Metallic oxide resistor storage unit and low-temperature photochemical preparation method thereof
A technology of resistance storage and resistance conversion, applied in the direction of electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of poor durability, slow reading and writing speed, high operating voltage, etc., and achieve the effect of good durability and good application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
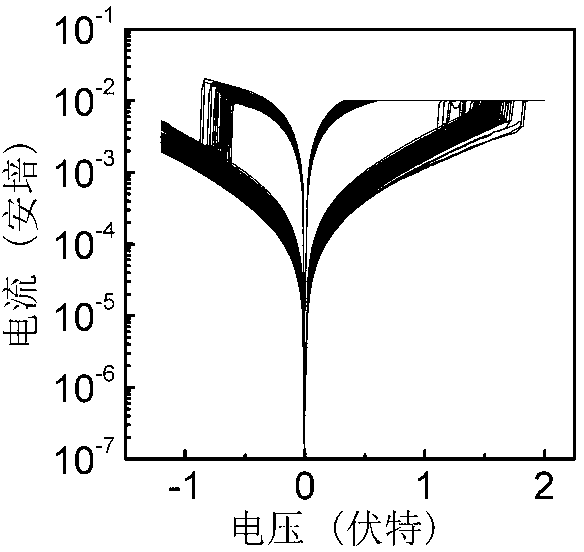
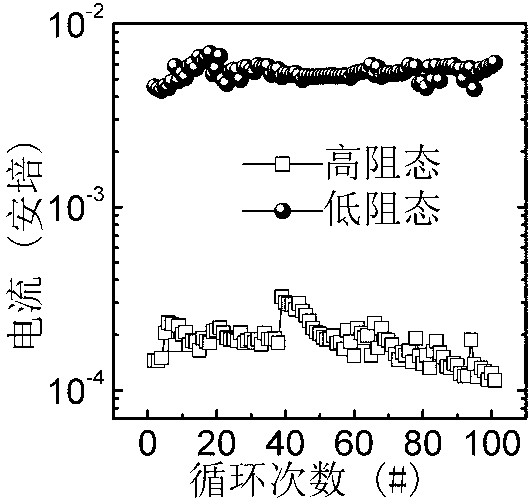
[0020] Structure and composition of resistive memory cells: Pt / InGaZnO / Pt resistive memory cells prepared by low-temperature chemical solution deposition and room temperature photochemical treatment, such as figure 1 As shown, the conductive bottom electrode and the conductive top electrode are both Pt, and the InGaZnO thin film is the resistance switching layer.
[0021] Preparation of resistive memory cells:
[0022] 1. Preparation of InGaZnO precursor solution: the solutes are indium nitrate hydrate, gallium nitrate hydrate and zinc acetate dihydrate respectively, and the solvent is ethylene glycol methyl ether. The mol ratio of hydrated indium nitrate, hydrated nitrate and zinc acetate dihydrate is 1: 1: 1, and then heated to 60 oC Stir at constant temperature for 3 hours until completely dissolved.
[0023] 2. Preparation of the conductive bottom electrode: select a p-type Si substrate, and first prepare SiO by thermal oxidation and sputtering 2 Layer and Ti adhesion ...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Structure and composition of resistive memory cells: Pt / InGa prepared by low temperature chemical solution deposition and room temperature photochemical treatment 1.5 ZnO / Pt resistive memory cells such as figure 1 As shown, the conductive bottom electrode and the conductive top electrode are both Pt, InGa 1.5 The ZnO thin film is the resistance switching layer.
[0030] Preparation of resistive memory cells:
[0031] 1. InGa 1.5 Preparation of ZnO precursor solution: the solutes are indium nitrate hydrate, gallium nitrate hydrate and zinc acetate dihydrate respectively, and the solvent is ethylene glycol methyl ether. The mol ratio of hydrated indium nitrate, hydrated nitrate and zinc acetate dihydrate is 1: 1.5: 1, and then heated to 60 oC Stir at constant temperature for 3 hours until completely dissolved.
[0032] 2. Preparation of the conductive bottom electrode: select a p-type Si substrate, and first prepare SiO by thermal oxidation and sputtering 2 Layer a...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Structure and composition of resistive memory cells: Pt / InGaZnO / TiN resistive memory cells prepared by low-temperature chemical solution deposition and room temperature photochemical treatment, such as figure 1 As shown, the conductive top electrode is Pt, the conductive bottom electrode is TiN, and the InGaZnO thin film is the resistance transition layer.
[0041] Preparation of resistive memory cells:
[0042] 1. Preparation of InGaZnO precursor solution: the solutes are indium nitrate hydrate, gallium nitrate hydrate and zinc acetate dihydrate respectively, and the solvent is ethylene glycol methyl ether. The mol ratio of hydrated indium nitrate, hydrated nitrate and zinc acetate dihydrate is 1: 1: 1, and then heated to 60 oC Stir at constant temperature for 3 hours until completely dissolved.
[0043] 2. Preparation of the conductive bottom electrode: select a p-type Si substrate, and first prepare SiO by thermal oxidation and sputtering 2 Layer and Ti adhesion ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com