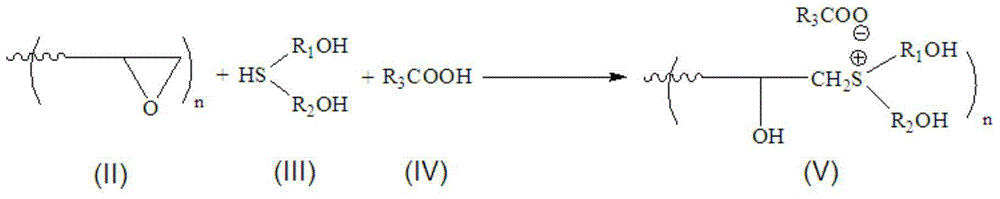Ionic curing agent and preparation method thereof
A curing agent and ionic technology, which is applied in the field of preparation of ionic curing agent, can solve the problems affecting the final performance of electrophoretic coatings, and achieve the effects of easy process control, difficult precipitation and stratification, and reduced heat release
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
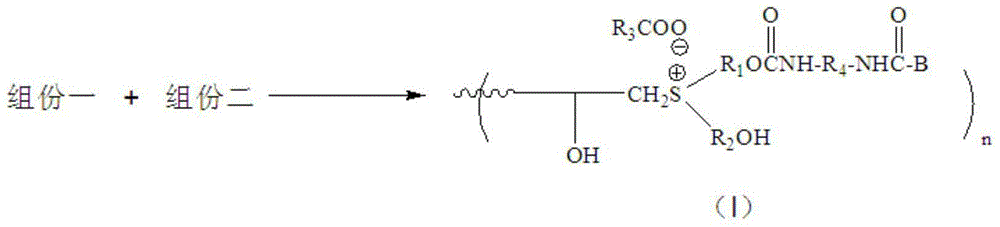
[0031] Component A (the molar ratio of epoxy group, polyhydroxy sulfide and monobasic organic acid in polyepoxide is 1:1:1)
[0032] In a 500 mL three-neck flask equipped with a stirrer and a thermometer, 101 g of butanediol diglycidyl ether (epoxy equivalent weight: 101), 122 g of bis(2-hydroxyethyl) sulfide and 60 g of acetic acid were successively added. Start stirring after the addition is complete. When the reaction system is evenly stirred, the temperature of the reaction system is raised to 80°C. During the heating process, there is an obvious exothermic phenomenon. The reaction system was maintained at 80°C for 1 hour, and the residual acid value of the reaction system was detected by sampling (initial theoretical acid value of the reaction system: 198 mgKOH / g). When the acid value was less than 10, the reaction was stopped.
[0033] Component B (the molar ratio of isocyanate group in polyisocyanate to compound containing active hydrogen: 1:0.5)
[0034] 522 g of tolu...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Component A (the molar ratio of epoxy group, polyhydroxy sulfide and monobasic organic acid in polyepoxide is 1:1.5:1)
[0042] In a 500 mL three-necked flask equipped with a stirrer and a thermometer, 101 g of butanediol diglycidyl ether (epoxy equivalent weight: 101), 183 g of bis(2-hydroxyethyl) sulfide and 60 g of acetic acid were sequentially added. Start stirring after the addition is complete. When the reaction system is evenly stirred, the temperature of the reaction system is raised to 80°C. During the heating process, there is an obvious exothermic phenomenon. The reaction system was maintained at 80°C for 1 hour, and the residual acid value of the reaction system was detected by sampling (initial theoretical acid value of the reaction system: 163 mgKOH / g). When the acid value was less than 8, the reaction was stopped.
[0043] Component B (the molar ratio of isocyanate group in polyisocyanate to compound containing active hydrogen: 1:0.65)
[0044] Add 522 g...
Embodiment 3
[0048] Change the polyepoxy compound in the component A of Example 1 into trimethylolpropane triglycidyl ether, and the polyhydroxy sulfide into 4-(3-hydroxypropylthio)-1-butanol, monobasic organic The acid is changed to butyric acid, the reaction temperature is changed to 60°C, and the reaction time is changed to 3h; the polyisocyanate in component B of Example 1 is changed to isophorone diisocyanate, and the compound containing active hydrogen is changed to ethylene glycol mono Butyl ether, the reaction temperature was changed to 50°C, and the reaction time was changed to 5h; the molar ratio of the hydroxyl group in component A and the isocyanate group in component B in Example 1 was changed to 1:0.7, and the reaction temperature was changed to 50°C, The reaction time was changed to 2 hours, and other reaction conditions were as described in Example 1, and finally an ionic curing agent different from Example 1 was obtained.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com