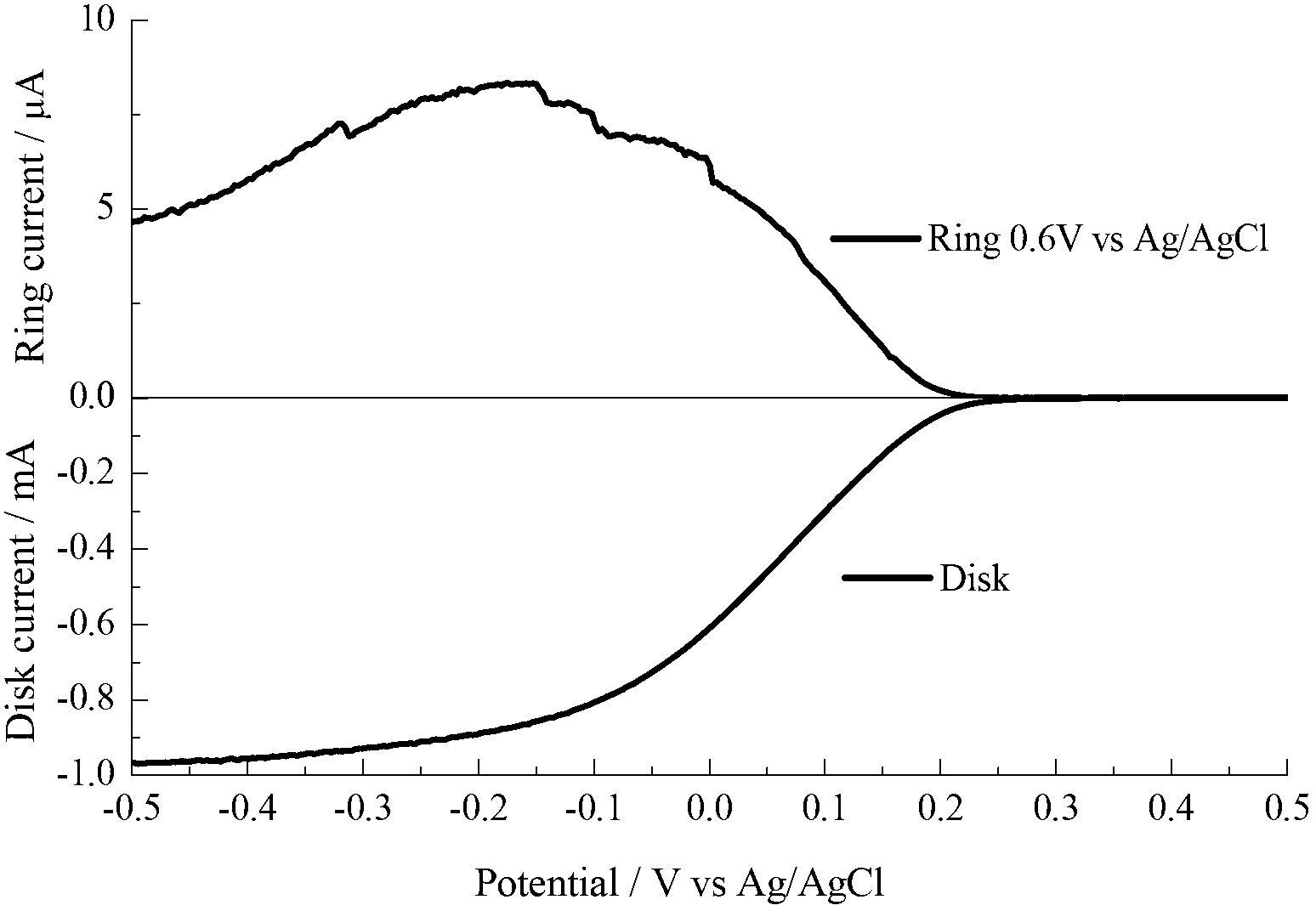
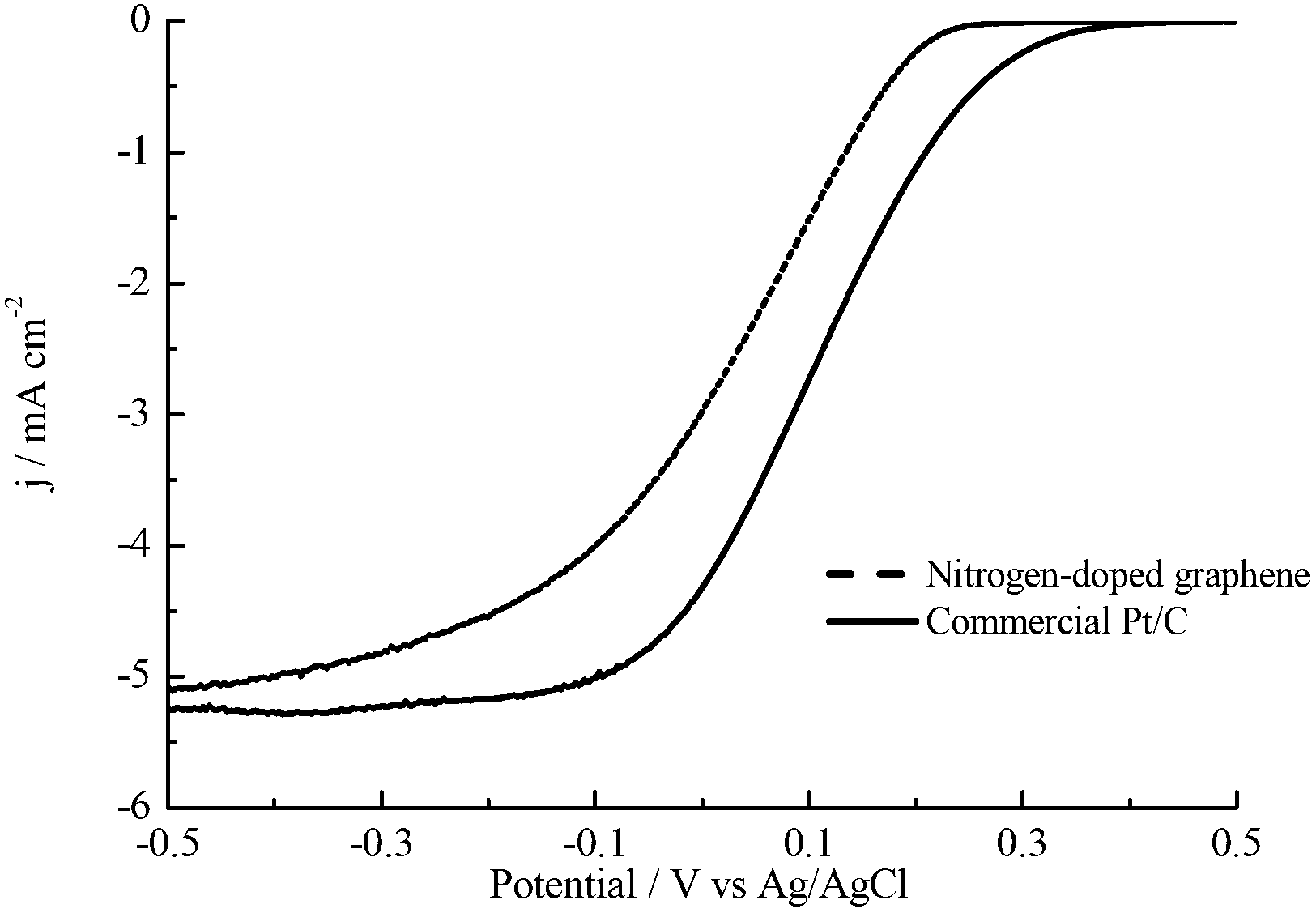
[0044] After adjusting the pH value of the graphene oxide solution to 10.02 with ammonia water, add a 1mol / L hydrazine hydrate solution with a volume ratio of 1:100, and then add a volume ratio of 1:25 with a mass fraction of 50% cyanide after the reduction reaction is completed. The amine aqueous solution is controlled by rotary evaporation with water temperature of 50° C., rotation rate of 100 rpm, and vacuum of 50 mbar to remove water to obtain a cyanamide-reduced graphene oxide composite material. The roasting conditions were then controlled to be a roasting temperature of 900° C., roasting for 60 min, and an argon flow rate of 50 mL / min. The product was cleaned with double distilled water and 50% ethanol solution respectively to obtain black powder nitrogen-doped graphene. In the 0.1mol / L, pH=7 phosphate buffer, the oxygen reduction electron transfer number was 3.75.
Embodiment 2
[0046] After adjusting the pH value of the graphene oxide solution to 10.02 with ammonia water, add a 1mol / L hydrazine hydrate solution with a volume ratio of 1:100, and then add a volume ratio of 1:25 with a mass fraction of 50% cyanide after the reduction reaction is completed. The amine aqueous solution is controlled by rotary evaporation with water temperature of 50° C., rotation rate of 100 rpm, and vacuum of 50 mbar to remove water to obtain a cyanamide-reduced graphene oxide composite material. The roasting conditions were then controlled to be a roasting temperature of 1000° C., roasting for 60 min, and an argon flow rate of 100 mL / min. The product was cleaned with double distilled water and 50% ethanol solution respectively to obtain black powder nitrogen-doped graphene. In the 0.1mol / L, pH=7 phosphate buffer, the oxygen reduction electron transfer number was 3.91.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com