Method for carbonized materials loaded in road green belt to purify run-off rainwater in situ
A technology of carbonization materials and green belts, applied in the field of environmental engineering, can solve the problems of low processing efficiency and unsuitable for large-scale use, and achieve the effect of reducing the concentration of pollutants, fast and efficient concentration of pollutants, and reducing greenhouse gas emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
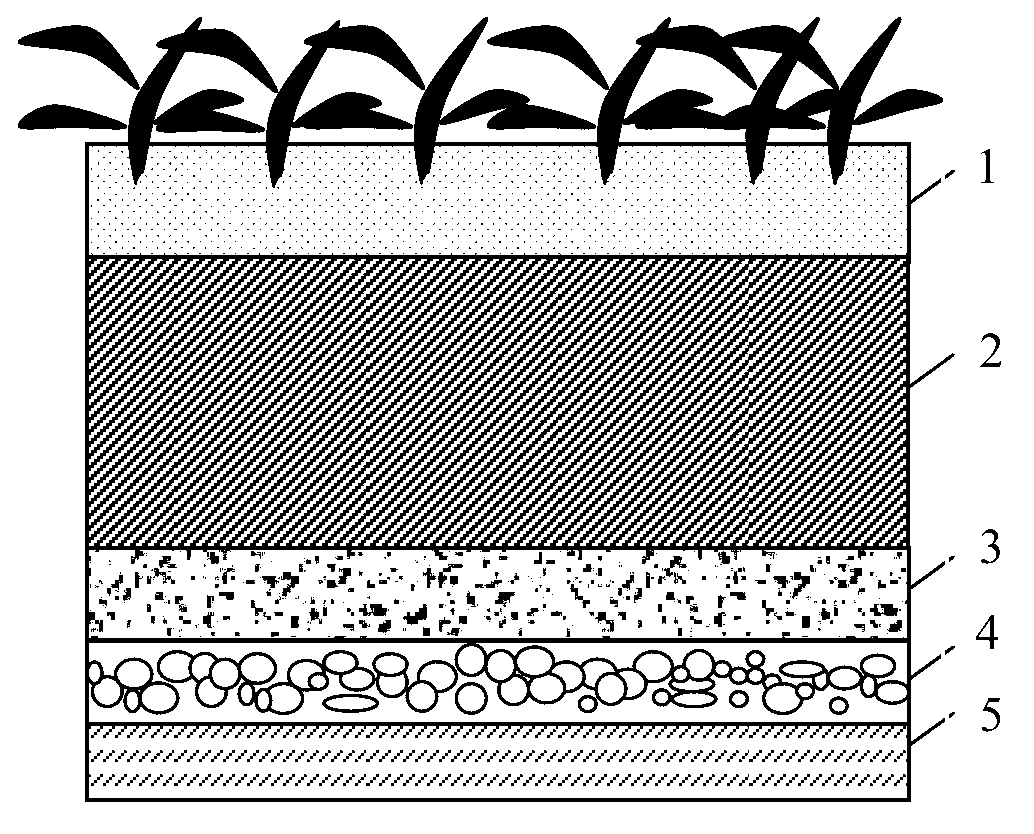
[0033] Take the straw from a farm in the suburbs of Shanghai, dry it, crush it to a particle size of 2 cm, heat it to 500°C in a nitrogen atmosphere and keep it for 4 hours to fully pyrolyze it into biochar. Afterwards, the biochar is taken out and pressed to a powder state with a particle size of 0.5-1 mm. In the simulated green belt device, a layer of pebbles with a particle size range of about 0.5-2cm is laid at the bottom as a drainage layer. Lay a 5cm biochar filter layer on top. A 10cm soil layer is placed on top of the biochar. The vegetation layer above the soil is 5 cm. The vegetation is green grass on the road. The green belt model area is 0.056m 2 , The rainfall in Shanghai is 50mm·h during heavy rain -1 Calculate, the rainfall amount discharged in 1h V=50×10 -3 ×0.056×10 3 =2.8L. Use tap water to artificially prepare simulated polluted runoff rainwater so that its pollutant content is: total phosphorus (TP) 20mg·L -1 , Ammonia nitrogen (NH 4 + -N)15mg·L -1 , Met...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Take barley grass from a city in Jiangsu Province, dry it, crush it to a particle size of 2cm, heat it to 500°C in a nitrogen atmosphere and keep it for 4 hours to fully pyrolyze it into biochar. Afterwards, the biochar is taken out and pressed to a powder state with a particle size of 0.5-1 mm. In the simulation device, a layer of pebbles with a particle size range of about 0.5-2cm is laid on the bottom as a drainage layer. Lay a 5cm biochar filter layer on top. The soil layer above the biochar is 10cm, and the vegetation layer above the soil is 5cm. The vegetation is green grass on the road. The green belt model area is 0.056m 2 , The rainfall in Shanghai is 50mm·h during heavy rain -1 Calculate, the rainfall amount discharged in 1h V=50×10 -3 ×0.056×10 3 =2.8L. Use tap water to artificially prepare simulated polluted runoff rainwater so that its pollutant content is: total phosphorus (TP) 15mg·L -1 , Ammonia nitrogen (NH 4 + -N)10mg·L -1 , Metallic lead (Pb) 0.6mg·...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Take the fallen leaves from the gardens in Minhang District, Shanghai, air-dry and crush them to a particle size of 2cm, heat them to 500°C in a nitrogen atmosphere and keep them for 4 hours to fully pyrolyze them into biochar. Afterwards, the biochar is taken out and pressed to a powder state with a particle size of 0.5-1 mm. In the simulated container, a layer of pebbles with a particle size range of about 0.5-2cm is laid on the bottom as a drainage layer, and a biochar filter layer of 8cm is laid on the top. The soil layer is 15cm above the biochar, and the vegetation layer above the soil is 8cm. The vegetation is green grass on the road. The green belt model area is 0.056m 2 , The rainfall in Shanghai is 50mm·h during heavy rain -1 Calculate, the rainfall amount discharged in 1h V=50×10 -3 ×0.056×10 3 =2.8L. Use tap water to artificially prepare simulated polluted runoff rainwater so that its pollutant content is: total phosphorus (TP) 20mg·L -1 , Ammonia nitrogen ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com