Blast furnace cold-intensifying and heat-avoiding type gradient brick distribution method
A gradient and heat-avoiding technology, applied in blast furnaces, blast furnace details, furnace types, etc., can solve the problems of small temperature gradient, inability to achieve longevity of the hearth and bottom of the hearth, and less cooling water, and achieve the effect of prolonging life.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 2500
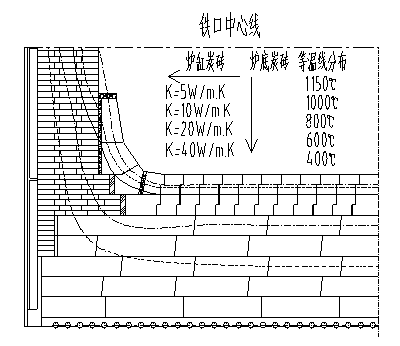
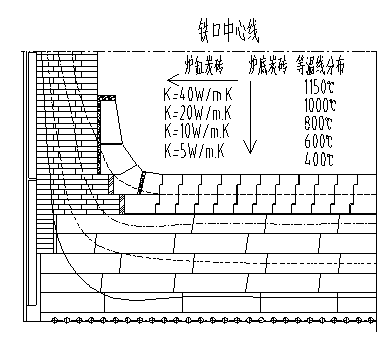
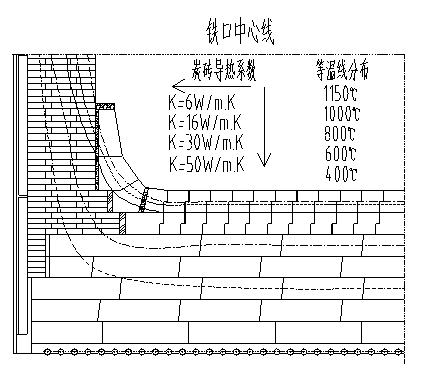
[0110] Example 2500m 3 For the specific temperature field distribution of the hearth bottom of the blast furnace, see Figure 4 .
[0111] 3. The specific structure is:
[0112] (1) Bottom structure from bottom to top: leveling layer 180mm, graphite brick 400mm, semi-graphite brick 400mm, microporous carbon brick 400mm, ultra-microporous carbon brick 800mm, ceramic cup 800mm, thermal conductivity respectively 20, 70, 20, 16, 20, 4.5 W / mK, the thermal conductivity of the refractory material gradually increases from near the hot surface of the molten iron to the cooling system, forming a gradient, which basically conforms to the gradient brick layout method of the present invention for raising cold and avoiding heat. The specific analysis is as follows:
[0113] Leveling layer: The traditional leveling layer adopts carbon ramming material, which has the problems of low actual thermal conductivity, unreliable ramming, and long construction time. The actual thermal conductivity...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com