Non-enzymatic SNP detection method based on DNA self-assembly
A technique for self-assembling, DNA strands
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
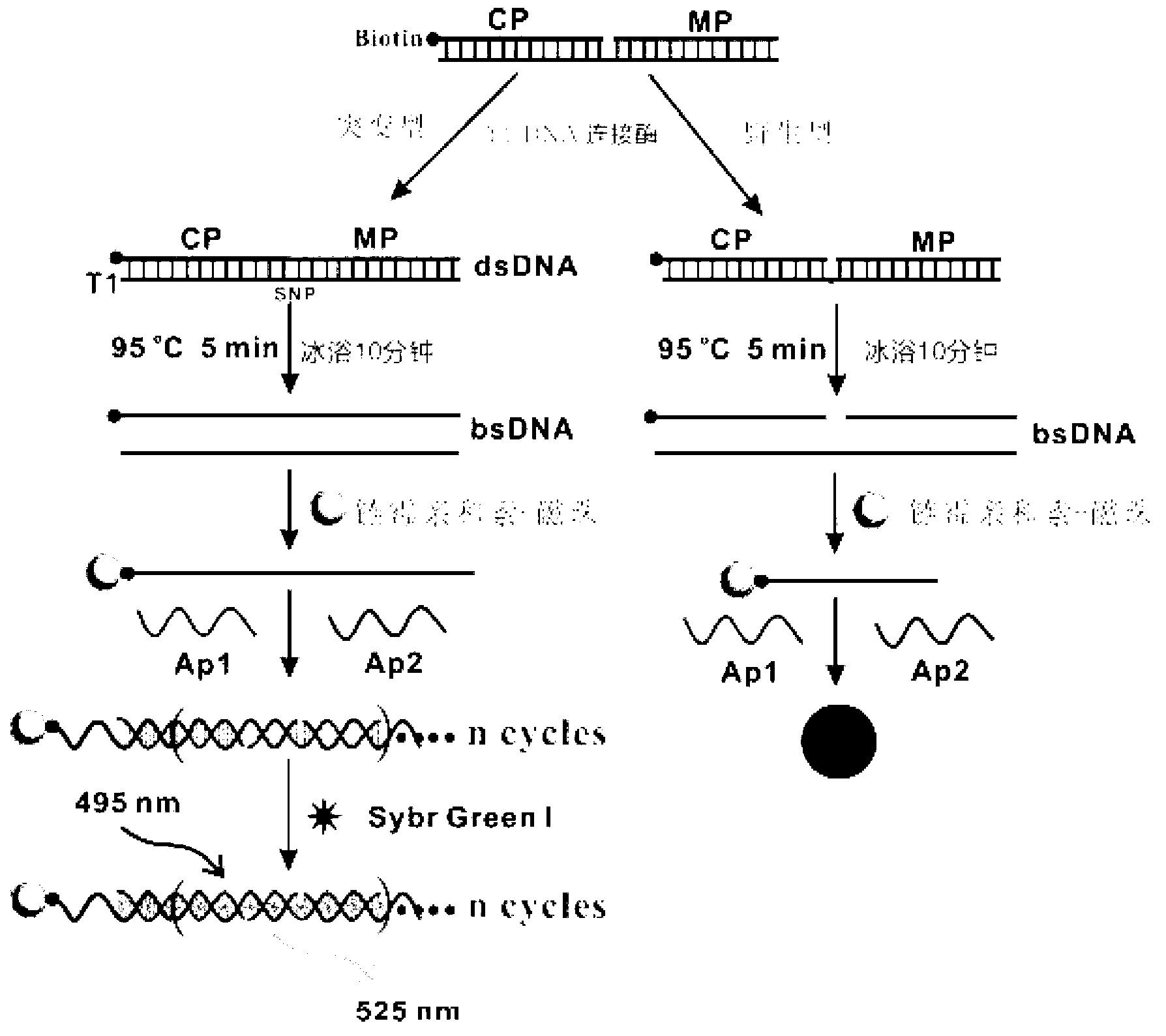
[0059] Primer design: Design and synthesize CP, MP, positive template T1, negative template WT1, AP1 and AP2, and couple biotin at the 3' end of CP. The specific nucleic acid sequence is as follows:
[0060] Among them, CP is completely complementary to the 5' end of T1, MP is completely complementary to the 3' end of T1, and the underlined A in T1 is the proto-oncogene BRAF T1799A For the SNP sites, AP1 and AP2, the underlined nucleic acids are complementary, and the parts marked in italics are also complementary.
[0061] and self-assembly of AP2:
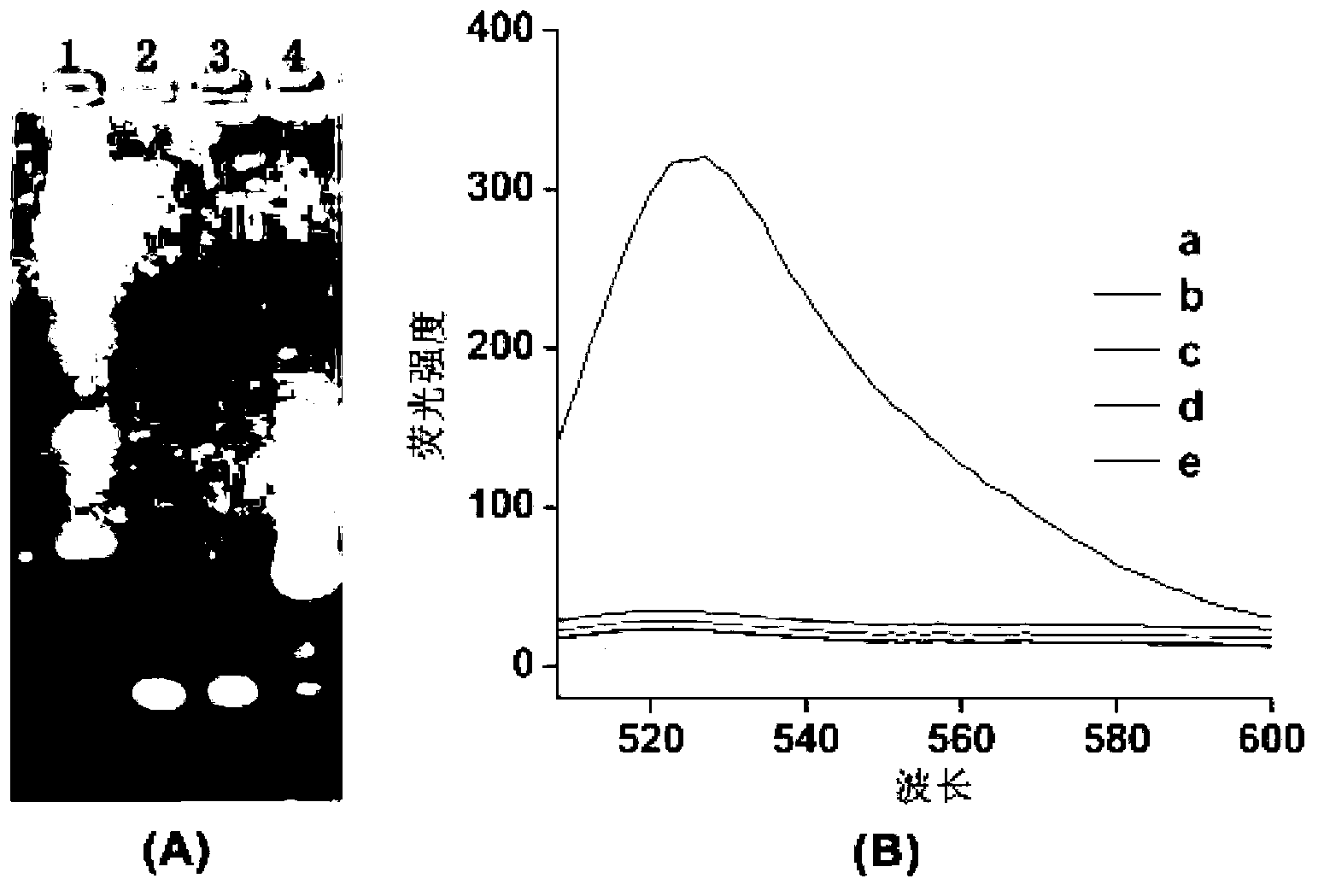
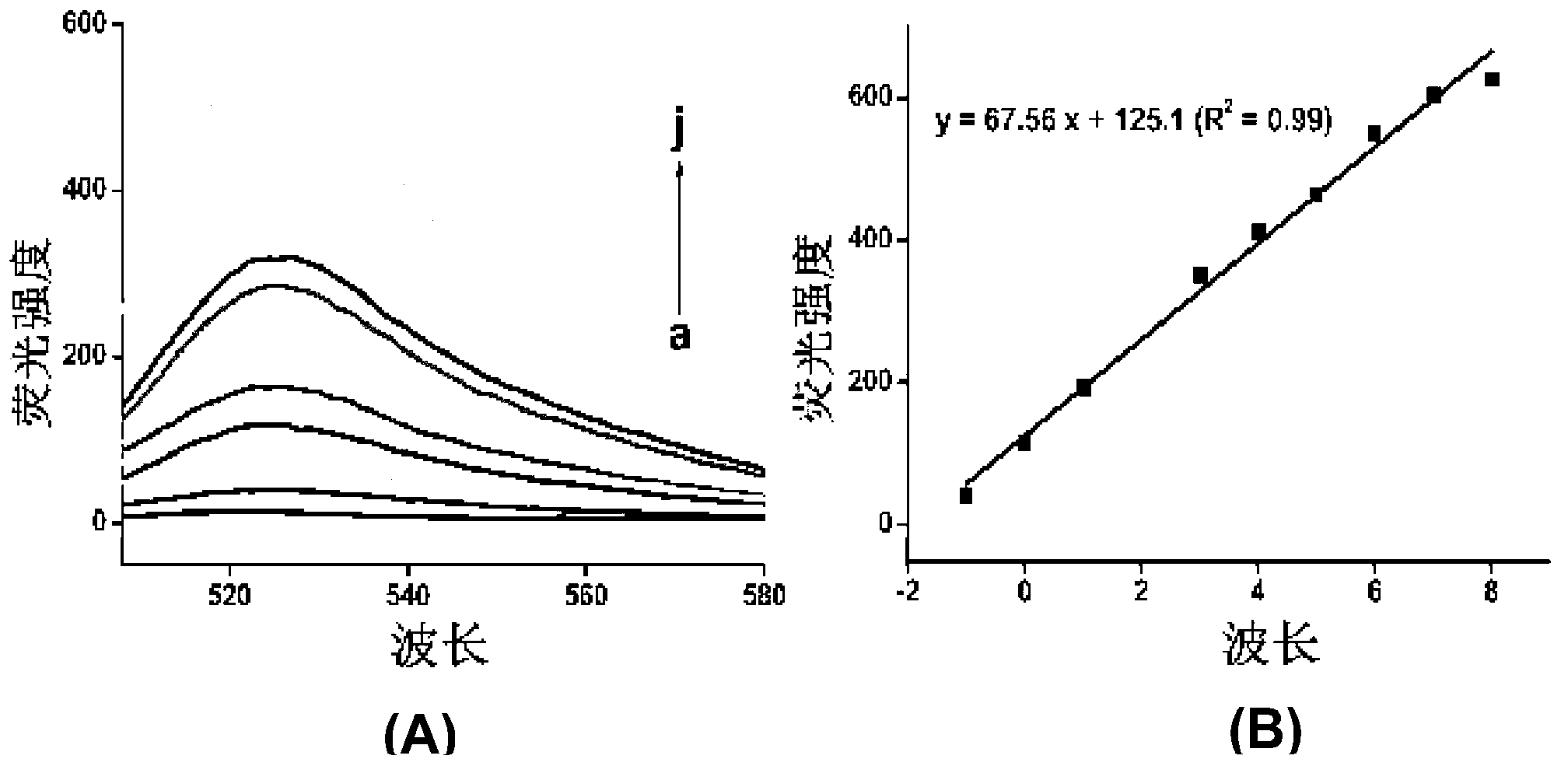
[0062] DNA agarose gel electrophoresis was used to verify whether AP1 and AP2 could self-assemble into long double strands. In the second and third lanes, 5 μL of 1 μM AP1 and 1 μM AP2 were added, and in the fourth lane, 5 μL (AP1+AP2) mixture was added, electrophoresis was performed at a constant voltage of 100 V for 30 min, and the final results were observed with an imaging system.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com